fall final study guide
... both males and females. a. True b. False 16. The law of independent assortment applies only to genes that are a. sex-linked. b. located on different chromosomes or are far apart on the same chromosome. c. located on the same chromosome. d. autosomal. 17. Humans can have blood phenotypes of A, AB, B, ...
... both males and females. a. True b. False 16. The law of independent assortment applies only to genes that are a. sex-linked. b. located on different chromosomes or are far apart on the same chromosome. c. located on the same chromosome. d. autosomal. 17. Humans can have blood phenotypes of A, AB, B, ...
Biology Final Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best
... thigh bone, are involved in walking. In whales, the pelvis and femur shown in Figure 16–1 are a. examples of fossils. b. vestigial structures. c. acquired traits. d. examples of natural variation. ...
... thigh bone, are involved in walking. In whales, the pelvis and femur shown in Figure 16–1 are a. examples of fossils. b. vestigial structures. c. acquired traits. d. examples of natural variation. ...
Section 3 Exam
... B. That is more efficient, less risky, and that requires less overall energy than asexual reproduction C. To avoid potential mutations in DNA replication associated with asexual reproduction D. For insuring that offspring have identical genetics as their parents 17. Which of the following statements ...
... B. That is more efficient, less risky, and that requires less overall energy than asexual reproduction C. To avoid potential mutations in DNA replication associated with asexual reproduction D. For insuring that offspring have identical genetics as their parents 17. Which of the following statements ...
DNA - SchoolRack
... • How does the tRNA know which amino acid to bring to the ribosome? • Each 3 bases in the mRNA (called a codon), codes for a single amino acid. • A tRNA molecule has three bases on it that are complementary to the codon, called an anticodon. • Each tRNA carries only the amino acid that it’s anticod ...
... • How does the tRNA know which amino acid to bring to the ribosome? • Each 3 bases in the mRNA (called a codon), codes for a single amino acid. • A tRNA molecule has three bases on it that are complementary to the codon, called an anticodon. • Each tRNA carries only the amino acid that it’s anticod ...
to print
... • When semen is deposited at the base of the uterus, the sperm must first cross the barrier of the cervix and then up the lining of the uterus into the Fallopian tubes to reach the egg. – Only one of the Fallopian tubes contains an egg, so many sperm travel in the wrong direction. – This process mus ...
... • When semen is deposited at the base of the uterus, the sperm must first cross the barrier of the cervix and then up the lining of the uterus into the Fallopian tubes to reach the egg. – Only one of the Fallopian tubes contains an egg, so many sperm travel in the wrong direction. – This process mus ...
6.G Meiosis Graphic Organizer 6.H Genetic Variation
... a. creating new DNA molecules from nucleotide sequences. b. rearranging nucleotides in a gene of an organism so that new traits appear in the development of an embryo. c. moving genes from a chromosome of one organism to a chromosome of a different organism. d. building a new species by combining ge ...
... a. creating new DNA molecules from nucleotide sequences. b. rearranging nucleotides in a gene of an organism so that new traits appear in the development of an embryo. c. moving genes from a chromosome of one organism to a chromosome of a different organism. d. building a new species by combining ge ...
Exam 3 Key Fa08
... malate into the bundle sheath cells, where Calvin cycle occurs. Malate breaks down, provide CO2 for the Calvin cycle. C4 plants use a spatial separation (two types of cells) of initial carbon fixation and calvin cycle in order to keep CO2 levels high in Calvin cycle. CAM plants use temporal separati ...
... malate into the bundle sheath cells, where Calvin cycle occurs. Malate breaks down, provide CO2 for the Calvin cycle. C4 plants use a spatial separation (two types of cells) of initial carbon fixation and calvin cycle in order to keep CO2 levels high in Calvin cycle. CAM plants use temporal separati ...
DNA, RNA and Proteins
... chromosomes are a closed loop, may contain protein, and are attached to the inner cell membrane. ...
