ome
... The human genome consists of approximately 3.1 billion base pairs. The genome is approximately 99.9% the same between individuals of all nationalities and backgrounds. Less than 2% of the human genome codes for genes. The vast majority of our DNA is non-protein coding. The genome contains approximat ...
... The human genome consists of approximately 3.1 billion base pairs. The genome is approximately 99.9% the same between individuals of all nationalities and backgrounds. Less than 2% of the human genome codes for genes. The vast majority of our DNA is non-protein coding. The genome contains approximat ...
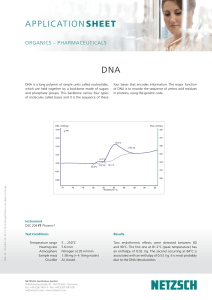
Application Sheet: DNA - NETZSCH Thermal Analysis
... APPLICATION SHEET ORGANICS – PHARMACEUTICALS ...
... APPLICATION SHEET ORGANICS – PHARMACEUTICALS ...
DNA Test Review
... 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. What are the types of RNA? 7. Messenger RNA is formed in the process of _____. 8. What happens during translation a ...
... 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. What are the types of RNA? 7. Messenger RNA is formed in the process of _____. 8. What happens during translation a ...
Chapter 3 Section 4
... The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be pr ...
... The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be pr ...
Code DNA!
... This is the process of copying DNA to RNA. The process of nuclear division in cells that produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell. ...
... This is the process of copying DNA to RNA. The process of nuclear division in cells that produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell. ...
5. Protein Synthesis
... 4. What part of the nucleotide is different about the 4 nucleotides of DNA? 5. Information flows from DNA to ________ to proteins. 6. What holds base pairs together? 7. What is the process of a cells making an exact copy of its DNA called? 8. What is a codon? 9. What is an anticodon and where is it ...
... 4. What part of the nucleotide is different about the 4 nucleotides of DNA? 5. Information flows from DNA to ________ to proteins. 6. What holds base pairs together? 7. What is the process of a cells making an exact copy of its DNA called? 8. What is a codon? 9. What is an anticodon and where is it ...
Biotechnology Key Terms and Concepts
... *Refer to textbook for more detail I. Biotechnology A. Definition-use of organisms to perform practical tasks for humans B. Much of biotechnology deals with analyzing and manipulating genomes of organisms at the molecular level (DNA technology) C. Genome-complete set of an organism’s genetic materia ...
... *Refer to textbook for more detail I. Biotechnology A. Definition-use of organisms to perform practical tasks for humans B. Much of biotechnology deals with analyzing and manipulating genomes of organisms at the molecular level (DNA technology) C. Genome-complete set of an organism’s genetic materia ...
Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... 14. What is the difference between the leading and lagging strand during replication? Why are Okazaki fragments required on the lagging strand? 15. What is a telomere? Why do they shorten over a period of time? In what types of cells can they be lengthened? By what enzyme? Chapter 17: From Gene to P ...
... 14. What is the difference between the leading and lagging strand during replication? Why are Okazaki fragments required on the lagging strand? 15. What is a telomere? Why do they shorten over a period of time? In what types of cells can they be lengthened? By what enzyme? Chapter 17: From Gene to P ...
DNA and Chromosomes
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
Journey Into dna
... How many cells does the human body contain? What is the only type of cell in the human body that contains no nucleus and therefore no nuclear DNA? Intestines: Is the DNA code from cell to cell in the human body the same? Cells: ...
... How many cells does the human body contain? What is the only type of cell in the human body that contains no nucleus and therefore no nuclear DNA? Intestines: Is the DNA code from cell to cell in the human body the same? Cells: ...
Vocabulary 7
... • When one of the 4 base pairs is : –(substitution) “replaced” or –(insertion) “added” or –(deletion) “removed” ...
... • When one of the 4 base pairs is : –(substitution) “replaced” or –(insertion) “added” or –(deletion) “removed” ...
VII. DNA/ GENES/ AND GENETICS • Describe the relationship
... Why can’t one cell in a multi-cellular organism function independently of that organism? Even though all cells in an organism contain the same genes, they can vary greatly in structure and function. How is this possible? What mechanism do cells use to turn genes on and off? Give examples of emerging ...
