Effects of increased concentrations of chloride on the expression of
... significantly increase or diminish in response to stress. Salinity also reduces synthesis of some proteins in certain plants and increases the hydrolysis of those proteins, leading to increasing of free amino acids (Kozlowski, 1997). According to the research conducted by Brou et al. (2007), superox ...
... significantly increase or diminish in response to stress. Salinity also reduces synthesis of some proteins in certain plants and increases the hydrolysis of those proteins, leading to increasing of free amino acids (Kozlowski, 1997). According to the research conducted by Brou et al. (2007), superox ...
Origins of Life PDF
... might have been the original life molecule. Unlike DNA, whose structure is constrained by a doublehelix, RNA is singled-stranded and can fold in a variety of sequence-specific structures (see Figure 1). This structural variety is essential for the ability of a molecule to carry out a range of chemic ...
... might have been the original life molecule. Unlike DNA, whose structure is constrained by a doublehelix, RNA is singled-stranded and can fold in a variety of sequence-specific structures (see Figure 1). This structural variety is essential for the ability of a molecule to carry out a range of chemic ...
Efficient Delivery of Dharmacon SMARTpool® siRNA
... siRNA-mediated gene knockdown is a powerful tool that has been used to identify gene function and elucidate biological pathways. Successful siRNA experiments involving knockdown of individual genes or collections of gene targets require efficient delivery of highly functional and specific siRNA mole ...
... siRNA-mediated gene knockdown is a powerful tool that has been used to identify gene function and elucidate biological pathways. Successful siRNA experiments involving knockdown of individual genes or collections of gene targets require efficient delivery of highly functional and specific siRNA mole ...
Chromatin: A sticky silence
... nucleus may vary in a regulated manner during development. In support of this idea, the strength of heterochromatin-mediated silencing in Drosophila was observed to decrease during differentiation [21]. In contrast, variegated expression of multiple copies of a globin gene in mice was seen to increa ...
... nucleus may vary in a regulated manner during development. In support of this idea, the strength of heterochromatin-mediated silencing in Drosophila was observed to decrease during differentiation [21]. In contrast, variegated expression of multiple copies of a globin gene in mice was seen to increa ...
pdf
... 3. What are the contacts between the protein and the binding site in DNA? a. Methylation interference reactions: When a purine that makes contact with the protein is methylated by dimethyl sulphate (DMS), the DNA will no longer bind to the protein. Thus, DNA is gently methylated (about one hit per m ...
... 3. What are the contacts between the protein and the binding site in DNA? a. Methylation interference reactions: When a purine that makes contact with the protein is methylated by dimethyl sulphate (DMS), the DNA will no longer bind to the protein. Thus, DNA is gently methylated (about one hit per m ...
Optimization of Electroporation Conditions for Jurkat Cells - Bio-Rad
... optimization of electroporation conditions prove to be challenging and time consuming. With the introduction of the Gene Pulser MXcell electroporation system, optimal electroporation conditions can be determined quickly, allowing scientists to perform experiments with minimal delay. In this note, we ...
... optimization of electroporation conditions prove to be challenging and time consuming. With the introduction of the Gene Pulser MXcell electroporation system, optimal electroporation conditions can be determined quickly, allowing scientists to perform experiments with minimal delay. In this note, we ...
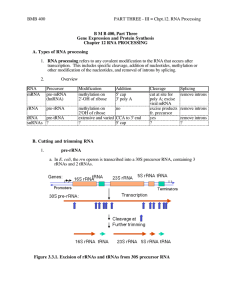
Chpt12_RNAProcessing.doc
... over-expression or ectopic expression of a defined gene were the cause of some pathology (e.g. some form of cancer), then reducing its expression could have therapeutic value. Other RNAs possibly involved in catalysis, such as the snRNAs involved in splicing pre-mRNA (discussed in the next section). ...
... over-expression or ectopic expression of a defined gene were the cause of some pathology (e.g. some form of cancer), then reducing its expression could have therapeutic value. Other RNAs possibly involved in catalysis, such as the snRNAs involved in splicing pre-mRNA (discussed in the next section). ...
Pseudo-Replication of [GADV]-Proteins and Origin of Life
... Furthermore, there are major weak points in the RNA world hypothesis [5,6]: (i) The numbers of atoms (in parentheses) of four nucleotides, AMP (37), UMP (34), GMP (37) or CMP (35), are much larger than those (in parentheses) of four amino acids, Gly (10), Ala (13), Asp (16) or Val (19). This means t ...
... Furthermore, there are major weak points in the RNA world hypothesis [5,6]: (i) The numbers of atoms (in parentheses) of four nucleotides, AMP (37), UMP (34), GMP (37) or CMP (35), are much larger than those (in parentheses) of four amino acids, Gly (10), Ala (13), Asp (16) or Val (19). This means t ...
