Document
... • Modified bases arise from chemical changes made to the four standard bases after transcription. (tRNA-modifying enzymes) • Common secondary structure – the cloverleaf structure ...
... • Modified bases arise from chemical changes made to the four standard bases after transcription. (tRNA-modifying enzymes) • Common secondary structure – the cloverleaf structure ...
Control of Gene Expression
... Proteins which control the expression of other genes Link the genome with the environment Activated by signals from outside the cell (e.g. hormones, sugar, etc.) Allow RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter so that transcription can begin Gene must also be exposed –DNA must unwind in that area. ...
... Proteins which control the expression of other genes Link the genome with the environment Activated by signals from outside the cell (e.g. hormones, sugar, etc.) Allow RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter so that transcription can begin Gene must also be exposed –DNA must unwind in that area. ...
Chapter 13
... Antisense genes block expression of their targets when introduced into eukaryotic cells. ...
... Antisense genes block expression of their targets when introduced into eukaryotic cells. ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... nucleus to the cytoplasm to initiate translation Codons = sequences of 3 bases Made during transcription ...
... nucleus to the cytoplasm to initiate translation Codons = sequences of 3 bases Made during transcription ...
The Molecular Genetics of Gene Expression
... Polymerases • RNA polymerases are large, multisubunit complexes whose active form is called the RNA polymerase holoenzyme • Bacterial cells have only one RNA polymerase holoenzyme, which contains six polypeptide chains • Eukaryotes have several types of RNA polymerase • RNA polymerase I transcribes ...
... Polymerases • RNA polymerases are large, multisubunit complexes whose active form is called the RNA polymerase holoenzyme • Bacterial cells have only one RNA polymerase holoenzyme, which contains six polypeptide chains • Eukaryotes have several types of RNA polymerase • RNA polymerase I transcribes ...
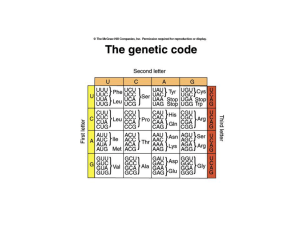
Features of the genetic code
... methyl thransferase adds methyl groups (-CH3) to the G and one or more of the first few bases of the RNA transcript. Capping and methylation is believed to be critical for efficient translation. • Addition of a poly A tail (100-200 As) at the 3’ end of the primary transcript by a poly-A-polymerase. ...
... methyl thransferase adds methyl groups (-CH3) to the G and one or more of the first few bases of the RNA transcript. Capping and methylation is believed to be critical for efficient translation. • Addition of a poly A tail (100-200 As) at the 3’ end of the primary transcript by a poly-A-polymerase. ...
Crossword Puzzle: Protein Synthesis
... 3. Sequence of nucleotides on DNA to with RNA polymerase will attach to start transcription 4. mRNA copying DNA's nucleotide sequence 5. 3 nucleotides on tRNA that match to a specific codon on mRNA 6. Type of RNA that helps make up ribosomes 7. Instructions for making proteins in cells 14. The numbe ...
... 3. Sequence of nucleotides on DNA to with RNA polymerase will attach to start transcription 4. mRNA copying DNA's nucleotide sequence 5. 3 nucleotides on tRNA that match to a specific codon on mRNA 6. Type of RNA that helps make up ribosomes 7. Instructions for making proteins in cells 14. The numbe ...
Distinguish between mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA. What molecule does
... of the ribosome's protein manufacturing machinery. rRNA are sub cellular structures that are composed of another kind of RNA. Each ribosome is composed of 2 subunits 1 large and 1 small when assembled it can bind to structures called Transfer RNA (tRNA) carrying amino acids. ...
... of the ribosome's protein manufacturing machinery. rRNA are sub cellular structures that are composed of another kind of RNA. Each ribosome is composed of 2 subunits 1 large and 1 small when assembled it can bind to structures called Transfer RNA (tRNA) carrying amino acids. ...
Protein Synthesis - Biology Junction
... transcription 4. mRNA copying DNA's nucleotide sequence 5. 3 nucleotides on tRNA that match to a specific codon on mRNA 6. Type of RNA that helps make up ribosomes 7. Instructions for making proteins in cells 14. The number of amino acids that exist 16. Number of strands making up RNA 19. DNA to RNA ...
... transcription 4. mRNA copying DNA's nucleotide sequence 5. 3 nucleotides on tRNA that match to a specific codon on mRNA 6. Type of RNA that helps make up ribosomes 7. Instructions for making proteins in cells 14. The number of amino acids that exist 16. Number of strands making up RNA 19. DNA to RNA ...
Topics covered on this exam include: cellular respiration
... 1. Compare and contrast DNA with RNA. How do they differ structurally? How are their functions different? 2. What are the components of a single nucleotide? Dow we find nucleotides in both RNA and DNA? 3. Be able to go between DNA DNA, DNA RNA and RNA RNA. 4. What are the three types of RNA? W ...
