Protein Synthesis - Madison County Schools
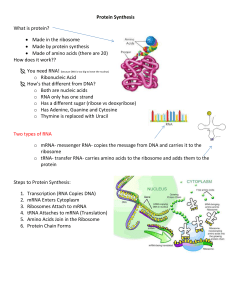
... What is protein? Made in the ribosome Made by protein synthesis Made of amino acids (there are 20) How does it work?? You need RNA! (because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus) o Ribonucleic Acid How’s that different from DNA? o Both are nucleic acids o RNA only has one strand o Has a dif ...
... What is protein? Made in the ribosome Made by protein synthesis Made of amino acids (there are 20) How does it work?? You need RNA! (because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus) o Ribonucleic Acid How’s that different from DNA? o Both are nucleic acids o RNA only has one strand o Has a dif ...
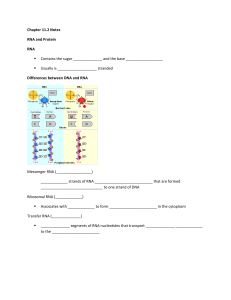
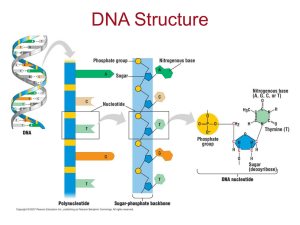
Chapter 11.2 Notes RNA and Protein RNA Contains the sugar and
... Messenger RNA (_________________) _____________ strands of RNA ____________________________ that are formed ______________________________ to one strand of DNA Ribosomal RNA (_____________) ...
... Messenger RNA (_________________) _____________ strands of RNA ____________________________ that are formed ______________________________ to one strand of DNA Ribosomal RNA (_____________) ...
Know your molecules organizer
... Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during replication Adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ ...
... Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during replication Adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ ...
DNA Connection
... • Nitrogen bases along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. • Proteins are long chains of individual amino acids. • A group 3 DNA bases codes for one specific amino acid. ...
... • Nitrogen bases along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. • Proteins are long chains of individual amino acids. • A group 3 DNA bases codes for one specific amino acid. ...
Protein Synthesis Notes: Transcription and Translation
... Codon: group of ___________ nucleotides on the messenger RNA that specifies one amino acid. 3. _______________ (transfer RNA) carries amino acids to the mRNA. 4. This tRNA has an ________________ that matches the codon on the mRNA strand. _____________________: group of 3 unpaired nucleotides on a t ...
... Codon: group of ___________ nucleotides on the messenger RNA that specifies one amino acid. 3. _______________ (transfer RNA) carries amino acids to the mRNA. 4. This tRNA has an ________________ that matches the codon on the mRNA strand. _____________________: group of 3 unpaired nucleotides on a t ...
Protein Synthesis
... -together with proteins it makes up ribosomes -assembled in nucleolus -large and small subunits come together ribosomes ...
... -together with proteins it makes up ribosomes -assembled in nucleolus -large and small subunits come together ribosomes ...
No Slide Title
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the DNA message out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm to ribosomes, the site of protein synthesis. ...
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the DNA message out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm to ribosomes, the site of protein synthesis. ...
Gene Expression Vocabulary
... 9. Messenger RNA: carries hereditary information from DNA and delivers it to the site of translation 10. Transfer RNA: acts as an interpreter molecule, translating mRNA sequences into amino acid sequences 11. Ribosomal RNA: help build proteins; they function at the sites of translation 12. Codons: t ...
... 9. Messenger RNA: carries hereditary information from DNA and delivers it to the site of translation 10. Transfer RNA: acts as an interpreter molecule, translating mRNA sequences into amino acid sequences 11. Ribosomal RNA: help build proteins; they function at the sites of translation 12. Codons: t ...
Chapter 15: Protein Synthesis
... • Each 3-base (triplet) sequence of the mRNA is a codon that specifies either a start codon, a particular amino acid, or a stop codon • Transfer RNA (tRNA) is another type of RNA – it is found free-floating in the cytoplasm and is responsible for carrying one amino acid – Remember amino acids are th ...
... • Each 3-base (triplet) sequence of the mRNA is a codon that specifies either a start codon, a particular amino acid, or a stop codon • Transfer RNA (tRNA) is another type of RNA – it is found free-floating in the cytoplasm and is responsible for carrying one amino acid – Remember amino acids are th ...
DNA/RNA.lecture
... B. George Beadle & Edward Tatum (early 1940’s) C. Overview: information flow & gene expression II. Transcription A. Structure 1. nucleotide differences 2. RNA 3. short B. When does this happen? C. 3 main kinds of RNA 1. messenger RNAs (mRNA) 2. Other 2 types of RNA - protein-producing machinery a. t ...
