Human Genome Project
... Human genome has far more repeat DNA than any other sequenced organism (over half). • Parasitic elements–45% of this repeat DNA is from selfish, parasitic DNA: – Transposable elements. – May play role in evolution. ...
... Human genome has far more repeat DNA than any other sequenced organism (over half). • Parasitic elements–45% of this repeat DNA is from selfish, parasitic DNA: – Transposable elements. – May play role in evolution. ...
From the principle of heredity to the molecular - diss.fu
... genomes, including that of man, contemporary molecular genetics is now focussing on genotype – phenotype correlations as a means of identifying functions for each of the human genes. ...
... genomes, including that of man, contemporary molecular genetics is now focussing on genotype – phenotype correlations as a means of identifying functions for each of the human genes. ...
A-DNA
... Proof chromosomes were hereditary factors – 1905: The first physical trait was linked to the presence of specific chromosomal material ...
... Proof chromosomes were hereditary factors – 1905: The first physical trait was linked to the presence of specific chromosomal material ...
Chapter 8
... • Gene: Segment of DNA that encodes a functional product, usually a protein – Usually codes for mRNA, but can also code for rRNA or tRNA ...
... • Gene: Segment of DNA that encodes a functional product, usually a protein – Usually codes for mRNA, but can also code for rRNA or tRNA ...
week7_DNA
... from 1 original egg and sperm • Every cell has the same DNA and the same genes • Except the gametes which have half the DNA/genes ...
... from 1 original egg and sperm • Every cell has the same DNA and the same genes • Except the gametes which have half the DNA/genes ...
MASTER SYLLABUS
... compare and contrast DNA and RNA structure. describe how the structure of DNA was determined. explain the determination of DNA as genetic material. explain the semiconservative replication of DNA. describe the structure of a chromosome in prokaryotic cells. describe the packaging of DNA into eukaryo ...
... compare and contrast DNA and RNA structure. describe how the structure of DNA was determined. explain the determination of DNA as genetic material. explain the semiconservative replication of DNA. describe the structure of a chromosome in prokaryotic cells. describe the packaging of DNA into eukaryo ...
Name Living Environment Test 10 1. Evidence that best supports the
... organisms (4) analysis of food chains and food webs 2. In sexually reproducing organisms, mutations can be inherited if they occur in (1) the egg, only (2) the sperm, only (3) any body cell of either the mother or the father (4) either the egg or the sperm 3. Compared to a normal body cell, a normal ...
... organisms (4) analysis of food chains and food webs 2. In sexually reproducing organisms, mutations can be inherited if they occur in (1) the egg, only (2) the sperm, only (3) any body cell of either the mother or the father (4) either the egg or the sperm 3. Compared to a normal body cell, a normal ...
Genetics - Doc Ireland
... • A mutation that makes it through one replication cycle becomes permanent. ...
... • A mutation that makes it through one replication cycle becomes permanent. ...
Multi-copy suppressor screen
... on a second plasmid to be tested, even though they may be lethal. The trick is to have the wild type gene on a URA3 plasmid and introduce the mutant gene on a second plasmid (LEU2 plasmid). Then you see if the strain will grow on medium containing 5-FOA. Cells will lose the URA3 plasmid when grown o ...
... on a second plasmid to be tested, even though they may be lethal. The trick is to have the wild type gene on a URA3 plasmid and introduce the mutant gene on a second plasmid (LEU2 plasmid). Then you see if the strain will grow on medium containing 5-FOA. Cells will lose the URA3 plasmid when grown o ...
Unit A - Topic 3.0 Notes
... behaviors, has been done for thousands of years. The Great Pyrenees (#2) is one of the oldest-known dog breeds, bred several thousand years ago to protect sheep herds from wolves(#1) and bears. The dachshund (#3) was bred about 600 years ago to hunt badgers in their underground dens. The toy poodle ...
... behaviors, has been done for thousands of years. The Great Pyrenees (#2) is one of the oldest-known dog breeds, bred several thousand years ago to protect sheep herds from wolves(#1) and bears. The dachshund (#3) was bred about 600 years ago to hunt badgers in their underground dens. The toy poodle ...
DNA - NRF IR Repository
... DNA stands for DeoxyriboNucleic Acid. It is a molecule that constitutes the genetic material of the cell. It is found in the chromosomes in the nucleus of the cell, as well as in other cellular organelles like the mitochodria in animals and chloroplasts in plants. DNA is the biological code that con ...
... DNA stands for DeoxyriboNucleic Acid. It is a molecule that constitutes the genetic material of the cell. It is found in the chromosomes in the nucleus of the cell, as well as in other cellular organelles like the mitochodria in animals and chloroplasts in plants. DNA is the biological code that con ...
