DNA and Genetic Engineering Midterm Review Chapter 12 Review
... and T, and G and C – which explained Chargaff’s rules. 14. Base pairing is the principle that hydrogen bonds form only between certain base pairs – A and T, and G and C. In DNA replication, base pairing ensures that the complementary strands produced are identical to the original strands. 16. DNA se ...
... and T, and G and C – which explained Chargaff’s rules. 14. Base pairing is the principle that hydrogen bonds form only between certain base pairs – A and T, and G and C. In DNA replication, base pairing ensures that the complementary strands produced are identical to the original strands. 16. DNA se ...
Study Guide for LS
... Cloning- process of making an identical copy of another organism using its DNA. Dolly, the sheep, is the first successfully cloned mammal because of genetic engineering. ...
... Cloning- process of making an identical copy of another organism using its DNA. Dolly, the sheep, is the first successfully cloned mammal because of genetic engineering. ...
What`s the Big Deal About DNA?
... 5. Describe why scientists would want to change how fast (or slow) organisms like salmon or grass grow. Do you think this should be done? Defend your answer. ...
... 5. Describe why scientists would want to change how fast (or slow) organisms like salmon or grass grow. Do you think this should be done? Defend your answer. ...
DNA extraction activity
... You will need Flash Player to run this simulation. Go to http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/labs/extraction/ Click on the “Start Lab” to begin. There are sound effects with this simulation, so if you’re in a lab, use headphones. 1. What are some reasons that scientists may need DNA samples? 2. T ...
... You will need Flash Player to run this simulation. Go to http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/labs/extraction/ Click on the “Start Lab” to begin. There are sound effects with this simulation, so if you’re in a lab, use headphones. 1. What are some reasons that scientists may need DNA samples? 2. T ...
GBE 214 TECNIQUES IN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
... describe the correct way for experiments design, sampling, collection of results, their analysis and interpretation, error detection and correction. The techniques presented in this course would provide students with an excellent resume for future career opportunities in biotechnology. The laborator ...
... describe the correct way for experiments design, sampling, collection of results, their analysis and interpretation, error detection and correction. The techniques presented in this course would provide students with an excellent resume for future career opportunities in biotechnology. The laborator ...
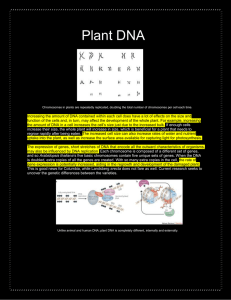
Plant DNA - The uniqueness of DNA
... The expression of genes, short stretches of DNA that encode all the outward characteristics of organisms, may also be influenced by DNA replication. Each chromosome is composed of a different set of genes, and so Arabidopsis thaliana’s five basic chromosomes contain five unique sets of genes. When t ...
... The expression of genes, short stretches of DNA that encode all the outward characteristics of organisms, may also be influenced by DNA replication. Each chromosome is composed of a different set of genes, and so Arabidopsis thaliana’s five basic chromosomes contain five unique sets of genes. When t ...
epigenomics - IES Valldemossa
... An Epigenome consists of a record of the chemical changes to the DNA and histone proteins of an organism. These changes can be passed down to an organism's offspring. ...
... An Epigenome consists of a record of the chemical changes to the DNA and histone proteins of an organism. These changes can be passed down to an organism's offspring. ...
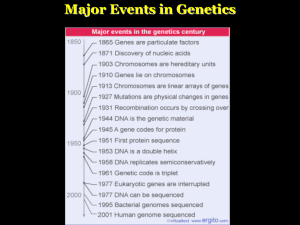
Major Events in Genetics
... A gene is a genetic sequence that codes for an RNA. In protein coding genes, the RNA codes for a protein. ...
... A gene is a genetic sequence that codes for an RNA. In protein coding genes, the RNA codes for a protein. ...
Gene Q
... a) Q; b) R; c) S; d) T; e) more than one of the above. 2. Based on the results shown, which gene(s) could be on the Y chromosome? a) Q; b) R; c) S; d) T; e) more than one of the above. 3. Which gene(s) must be autosomal and homozygous for a particular ASO? a) Q; b) R; c) S; d) T; e) more than one of ...
... a) Q; b) R; c) S; d) T; e) more than one of the above. 2. Based on the results shown, which gene(s) could be on the Y chromosome? a) Q; b) R; c) S; d) T; e) more than one of the above. 3. Which gene(s) must be autosomal and homozygous for a particular ASO? a) Q; b) R; c) S; d) T; e) more than one of ...