... chromosomes are a closed loop, may contain protein, and are attached to the inner cell membrane. ...
SI Worksheet 12
... a. they contain different sets of genes b. they are differentiated c. they contain different operons d. different genes are switched on and off in each e. they contain different histones 2. DNA packing - the way DNA is folded into chromosomes- affects gene expression by a. controlling access to DNA ...
... a. they contain different sets of genes b. they are differentiated c. they contain different operons d. different genes are switched on and off in each e. they contain different histones 2. DNA packing - the way DNA is folded into chromosomes- affects gene expression by a. controlling access to DNA ...
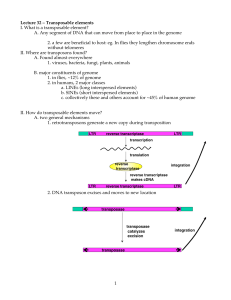
Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element?
... Lecture 32 – Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element? A. Any segment of DNA that can move from place to place in the genome 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. vir ...
... Lecture 32 – Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element? A. Any segment of DNA that can move from place to place in the genome 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. vir ...
Genetics 101 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... One look around a room tells you that each person has slight differences in their physical make up — and therefore in their DNA. These subtle variations in DNA are called polymorphisms (literally "many forms"). Many of these gene polymorphisms account for slight differences between people such as ha ...
... One look around a room tells you that each person has slight differences in their physical make up — and therefore in their DNA. These subtle variations in DNA are called polymorphisms (literally "many forms"). Many of these gene polymorphisms account for slight differences between people such as ha ...
Ch 13 Jeopardy
... bacterial DNA on the hands of criminals may provide a clue as to where that person was when the crime was committed. d. ...
... bacterial DNA on the hands of criminals may provide a clue as to where that person was when the crime was committed. d. ...
DNA Paternity Test RFLP analysis (Restriction Fragment Length
... sequences -each enzyme recognizes and cuts DNA at a different base sequence e.g. BamHI XXXXXXXXGGATCCXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXCCTAGGXXXXXXXXXX -due to spontaneous mutations over time, different people have slightly different base sequences in their DNA -if mutation creates or deletes a restriction site in ...
... sequences -each enzyme recognizes and cuts DNA at a different base sequence e.g. BamHI XXXXXXXXGGATCCXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXCCTAGGXXXXXXXXXX -due to spontaneous mutations over time, different people have slightly different base sequences in their DNA -if mutation creates or deletes a restriction site in ...
Sem2 Final SG 12 Part1
... 2. What causes speciation? 3. What evidence do we have to support the theory of evolution by natural selection? 4. Describe the 3 key ingredients that lead to biological evolution. 5. What are homologous structures and what do they tell us about how organisms evolved? Protein Synthesis 6. What are t ...
... 2. What causes speciation? 3. What evidence do we have to support the theory of evolution by natural selection? 4. Describe the 3 key ingredients that lead to biological evolution. 5. What are homologous structures and what do they tell us about how organisms evolved? Protein Synthesis 6. What are t ...
Name: Biochemistry 465 Hour exam II Spring 2006
... A) fragment of DNA resulting from endonuclease action. B) fragment of RNA that is a subunit of the 30S ribosome. C) piece of DNA that is synthesized in the 3' ® 5' direction. D) segment of DNA that is an intermediate in the synthesis of the lagging strand. E) segment of mRNA synthesized by RNA polym ...
... A) fragment of DNA resulting from endonuclease action. B) fragment of RNA that is a subunit of the 30S ribosome. C) piece of DNA that is synthesized in the 3' ® 5' direction. D) segment of DNA that is an intermediate in the synthesis of the lagging strand. E) segment of mRNA synthesized by RNA polym ...
10th Grade Genetics Content - Red Clay Secondary Science Wiki
... Standard 6.4.B The scientific investigation of cellular chemistry enables the biotechnology industry to produce medicines foods and other products for the benefit of society (Essential) Standard 7.1.A Hereditary/genetic information in chromosomes is contained in molecules of DNA. Genes are sections ...
