Chapter 12 SWBAT`s and Standards
... What happens during DNA replication? What are the three main types of RNA? What is transcription? What is translation? What are mutations? How are lac genes turned off and on? How are most eukaryotic genes controlled? ...
... What happens during DNA replication? What are the three main types of RNA? What is transcription? What is translation? What are mutations? How are lac genes turned off and on? How are most eukaryotic genes controlled? ...
With the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have
... Since the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have access to more information than ever before about our genetic make-up. The human genome contains 3 billion base pairs of DNA, encoding an estimated 25,000 genes, which are the basic units of heredity. This course addresses questions such ...
... Since the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have access to more information than ever before about our genetic make-up. The human genome contains 3 billion base pairs of DNA, encoding an estimated 25,000 genes, which are the basic units of heredity. This course addresses questions such ...
Genetic Engineering
... • Hundreds of useful bacterial strains have been produced • Bacteria can even digest oil ...
... • Hundreds of useful bacterial strains have been produced • Bacteria can even digest oil ...
Nucleic Acids - faculty at Chemeketa
... What will be the composition of the DNA strand complementary to –AGCCA– ? a. b. c. d. ...
... What will be the composition of the DNA strand complementary to –AGCCA– ? a. b. c. d. ...
CS 262—Lecture 1 Notes • 4-‐5 HWs, 3 late days • (Optional
... • Gene transcription: Transcription factors recognize binding sites in DNA, recruits RNA polymerase o RNA polymerases actually transcribes the DNA strand o Presence or absence of transcription factor dictates whether ...
... • Gene transcription: Transcription factors recognize binding sites in DNA, recruits RNA polymerase o RNA polymerases actually transcribes the DNA strand o Presence or absence of transcription factor dictates whether ...
STUDY GUIDE
... 3. A change in the DNA structure of a cell that affects the instructions for making protein is called what? A. a mutation C. a misprint B. a clone D. a splice 4. Rings of DNA found in bacteria are responsible for a great deal of the exchange of genetic information that occurs in nature. What are the ...
... 3. A change in the DNA structure of a cell that affects the instructions for making protein is called what? A. a mutation C. a misprint B. a clone D. a splice 4. Rings of DNA found in bacteria are responsible for a great deal of the exchange of genetic information that occurs in nature. What are the ...
notes
... Bacteria provide the means • Bacteria have been vital in developing DNA technology • Thermus aquaticus (which lives in hot springs) provides DNA polymerase enzyme for PCR • Escherichia coli (which lives in our guts) provides “plasmids” (mini-chromosomes) used in cloning • 100s of bacterial species ...
... Bacteria provide the means • Bacteria have been vital in developing DNA technology • Thermus aquaticus (which lives in hot springs) provides DNA polymerase enzyme for PCR • Escherichia coli (which lives in our guts) provides “plasmids” (mini-chromosomes) used in cloning • 100s of bacterial species ...
AP Biology
... 4. What is the central dogma? Discuss the life cycle of a typical retrovirus. How does the discovery of retroviruses require revision of the central dogma? ...
... 4. What is the central dogma? Discuss the life cycle of a typical retrovirus. How does the discovery of retroviruses require revision of the central dogma? ...
Genetic selection and variation
... Genes are a specific sequences of DNA located on the chromosomes. Chromosomes consist of proteins (histones) combined with two complementary chains of DNA. ...
... Genes are a specific sequences of DNA located on the chromosomes. Chromosomes consist of proteins (histones) combined with two complementary chains of DNA. ...
Genomics and Forensics - MCCC Faculty & Staff Web Pages
... Genetic maps: relative arrangement and approximate distance of genes on chromosomes (recombination mapping) ...
... Genetic maps: relative arrangement and approximate distance of genes on chromosomes (recombination mapping) ...
Chapter 11 Concept Check Questions
... 1.What are the three parts of a nucleotide? Which parts make up the backbone of a DNA strand? ...
... 1.What are the three parts of a nucleotide? Which parts make up the backbone of a DNA strand? ...
Gene Regulation
... Some genes are regulated (turned off and on) by repressor proteins While others use proteins that enhance the rate of transcription. Operons are generally not found in Eukaryotes. Gene regulation is controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex that those of the la ...
... Some genes are regulated (turned off and on) by repressor proteins While others use proteins that enhance the rate of transcription. Operons are generally not found in Eukaryotes. Gene regulation is controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex that those of the la ...
Genetic Markers
... non-coding DNA may or may not affect phenotype • SNPs can cause Restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) if in a restriction enzyme site • Tandem repeat sequences (or microsatellies), such as dinucleotides (CA)n, tri- and tetra-nucleotides, that are variable for the number of repeats. • Mos ...
... non-coding DNA may or may not affect phenotype • SNPs can cause Restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) if in a restriction enzyme site • Tandem repeat sequences (or microsatellies), such as dinucleotides (CA)n, tri- and tetra-nucleotides, that are variable for the number of repeats. • Mos ...
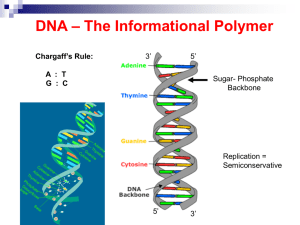
DNA Connection
... DNA is made up of 4 nitrogen bases. Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) ...
... DNA is made up of 4 nitrogen bases. Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) ...
Genetic Engineering
... • Used to make millions of copies of select section of DNA • When small amount of DNA are found but large amounts are needed for analysis • Semen, blood, other tissues, long-dead specimens – DNA from all can be amplified • Thermus aquaticus – hot springs bacterium • http://www.dnalc.org/ddnalc.org/r ...
... • Used to make millions of copies of select section of DNA • When small amount of DNA are found but large amounts are needed for analysis • Semen, blood, other tissues, long-dead specimens – DNA from all can be amplified • Thermus aquaticus – hot springs bacterium • http://www.dnalc.org/ddnalc.org/r ...
Study Guide to Chapter 5 Ð DNA
... ______________________ a) transcription b) translation, in which a DNA serves as a template to make a strand of ___________________ a) mRNA b) tRNA. This occurs in __________ a) the nucleus b) the ribosome). Once the strand is complete it detaches from DNA. The second step in making a protein is cal ...
... ______________________ a) transcription b) translation, in which a DNA serves as a template to make a strand of ___________________ a) mRNA b) tRNA. This occurs in __________ a) the nucleus b) the ribosome). Once the strand is complete it detaches from DNA. The second step in making a protein is cal ...
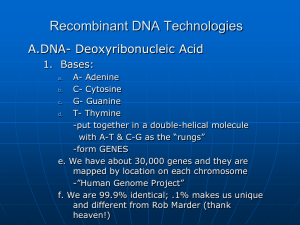
Recombinant DNA Technologies
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...