... Why can’t one cell in a multi-cellular organism function independently of that organism? Even though all cells in an organism contain the same genes, they can vary greatly in structure and function. How is this possible? What mechanism do cells use to turn genes on and off? Give examples of emerging ...
2.5.4. DNA Revision Qs
... 4 Heredity is the passing on of features from one generation to another by means of ________________________________________. ...
... 4 Heredity is the passing on of features from one generation to another by means of ________________________________________. ...
2D Barcode Quiz
... Proteins are polymers consisting of building blocks called amino acids All proteins begin with the amino acid Methionine A codon is a series of four sequential nucleotides which codes for an amino acid Polymerase is an enzyme which breaks down DNA molecules Transcription is the process of making an ...
... Proteins are polymers consisting of building blocks called amino acids All proteins begin with the amino acid Methionine A codon is a series of four sequential nucleotides which codes for an amino acid Polymerase is an enzyme which breaks down DNA molecules Transcription is the process of making an ...
DNA Replication
... • "Phenotype" is an organism's actual observed properties, such as morphology, development, or behaviour ...
... • "Phenotype" is an organism's actual observed properties, such as morphology, development, or behaviour ...
Section 6-3
... There are three methods people have created to develop organisms with desired traits ...
... There are three methods people have created to develop organisms with desired traits ...
Eukaryotic Gene Expression ppt
... Have a nuclear envelope Many are multicellular with specialized cells All cells have full sets of chromosomes Not all genes need to be turned on (expressed) ...
... Have a nuclear envelope Many are multicellular with specialized cells All cells have full sets of chromosomes Not all genes need to be turned on (expressed) ...
Epigenetics
... • The second kind of mark, called histone modification, indirectly affects the DNA in your genome. • Histones are proteins which enable DNA's molecules to be wound up neatly into chromosomes inside the cell nucleus. • A variety of chemical tags can grab hold of the tails of histones, changing how t ...
... • The second kind of mark, called histone modification, indirectly affects the DNA in your genome. • Histones are proteins which enable DNA's molecules to be wound up neatly into chromosomes inside the cell nucleus. • A variety of chemical tags can grab hold of the tails of histones, changing how t ...
Chapter 10 Section 3 Notes Answer Key
... I. DNA A. DNA- a chemical that contains information an organism needs to grow and function 1. Watson and Crick made and accurate model of DNA in 1953 2. The structure of DNA is similar to a twisted ladder. a. The sides of the ladder are made up of sugarphosphate molecules. b. The rungs of the ladder ...
... I. DNA A. DNA- a chemical that contains information an organism needs to grow and function 1. Watson and Crick made and accurate model of DNA in 1953 2. The structure of DNA is similar to a twisted ladder. a. The sides of the ladder are made up of sugarphosphate molecules. b. The rungs of the ladder ...
Genetics - FAQ`s - El Camino College
... consist of phosphates, sugars and four chemical bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine). WHAT IS A CHROMOSOME? A threadlike structure found in the nucleus of the cell that contains the hereditary material. A chromosome is made up of one tightly coiled DNA molecule. Humans have 46 chromosomes ...
... consist of phosphates, sugars and four chemical bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine). WHAT IS A CHROMOSOME? A threadlike structure found in the nucleus of the cell that contains the hereditary material. A chromosome is made up of one tightly coiled DNA molecule. Humans have 46 chromosomes ...
Biology Packet 7: DNA & RNA
... Explain the function of DNA. Summarize the relationship between genes and DNA. Describe the overall structure of the DNA molecule. Describe the three components of a nucleotide. Explain the base pairing rules. Relate the role of the base pairing rules to the structure of DNA. Summarize the events of ...
... Explain the function of DNA. Summarize the relationship between genes and DNA. Describe the overall structure of the DNA molecule. Describe the three components of a nucleotide. Explain the base pairing rules. Relate the role of the base pairing rules to the structure of DNA. Summarize the events of ...
Genomics - West High School
... way to study biology? Genomics: Using tools to study all the genes in an organism (the entire genome) simultaneously once its sequence is known. (~ 190 organisms as of March ...
... way to study biology? Genomics: Using tools to study all the genes in an organism (the entire genome) simultaneously once its sequence is known. (~ 190 organisms as of March ...