... Standard 6.4.B The scientific investigation of cellular chemistry enables the biotechnology industry to produce medicines foods and other products for the benefit of society (Essential) Standard 7.1.A Hereditary/genetic information in chromosomes is contained in molecules of DNA. Genes are sections ...
Presentation
... – Inhalation of genetically engineered viruses containing “good” genes has been attempted up to this point, gene therapy has not been very successful ...
... – Inhalation of genetically engineered viruses containing “good” genes has been attempted up to this point, gene therapy has not been very successful ...
Genetic conditions - Centre for Genetics Education
... incorrect so a faulty protein is made or the control switch is changed. A variation in a gene that creates a fault is called a pathogenic variant or mutation. These are quite rare. A DNA mutation may cause a problem for one cell type but not another, since not all cells use all of the possible prote ...
... incorrect so a faulty protein is made or the control switch is changed. A variation in a gene that creates a fault is called a pathogenic variant or mutation. These are quite rare. A DNA mutation may cause a problem for one cell type but not another, since not all cells use all of the possible prote ...
Ch 12-15 Unit Overvi..
... similar to mitosis? Does meiosis I or II reduce the chromosome number by half? How is anaphase I different from anaphase II? Metaphase I from II? When does cross over take place? Independent assortment? Segregation? Role of cohesion protein Name three sources of variation arising from sexual reprodu ...
... similar to mitosis? Does meiosis I or II reduce the chromosome number by half? How is anaphase I different from anaphase II? Metaphase I from II? When does cross over take place? Independent assortment? Segregation? Role of cohesion protein Name three sources of variation arising from sexual reprodu ...
Biology Final Study Guide
... a food web or chain and why? 14. What are the three types of symbiotic relationships and give an example of each? 15. Draw logistic and exponential growth models. 16. Compare & contrast chloroplast & mitochondria (job, what cell types have it, equation) 17. What are the main steps in the water, carb ...
... a food web or chain and why? 14. What are the three types of symbiotic relationships and give an example of each? 15. Draw logistic and exponential growth models. 16. Compare & contrast chloroplast & mitochondria (job, what cell types have it, equation) 17. What are the main steps in the water, carb ...
Crossing natural barriers to genetic manipulations
... cells carrying this hybrid plasmid are allowed to insert the chimeric T-DNA into tobacco, petunia, cowpea, and sunflower cells by natural infection. Although such genes have been transferred to plants, these genes are not stably maintained, particularly during meiosis (chromosome reduction, division ...
... cells carrying this hybrid plasmid are allowed to insert the chimeric T-DNA into tobacco, petunia, cowpea, and sunflower cells by natural infection. Although such genes have been transferred to plants, these genes are not stably maintained, particularly during meiosis (chromosome reduction, division ...
DNA Structure and Function
... • At Initiation RNA polymerase binds start of gene and uncoils DNA. • At Elongation RNA polymerase moves along the gene briefly binding nucleotides to DNA (only about 10 nucleotides at a time), as the RNA nucleotides join together in a making a single complimentary strand • At Termination the mRNA m ...
... • At Initiation RNA polymerase binds start of gene and uncoils DNA. • At Elongation RNA polymerase moves along the gene briefly binding nucleotides to DNA (only about 10 nucleotides at a time), as the RNA nucleotides join together in a making a single complimentary strand • At Termination the mRNA m ...
Name - PSUSDscienceresources
... the tongue. This is because A cells in the tongue do not contain amylase genes. B cells in the tongue do not express the amylase genes. C DNA varies from cell to cell based on the cell's needs. D cells in the tongue send amylase to the salivary gland cells. ...
... the tongue. This is because A cells in the tongue do not contain amylase genes. B cells in the tongue do not express the amylase genes. C DNA varies from cell to cell based on the cell's needs. D cells in the tongue send amylase to the salivary gland cells. ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.