... 1. Compare and contrast DNA with RNA. How do they differ structurally? How are their functions different? 2. What are the components of a single nucleotide? Dow we find nucleotides in both RNA and DNA? 3. Be able to go between DNA DNA, DNA RNA and RNA RNA. 4. What are the three types of RNA? W ...
Section 5-4
... – Messenger RNA is a molecule that transfers the information on DNA to the ribosomes – Transfer RNA is a molecule that brings the amino acids to the ribosomes ...
... – Messenger RNA is a molecule that transfers the information on DNA to the ribosomes – Transfer RNA is a molecule that brings the amino acids to the ribosomes ...
Biology Ch 10 How Proteins are Made
... • DNA is unwound and unzipped at the site of the gene to be expressed (promoter) • RNA polymerase adds the complementary nucleotides to the exposed DNA nucleotides – Every three mRNA bases is called a codon ...
... • DNA is unwound and unzipped at the site of the gene to be expressed (promoter) • RNA polymerase adds the complementary nucleotides to the exposed DNA nucleotides – Every three mRNA bases is called a codon ...
Study Guide
... How are the functions of mRNA and tRNA different? Describe the process of transcription and translation. What is a codon? What is an anticodon? How are they related? Why is RNA necessary for expressing the code in DNA? How does an organism’s DNA code for its traits? Summarize the process ...
... How are the functions of mRNA and tRNA different? Describe the process of transcription and translation. What is a codon? What is an anticodon? How are they related? Why is RNA necessary for expressing the code in DNA? How does an organism’s DNA code for its traits? Summarize the process ...
DNA Transcription Translation The Central Dogma Trait RNA
... The same genetic information is in all 100 trillion cells of any one person. Different cells use the same blueprint in different ways. ...
... The same genetic information is in all 100 trillion cells of any one person. Different cells use the same blueprint in different ways. ...
Chapter 10 Lesson 1
... a. One nucleotide is substituted for another. This only changes one a.acid B. Mutagen 1. Def – External agents that cause mutations a. Ex: radiation, high temp, chemicals, environmental factors C. Mutations 1. Body cells – only cause problems in person 2. Sex cells – problems are passed from generat ...
... a. One nucleotide is substituted for another. This only changes one a.acid B. Mutagen 1. Def – External agents that cause mutations a. Ex: radiation, high temp, chemicals, environmental factors C. Mutations 1. Body cells – only cause problems in person 2. Sex cells – problems are passed from generat ...
PowerPoint
... The same genetic information is in all 100 trillion cells of any one person. Different cells use the same blueprint in different ways. ...
... The same genetic information is in all 100 trillion cells of any one person. Different cells use the same blueprint in different ways. ...
Write True if the statement is true
... 2. Messenger RNA carries copies of the instructions for making proteins from DNA to other parts of the cell. 3. RNA polymerase transfers amino acids to ribosomes. 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme that assembles a complementary st ...
... 2. Messenger RNA carries copies of the instructions for making proteins from DNA to other parts of the cell. 3. RNA polymerase transfers amino acids to ribosomes. 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme that assembles a complementary st ...
RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS (ch. 17) TERMS TO KNOW: RNA polymerase - the enzyme responsible for RNA transcription. Moves along gene and bonds appropriate RNA nucleotide to complimentary DNA nucleotide. Promoter - binding site on gene that RNA polymerase attaches to at the start of transcription. Codon ...
... RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS (ch. 17) TERMS TO KNOW: RNA polymerase - the enzyme responsible for RNA transcription. Moves along gene and bonds appropriate RNA nucleotide to complimentary DNA nucleotide. Promoter - binding site on gene that RNA polymerase attaches to at the start of transcription. Codon ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis - Kent City School District
... Elongation adds new RNA bases, including Uracil, down the exposed DNA bases Termination occurs when RNA polymerase hits the “stop” signal and detaches the new single strand of RNA ...
... Elongation adds new RNA bases, including Uracil, down the exposed DNA bases Termination occurs when RNA polymerase hits the “stop” signal and detaches the new single strand of RNA ...
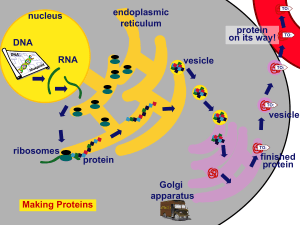
From Gene to Protein
... polypeptide, then there must be a process by which information on the DNA is conveyed to the protein making machinery of the cell ...
... polypeptide, then there must be a process by which information on the DNA is conveyed to the protein making machinery of the cell ...
Ch 17 From Gene to Protei
... 1. Transcription cannot begin in eukaryotic cells until a. the two DNA strands have completely separated and exposed the promoter. b. several transcription factors have bound to the promoter. c. the 5' caps are removed from the mRNA. d. the DNA introns are removed from the template. e. DNA nucleases ...
... 1. Transcription cannot begin in eukaryotic cells until a. the two DNA strands have completely separated and exposed the promoter. b. several transcription factors have bound to the promoter. c. the 5' caps are removed from the mRNA. d. the DNA introns are removed from the template. e. DNA nucleases ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.