Single Processing Center Models for Human Dicer and Bacterial
... processing of both strands in the central region of the substrate has taken place. The requirement for the primary processing event explains why no labeled products diagnostic of the cleavage at complementary sites on opposite RNA strands could be identified (Supplemental Figure S3 available on Cell ...
... processing of both strands in the central region of the substrate has taken place. The requirement for the primary processing event explains why no labeled products diagnostic of the cleavage at complementary sites on opposite RNA strands could be identified (Supplemental Figure S3 available on Cell ...
Using real time RT-PCR analysis to determine multiple gene
... 2004 very little is known about the molecular pathways regulating gonad development for the limited number of genes that have been identified. As the list of genes increases, studying their interactions will become even more daunting. One approach to investigate gene interactions in genital ridge de ...
... 2004 very little is known about the molecular pathways regulating gonad development for the limited number of genes that have been identified. As the list of genes increases, studying their interactions will become even more daunting. One approach to investigate gene interactions in genital ridge de ...
Structure-Function Relations in E. coli 16s RNA
... No part of 16s RNA has been associated with a proofreading function. Several proteins, however, are known to be involved in regulating translational fidelity. Elongation factor Tu and S4, Sl 1, S12, and S17 have all been shown to affect the error rate profoundly (Gavrilova et al., 1981, and referenc ...
... No part of 16s RNA has been associated with a proofreading function. Several proteins, however, are known to be involved in regulating translational fidelity. Elongation factor Tu and S4, Sl 1, S12, and S17 have all been shown to affect the error rate profoundly (Gavrilova et al., 1981, and referenc ...
A Survey of Intron Research in Genetics
... The existence of the intron-exon structure has been particularly intriguing. Introns are only found in eukaryotic genomes and make up a large portion of the DNA in eukaryotic genomes. In humans, for example, approximately 30% of the human genome is made up of introns [1]. Only about 3% consists of c ...
... The existence of the intron-exon structure has been particularly intriguing. Introns are only found in eukaryotic genomes and make up a large portion of the DNA in eukaryotic genomes. In humans, for example, approximately 30% of the human genome is made up of introns [1]. Only about 3% consists of c ...
Identification of a mitochondrial ATP synthase small subunit gene
... was localized in mitochondria using the green fluorescent protein (GFP) marker. Analysis of RMtATP6 mRNA levels suggested that the expression of this gene was induced by stress from sodium carbonates and other sodium salts. Transgenic tobacco overexpressing the RMtATP6 gene had greater tolerance to s ...
... was localized in mitochondria using the green fluorescent protein (GFP) marker. Analysis of RMtATP6 mRNA levels suggested that the expression of this gene was induced by stress from sodium carbonates and other sodium salts. Transgenic tobacco overexpressing the RMtATP6 gene had greater tolerance to s ...
Synthesis of RNA - Stamm revision
... chemical synthesis of modified RNA and enzymatic ligation methods. Recent examples involve the convertible nucleoside approach and thiol-specific RNA labelling together with enzymatic ligation for engineering of pre-mRNA and snRNA constructs [14-15]. In these studies, a site-specifically attached hy ...
... chemical synthesis of modified RNA and enzymatic ligation methods. Recent examples involve the convertible nucleoside approach and thiol-specific RNA labelling together with enzymatic ligation for engineering of pre-mRNA and snRNA constructs [14-15]. In these studies, a site-specifically attached hy ...
PDF
... Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon in mammals whereby the expression of a subset of autosomal genes is restricted to one of the parental chromosomes such that they are expressed either from the maternal or the paternal chromosome. So far more than 80 imprinted genes have been identified ...
... Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon in mammals whereby the expression of a subset of autosomal genes is restricted to one of the parental chromosomes such that they are expressed either from the maternal or the paternal chromosome. So far more than 80 imprinted genes have been identified ...
Prokaryotic Regulation of Transcription
... polycictronic, can have several genes involved in a metabolic pathway expressed together (coordinated expression) Control translation and degradation of protein product ...
... polycictronic, can have several genes involved in a metabolic pathway expressed together (coordinated expression) Control translation and degradation of protein product ...
Characterization of Two Rice MADS Box Genes That Control
... protein (Figs. 1 and 2). This region is the most conserved region as observed from other MADS box genes. The second conserved domain, the K box, is located between the residues 95 and 160 in both OsMADS7 and OsMADS8 (Figs. 1 and 2) . The genes contain two variable regions, the I region between the M ...
... protein (Figs. 1 and 2). This region is the most conserved region as observed from other MADS box genes. The second conserved domain, the K box, is located between the residues 95 and 160 in both OsMADS7 and OsMADS8 (Figs. 1 and 2) . The genes contain two variable regions, the I region between the M ...
NO!!!!!