Me oh Mi!
... If gametes of an organism have 16 chromosomes, how many would one of its skin cells have? ...
... If gametes of an organism have 16 chromosomes, how many would one of its skin cells have? ...
Epigenetics - UNM Biology
... transcriptional and posttranscriptional level of gene activity as well as at the level of protein translation and posttranslational modifications. • Mechanisms include: ...
... transcriptional and posttranscriptional level of gene activity as well as at the level of protein translation and posttranslational modifications. • Mechanisms include: ...
Name:
... of DNA. Why do you think this is so, instead of simply starting at one end and working towards the other? 7. Why does the information encoded in DNA need to be copied onto RNA? ...
... of DNA. Why do you think this is so, instead of simply starting at one end and working towards the other? 7. Why does the information encoded in DNA need to be copied onto RNA? ...
Two Epigenetic Mechanisms
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
Sources of DNA
... called plasmids. They contain a few nonessential genes. These genes code for extra traits that help bacteria survive some extraordinary circumstances, such as antibiotics or extreme ...
... called plasmids. They contain a few nonessential genes. These genes code for extra traits that help bacteria survive some extraordinary circumstances, such as antibiotics or extreme ...
HomeworkCh7
... b. What is the role of transcription factors in Archaea and Eukarya? Hint. Same as sigma factors in bacteria. c. What is a promotor? d. What are the three main phases of RNA synthesis? e. Can more than one copy of the gene be copied at the same time? 6. Translation a. What is translation? Why do you ...
... b. What is the role of transcription factors in Archaea and Eukarya? Hint. Same as sigma factors in bacteria. c. What is a promotor? d. What are the three main phases of RNA synthesis? e. Can more than one copy of the gene be copied at the same time? 6. Translation a. What is translation? Why do you ...
Name Ch 12 Study Guide
... 14) List the pieces of information about DNA structure that Rosalind Franklin discovered through her x-ray diffraction research. 15) What is DNA Replication? ...
... 14) List the pieces of information about DNA structure that Rosalind Franklin discovered through her x-ray diffraction research. 15) What is DNA Replication? ...
Fall 2005 Due: 9/9 GENETICS Homework 1 1. (1 point) The
... following table. Give the order of compound A, B, C, and D in a biochemical pathway. Outline a biochemical pathway ...
... following table. Give the order of compound A, B, C, and D in a biochemical pathway. Outline a biochemical pathway ...
Slide 1
... DNA in eukaryotes (but not in bacteria and Archae) is twisted around protein complexes called histones. They are positively charged proteins that interact with the negatively charged DNA. Each ”ball” is called a nucleosome. ...
... DNA in eukaryotes (but not in bacteria and Archae) is twisted around protein complexes called histones. They are positively charged proteins that interact with the negatively charged DNA. Each ”ball” is called a nucleosome. ...
Non-Mendelian Genetics Test Review
... pairs so that they may be visualized to determine abnormalities. ...
... pairs so that they may be visualized to determine abnormalities. ...
DNA
... *is passed from one generation to the next in chromosomes. *looks like a ladder, twisted around itself, called a double helix DNA Timeline Facts… Early 1950’s o 1st picture of DNA taken by Rosalind Franklin using an X-ray machine. ...
... *is passed from one generation to the next in chromosomes. *looks like a ladder, twisted around itself, called a double helix DNA Timeline Facts… Early 1950’s o 1st picture of DNA taken by Rosalind Franklin using an X-ray machine. ...
Genetic Engineering
... • Hundreds of useful bacterial strains have been produced • Bacteria can even digest oil ...
... • Hundreds of useful bacterial strains have been produced • Bacteria can even digest oil ...
Gene Expression (Epigenetics)
... • The impact of DNA methylation and histone acetylation on gene expression. • The role of oncogenes, protooncogenes, and tumor suppressor genes ...
... • The impact of DNA methylation and histone acetylation on gene expression. • The role of oncogenes, protooncogenes, and tumor suppressor genes ...
Webquest
... Please tour the following website based on the DNA content you have been learning recently. They will show you visually some of what is going on and help you to understand exactly what it happening. You will have to answer some questions based on what you see. 1. First go to the page: http://learn.g ...
... Please tour the following website based on the DNA content you have been learning recently. They will show you visually some of what is going on and help you to understand exactly what it happening. You will have to answer some questions based on what you see. 1. First go to the page: http://learn.g ...