DNA
... Sickle-cell anemia is a disorder resulting from a mutation that leads to the production of an abnormal protein. Which component of the DNA molecule provides instructions for the production of the protein? A The phosphate groups B The sugar molecules C The sequence of nitrogen bases D The bonds that ...
... Sickle-cell anemia is a disorder resulting from a mutation that leads to the production of an abnormal protein. Which component of the DNA molecule provides instructions for the production of the protein? A The phosphate groups B The sugar molecules C The sequence of nitrogen bases D The bonds that ...
Genetic Technology - Solon City Schools
... 3. After the foreign DNA has been spliced (glued) into the plasmid using an enzyme DNA ligase, the rDNA is transferred into a bacterial cell or other organism 4. Now organism is called a Transgenic Organismorganisms that contain functional recombinant DNA (rDNA) from a different organism ...
... 3. After the foreign DNA has been spliced (glued) into the plasmid using an enzyme DNA ligase, the rDNA is transferred into a bacterial cell or other organism 4. Now organism is called a Transgenic Organismorganisms that contain functional recombinant DNA (rDNA) from a different organism ...
Genomics
... to wild-type Coupling Microarrays and Yeast Genetics: Mutant v. Wild-type Cell type 1 = WT Cell type 2 = Mutant ...
... to wild-type Coupling Microarrays and Yeast Genetics: Mutant v. Wild-type Cell type 1 = WT Cell type 2 = Mutant ...
Biology 445K Winter 2007 DNA Fingerprinting • For Friday 3/9 lab: in
... the genome that consist of repeated sequences. The repeat size is usually 10-60 base pairs long and the number of repeats varies from less than ten to several dozen. These sites, which are scattered throughout the genome, are usually “anonymous” markers in the sense that the repeat number does not a ...
... the genome that consist of repeated sequences. The repeat size is usually 10-60 base pairs long and the number of repeats varies from less than ten to several dozen. These sites, which are scattered throughout the genome, are usually “anonymous” markers in the sense that the repeat number does not a ...
Biotechnology - Biology Junction
... enabling plants to produce new proteins Protect crops from insects: BT corn corn produces a bacterial toxin that kills corn borer (caterpillar pest of corn) ...
... enabling plants to produce new proteins Protect crops from insects: BT corn corn produces a bacterial toxin that kills corn borer (caterpillar pest of corn) ...
Study guide for Chapter3: Cell division and Chapter 4
... 1. Define the following terms: Chromosomes, Chromatids, DNA, Cell cycle, Haploid, Diploid Cell Division, Unicellular, Multicellular, Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic, Nucleus, Fertilization, Asexual Reproduction sexual reproduction, Allele, and Gamete 2. Describe what type of relationship DNA, Nucleus, Genes ...
... 1. Define the following terms: Chromosomes, Chromatids, DNA, Cell cycle, Haploid, Diploid Cell Division, Unicellular, Multicellular, Prokaryotic, Eukaryotic, Nucleus, Fertilization, Asexual Reproduction sexual reproduction, Allele, and Gamete 2. Describe what type of relationship DNA, Nucleus, Genes ...
Sunlight Water Entropy
... folding chemistry and cell type differentiation via supercoiled DNA in the context of the physiology of reproduction. [4] Distinct nutrient energy-dependent pathways link microRNA biogenesis from RNAs to biological functions, but the distinct pathways are typically examined collectively. [5] The col ...
... folding chemistry and cell type differentiation via supercoiled DNA in the context of the physiology of reproduction. [4] Distinct nutrient energy-dependent pathways link microRNA biogenesis from RNAs to biological functions, but the distinct pathways are typically examined collectively. [5] The col ...
Mock Exam 3 Chapters 14-18 Anthony Todd http
... c. MIH which inhibits the formation of Mullerian ducts so male development can continue d. A and B are correct e. B and C are correct Use the following information for Questions 15 and 16: A dominant sex-linked gene B produces white bars on black chickens. A clutch of chickens has equal numbers of b ...
... c. MIH which inhibits the formation of Mullerian ducts so male development can continue d. A and B are correct e. B and C are correct Use the following information for Questions 15 and 16: A dominant sex-linked gene B produces white bars on black chickens. A clutch of chickens has equal numbers of b ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

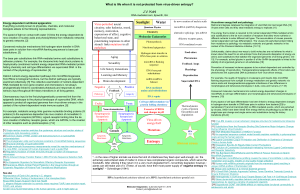
Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.