... Small RNAs can regulated mRNA stability and use. RNA interference (RNAi) leads to mRNA degradation induced by presence of foreign double-stranded RNA, which may be present during certain viral infection. *Dicer: a ribonuclease, cleaves double-stranded RNA into 21nucleotide fragments. Single-stranded ...
... Small RNAs can regulated mRNA stability and use. RNA interference (RNAi) leads to mRNA degradation induced by presence of foreign double-stranded RNA, which may be present during certain viral infection. *Dicer: a ribonuclease, cleaves double-stranded RNA into 21nucleotide fragments. Single-stranded ...
pdf
... (1) The 3'-OH of the guanine nucleotide is the nucleophile that attacks and joins to the 5' phosphate of the first nucleotide of the intron. (2) This leaves the 3'-OH of the last nucleotide of the upstream exon available to attack and join the 5' phosphate of the first nucleotide of the downstream e ...
... (1) The 3'-OH of the guanine nucleotide is the nucleophile that attacks and joins to the 5' phosphate of the first nucleotide of the intron. (2) This leaves the 3'-OH of the last nucleotide of the upstream exon available to attack and join the 5' phosphate of the first nucleotide of the downstream e ...
Chapter 17
... Split Genes and RNA Splicing • Most eukaryotic genes and their RNA transcripts have long noncoding stretches of nucleotides that lie between coding regions • These noncoding regions are called intervening sequences, or introns • The other regions are called exons because they are eventually express ...
... Split Genes and RNA Splicing • Most eukaryotic genes and their RNA transcripts have long noncoding stretches of nucleotides that lie between coding regions • These noncoding regions are called intervening sequences, or introns • The other regions are called exons because they are eventually express ...
in plant physiology
... versus 3 Mbp in cyanobacteria), chloroplast gene expression is regulated by more complex systems compared to the simple prokaryotic regulatory system. Chloroplast gene expression is mediated by two distinct types of RNA polymerase (RNAP) and is highly dependent on post-transcriptional regulation, su ...
... versus 3 Mbp in cyanobacteria), chloroplast gene expression is regulated by more complex systems compared to the simple prokaryotic regulatory system. Chloroplast gene expression is mediated by two distinct types of RNA polymerase (RNAP) and is highly dependent on post-transcriptional regulation, su ...
Answers questions chapter 14
... intron boundary. Once bound, they help recruit the splicing machinery, thereby ensuring that splicing occurs at sites close to exon-intron boundaries (where it should occur) rather than at cryptic sites located far from any exons. g. Describe the two types of RNA editing, outlining the different ste ...
... intron boundary. Once bound, they help recruit the splicing machinery, thereby ensuring that splicing occurs at sites close to exon-intron boundaries (where it should occur) rather than at cryptic sites located far from any exons. g. Describe the two types of RNA editing, outlining the different ste ...
5 - Parkway C-2
... Split Genes and RNA Splicing • Most eukaryotic genes and their RNA transcripts have long noncoding stretches of nucleotides that lie between coding regions • These noncoding regions are called intervening sequences, or introns • The other regions are called exons because they are eventually express ...
... Split Genes and RNA Splicing • Most eukaryotic genes and their RNA transcripts have long noncoding stretches of nucleotides that lie between coding regions • These noncoding regions are called intervening sequences, or introns • The other regions are called exons because they are eventually express ...
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression, typically by causing the destruction of specific mRNA molecules. Historically, it was known by other names, including co-suppression, post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), and quelling. Only after these apparently unrelated processes were fully understood did it become clear that they all described the RNAi phenomenon. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which they published in 1998.Two types of small ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – are central to RNA interference. RNAs are the direct products of genes, and these small RNAs can bind to other specific messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and either increase or decrease their activity, for example by preventing an mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference has an important role in defending cells against parasitic nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. It also influences development.The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes, including animals, and is initiated by the enzyme Dicer, which cleaves long double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules into short double-stranded fragments of ~20 nucleotide siRNAs. Each siRNA is unwound into two single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), the passenger strand and the guide strand. The passenger strand is degraded and the guide strand is incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The most well-studied outcome is post-transcriptional gene silencing, which occurs when the guide strand pairs with a complementary sequence in a messenger RNA molecule and induces cleavage by Argonaute, the catalytic component of the RISC complex. In some organisms, this process spreads systemically, despite the initially limited molar concentrations of siRNA.RNAi is a valuable research tool, both in cell culture and in living organisms, because synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can selectively and robustly induce suppression of specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that systematically shut down each gene in the cell, which can help to identify the components necessary for a particular cellular process or an event such as cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology, medicine and insecticides.





![Pseudo-Replication of [GADV]-Proteins and Origin of Life](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015397345_1-c189eb37b7232bb5a87b48dfe8b0c10b-300x300.png)