... B. George Beadle & Edward Tatum (early 1940’s) C. Overview: information flow & gene expression II. Transcription A. Structure 1. nucleotide differences 2. RNA 3. short B. When does this happen? C. 3 main kinds of RNA 1. messenger RNAs (mRNA) 2. Other 2 types of RNA - protein-producing machinery a. t ...
outline File - selu moodle
... Begins at a promoter transcribes the transcription unit ends at the terminator Promoter – sequence within DNA Elongation uses RNA polymerase to add ribonucleotides that are complementary to the template strand Most common mechanism for termination is the formation of a hairpin structure In proka ...
... Begins at a promoter transcribes the transcription unit ends at the terminator Promoter – sequence within DNA Elongation uses RNA polymerase to add ribonucleotides that are complementary to the template strand Most common mechanism for termination is the formation of a hairpin structure In proka ...
Document
... Introns are removed from the primary transcript and exons are spliced together to make mRNA. In some genes more than 90% of the pre-mRNA is destroyed, never to appear in the mRNA. ...
... Introns are removed from the primary transcript and exons are spliced together to make mRNA. In some genes more than 90% of the pre-mRNA is destroyed, never to appear in the mRNA. ...
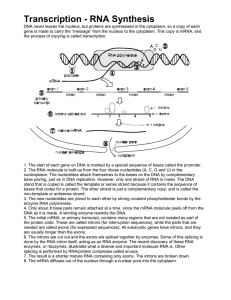
Transcription
... base pairing, just as in DNA replication. However, only one strand of RNA is made. The DNA stand that is copied is called the template or sense strand because it contains the sequence of bases that codes for a protein. The other strand is just a complementary copy, and is called the non-template or ...
... base pairing, just as in DNA replication. However, only one strand of RNA is made. The DNA stand that is copied is called the template or sense strand because it contains the sequence of bases that codes for a protein. The other strand is just a complementary copy, and is called the non-template or ...
Protein Synthesis Questions
... 6. Name the four different bases that make up each nucleotide. Bonus – What is Chargaff’s Rule? ...
... 6. Name the four different bases that make up each nucleotide. Bonus – What is Chargaff’s Rule? ...
Protein Synthesis Review Sheet
... Due the Day of the Test NAME _______________________________ I. RNA 1. What does ‘RNA’ stand for? 2. What are the 4 bases of RNA and how do they pair up? a. b. c. d. 3. Name the two types of RNA and the basic function of each. II. Protein Synthesis List the 5 steps of protein synthesis here (use sep ...
... Due the Day of the Test NAME _______________________________ I. RNA 1. What does ‘RNA’ stand for? 2. What are the 4 bases of RNA and how do they pair up? a. b. c. d. 3. Name the two types of RNA and the basic function of each. II. Protein Synthesis List the 5 steps of protein synthesis here (use sep ...
Three Types of RNA and Their Functions
... Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA is more often found in nature as a single-strand composition. There are three main types of RNA, mRNA, tRNA and rRNA, and they play active roles within p ...
... Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA is more often found in nature as a single-strand composition. There are three main types of RNA, mRNA, tRNA and rRNA, and they play active roles within p ...
Presentation title: Introduction to RNA
... The central dogma of genetics is that the genome, comprised of DNA, encodes many thousands of genes that can be transcribed into RNA. Following this, the RNA may be translated into amino acids giving a functional protein. While the genome of an individual will be identical for each cell througho ...
... The central dogma of genetics is that the genome, comprised of DNA, encodes many thousands of genes that can be transcribed into RNA. Following this, the RNA may be translated into amino acids giving a functional protein. While the genome of an individual will be identical for each cell througho ...
Distinguish between these 3 root types: - mvhs
... Ribosome– The “workbench” where translation takes place. Catalyzes the formation of __________ bonds between amino acids to form the polypeptide chain. Made of ________ and rRNA. ...
... Ribosome– The “workbench” where translation takes place. Catalyzes the formation of __________ bonds between amino acids to form the polypeptide chain. Made of ________ and rRNA. ...
How do we get proteins? - Sebastian Charter Junior High
... DNA is used to make a single strand of RNA that is ...
... DNA is used to make a single strand of RNA that is ...
RNA
... • Phenotype = physical and chemical state • The phenotype is determined by the proteins synthesised when the genes are expressed ...
... • Phenotype = physical and chemical state • The phenotype is determined by the proteins synthesised when the genes are expressed ...
January 7, 2014 Notes Transcription: process of copying DNA into
... January 7, 2014 Notes Transcription: process of copying DNA into an RNA template. (Occurs in nucleus) ...
... January 7, 2014 Notes Transcription: process of copying DNA into an RNA template. (Occurs in nucleus) ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.