Study Guide for LS
... - a half-filled square or circle indicates that the person is a carrier of a certain trait but does not show the trait. - Most genetic disorders, such as Cystic Fibrosis, are due to a recessive gene. ...
... - a half-filled square or circle indicates that the person is a carrier of a certain trait but does not show the trait. - Most genetic disorders, such as Cystic Fibrosis, are due to a recessive gene. ...
Mutations
... How Cells Make Proteins • Key concept: “During protein synthesis, the cell uses information from a gene on a chromosome to produce a specific protein.” • Messenger RNA- copies the coded message from the DNA in the nucleus, and carries the message to the ribosome in the cytoplasm • RNA is similar to ...
... How Cells Make Proteins • Key concept: “During protein synthesis, the cell uses information from a gene on a chromosome to produce a specific protein.” • Messenger RNA- copies the coded message from the DNA in the nucleus, and carries the message to the ribosome in the cytoplasm • RNA is similar to ...
2 Types of Selective Breeding
... For thousands of years people have tried to produce __________________________ with desirable traits _________ methods that people use to develop organisms with desirable traits: 1) Selective Breeding – a process of selecting a few organisms with _______________ to serve as parents of the __________ ...
... For thousands of years people have tried to produce __________________________ with desirable traits _________ methods that people use to develop organisms with desirable traits: 1) Selective Breeding – a process of selecting a few organisms with _______________ to serve as parents of the __________ ...
DNA!
... • The material in the nucleus that contains all of the cell’s genetic information. • The nucleus contains the master set of instructions that determines • what each cell will become, ...
... • The material in the nucleus that contains all of the cell’s genetic information. • The nucleus contains the master set of instructions that determines • what each cell will become, ...
DNA Glossary - FutureLearn
... the male gender- determining Y chromosome is a different size and shape to the X chromosome. ...
... the male gender- determining Y chromosome is a different size and shape to the X chromosome. ...
Study_Guide
... State that deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a polynucleotide, usually double-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containi ...
... State that deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a polynucleotide, usually double-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containi ...
Access Slides
... The “histone code” hypothesis : the pattern of post-translational modifications occurring on the histone tails serves as binding sites for specific proteins. ...
... The “histone code” hypothesis : the pattern of post-translational modifications occurring on the histone tails serves as binding sites for specific proteins. ...
PCR Study Questions
... 5. Which characteristic of DNA’s structure contributes most to the ‘melting point’ determination? ...
... 5. Which characteristic of DNA’s structure contributes most to the ‘melting point’ determination? ...
The Story of DNA vs. RNA
... § Proteins help to determine the size, shape and many other traits of an organism. ...
... § Proteins help to determine the size, shape and many other traits of an organism. ...
REVIEW OF MOLECULAR GENETICS - Pascack Valley Regional
... DNA library - a random collection of DNA fragments from an organism cloned into a vector Ideally contains at least one copy of every DNA sequence. Easily maintained in the laboratory Can be manipulated in various ways to facilitate the isolation of a DNA fragment of interest to a scientist. Num ...
... DNA library - a random collection of DNA fragments from an organism cloned into a vector Ideally contains at least one copy of every DNA sequence. Easily maintained in the laboratory Can be manipulated in various ways to facilitate the isolation of a DNA fragment of interest to a scientist. Num ...
Concept 20.1 A. -Plasmid is the cloning vector.
... - Expression of a Eukaryotic gene in a Prokaryote may be difficult because of a) Different aspects of gene expression: - To overcome difficulties in promoters, and other control sequences we use an expression vector. - This vector contains a very active prokaryotic promoter just upstream of a restri ...
... - Expression of a Eukaryotic gene in a Prokaryote may be difficult because of a) Different aspects of gene expression: - To overcome difficulties in promoters, and other control sequences we use an expression vector. - This vector contains a very active prokaryotic promoter just upstream of a restri ...
Given the following two evolutionary conserved eukaryotic genes A
... Gene A and B are transcription factors. One is a repressor of transcription and one is an activator of transcription, but you don’t know which is which. Both bind to DNA: protein A binds to DNA element AA and protein B binds to DNA element BB. Each DNA binding portion, activation portion and repress ...
... Gene A and B are transcription factors. One is a repressor of transcription and one is an activator of transcription, but you don’t know which is which. Both bind to DNA: protein A binds to DNA element AA and protein B binds to DNA element BB. Each DNA binding portion, activation portion and repress ...
Chapter 12 SWBAT`s and Standards
... Genes are a set of instructions encoded in the DNA sequence of each organism that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins characteristic of that organism. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. ...
... Genes are a set of instructions encoded in the DNA sequence of each organism that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins characteristic of that organism. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. ...
Cell Transformation Chapter 13-3
... B. Genetic Marker- can be a gene for antibiotic resistance that is spliced onto the gene that researchers want expressed. 1. Use a restriction enzyme to cut plasmid and use same enzyme to cut out segment of DNA 2. This creates ends with nucleotides that match “sticky ends” 3. Allows bacteria with th ...
... B. Genetic Marker- can be a gene for antibiotic resistance that is spliced onto the gene that researchers want expressed. 1. Use a restriction enzyme to cut plasmid and use same enzyme to cut out segment of DNA 2. This creates ends with nucleotides that match “sticky ends” 3. Allows bacteria with th ...
DNA Structure
... The order of the nucleotides (bases) in a DNA sequence is a code that provides instructions for making proteins. •A segment of DNA that codes for a specific protein is called a gene. ...
... The order of the nucleotides (bases) in a DNA sequence is a code that provides instructions for making proteins. •A segment of DNA that codes for a specific protein is called a gene. ...
Ch. 19 – Eukaryotic Genomes
... Extra copies of genes (like those for RNA) can be beneficial in the embryo Conversely it is also observed in cancer cells Transposons: regions of DNA that can move from one location to another…position effects this impact. 10% of human genome, 50% in some plants Retrotransposons : move with help of ...
... Extra copies of genes (like those for RNA) can be beneficial in the embryo Conversely it is also observed in cancer cells Transposons: regions of DNA that can move from one location to another…position effects this impact. 10% of human genome, 50% in some plants Retrotransposons : move with help of ...
Sc9 - a 3.1(student notes)
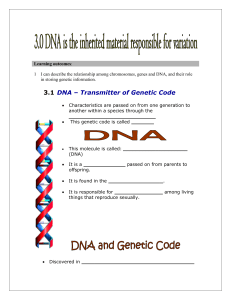
... Learning outcomes: 1 I can describe the relationship among chromosomes, genes and DNA, and their role in storing genetic information. ...
... Learning outcomes: 1 I can describe the relationship among chromosomes, genes and DNA, and their role in storing genetic information. ...
01 - Educator Pages
... A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for RNA and protein. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes lined up like the cars of a train. When genes are being used, the strand of DNA is stretched out so that the information it contains can be decoded and used to direct the synthesis of proteins ...
... A gene is a segment of DNA that codes for RNA and protein. A single molecule of DNA has thousands of genes lined up like the cars of a train. When genes are being used, the strand of DNA is stretched out so that the information it contains can be decoded and used to direct the synthesis of proteins ...
STUDY GUIDE for MICROBIAL GENETICS 1. Define the following
... What is the Rolling Circle Model of bacterial DNA replication? In other words, describe the bidirectionality of bacterial DNA replication. Describe transcription and translation. a. What is the function of RNA Polymerase? b. In prokaryotic cells, where does transcription occur? In eukaryotic cells, ...
... What is the Rolling Circle Model of bacterial DNA replication? In other words, describe the bidirectionality of bacterial DNA replication. Describe transcription and translation. a. What is the function of RNA Polymerase? b. In prokaryotic cells, where does transcription occur? In eukaryotic cells, ...
Study Guide Unit 4 - Mrs. Wolodkowicz`s Biological Realm
... functions of tRNA & mRNA the laws of segregation & independent assortment the terms: dominant, recessive, genotype, phenotype, homozygous, heterozygous, heredity, genetics, purebred, hybrid, codominant, incomplete dominance, polygenic, pigment, alleles, fertilization, gene, gamete, pedigree, m ...
... functions of tRNA & mRNA the laws of segregation & independent assortment the terms: dominant, recessive, genotype, phenotype, homozygous, heterozygous, heredity, genetics, purebred, hybrid, codominant, incomplete dominance, polygenic, pigment, alleles, fertilization, gene, gamete, pedigree, m ...