How Proteins are Made
... but mutations in gametes are passed on to offspring. B. Mutations can involve a change in a single nucleotide (point mutation) or an entire gene. 1. Point mutation - a change in a single nucleotide 2. Gene rearrangement – movement of an entire gene 3. Insertion – a sizable length of DNA is inserted ...
... but mutations in gametes are passed on to offspring. B. Mutations can involve a change in a single nucleotide (point mutation) or an entire gene. 1. Point mutation - a change in a single nucleotide 2. Gene rearrangement – movement of an entire gene 3. Insertion – a sizable length of DNA is inserted ...
Central Dogma.pptx
... DNA’s message (gene) is expressed (turned on) by first being transcribed into RNA (mRNA, tRNA or rRNA) mRNA=messenger RNA, carries DNA’s message to be later translated into proteins with the help of tRNA and the ribosome. ...
... DNA’s message (gene) is expressed (turned on) by first being transcribed into RNA (mRNA, tRNA or rRNA) mRNA=messenger RNA, carries DNA’s message to be later translated into proteins with the help of tRNA and the ribosome. ...
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
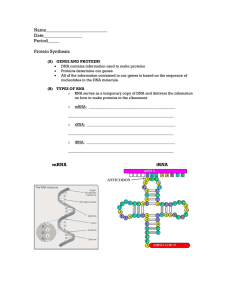
... All of the information contained in our genes is based on the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. (B) TYPES OF RNA o RNA serves as a temporary copy of DNA and delivers the infomation on how to make proteins to the ribosomes o ...
... All of the information contained in our genes is based on the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. (B) TYPES OF RNA o RNA serves as a temporary copy of DNA and delivers the infomation on how to make proteins to the ribosomes o ...
PG1005 Lecture 17 Gene Transcription
... Principal Type of RNA (1) There are 5 types you need to know about All have a role in the control of gene expression Not all are intermediate “central dogma” codes however 1) mRNA -Messenger RNA (<2000bp) is the direct coding intermediate for the production of proteins. Passes through various steps ...
... Principal Type of RNA (1) There are 5 types you need to know about All have a role in the control of gene expression Not all are intermediate “central dogma” codes however 1) mRNA -Messenger RNA (<2000bp) is the direct coding intermediate for the production of proteins. Passes through various steps ...
second of Chapter 10: RNA processing
... prokaryotic mRNA = primary transcript Eukaryotic transcripts are converted into mRNA through RNA processing: – Modification of the 5’ end – Extension of 3’ end – Excision of untranslated embedded sequences. ...
... prokaryotic mRNA = primary transcript Eukaryotic transcripts are converted into mRNA through RNA processing: – Modification of the 5’ end – Extension of 3’ end – Excision of untranslated embedded sequences. ...
powerpoint
... A. TRANSCRIPTION IS THE DNA-DIRECTED SYNTHESIS OF RNA: A CLOSER LOOK • RNA SYNTHESIS ON A DNA TEMPLATES IS CATALYZED BY RNA POLYMERASE • IT FOLLOWS THE SAME BASE PIRING RULES AS DNA REPLICATION, EXCEPT THAT IN RNA, URACIL SUBSTITUTES FOR THYMINE • PROMOTERS, SPECIFIC NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCES AT THE STAR ...
... A. TRANSCRIPTION IS THE DNA-DIRECTED SYNTHESIS OF RNA: A CLOSER LOOK • RNA SYNTHESIS ON A DNA TEMPLATES IS CATALYZED BY RNA POLYMERASE • IT FOLLOWS THE SAME BASE PIRING RULES AS DNA REPLICATION, EXCEPT THAT IN RNA, URACIL SUBSTITUTES FOR THYMINE • PROMOTERS, SPECIFIC NUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCES AT THE STAR ...
Unit 7 Study Guide ANSWERS 2014
... 10. What determines the specificity of a protein? The order of the nitrogenous bases in the DNA 11. In a eukaryotic cell, where does mRNA processing take place? During Transcription 12. What are the two processes that link the gene to the protein? Transcription and Translation 13. Proteins are made ...
... 10. What determines the specificity of a protein? The order of the nitrogenous bases in the DNA 11. In a eukaryotic cell, where does mRNA processing take place? During Transcription 12. What are the two processes that link the gene to the protein? Transcription and Translation 13. Proteins are made ...
Quiz 3-DNA.doc
... 7. How many amino acids are there? a. 20 b. 30 c. 40 d. 10 8. The disease that stops someone’s hemoglobin from getting to part of their body is called: a. Sickle-cell anemia b. Platelet dialysis c. Hemoglobina pseudomona d. Alzheimers 9. Only ___% of genes produce protein a. 1 b. 10 c. 20 d. 30 e. 4 ...
... 7. How many amino acids are there? a. 20 b. 30 c. 40 d. 10 8. The disease that stops someone’s hemoglobin from getting to part of their body is called: a. Sickle-cell anemia b. Platelet dialysis c. Hemoglobina pseudomona d. Alzheimers 9. Only ___% of genes produce protein a. 1 b. 10 c. 20 d. 30 e. 4 ...
Expressing Genetic Information
... 1. Study the scanning electron micrograph of human chromosomes during mitosis. Locate the chromatids and centromere. Now, study the fine detail of the chromatin. How would you describe it? 2. What is stored in the chromatin, the genetic material of DNA? 3. Genes are discrete units of DNA that act in ...
... 1. Study the scanning electron micrograph of human chromosomes during mitosis. Locate the chromatids and centromere. Now, study the fine detail of the chromatin. How would you describe it? 2. What is stored in the chromatin, the genetic material of DNA? 3. Genes are discrete units of DNA that act in ...
CS4030: Tutorial 1- Biological Issues (from Bioinformatics ch 1)
... portions that correspond to transcription and translation and indicate what enzymes are responsible for those important steps. 3. Examine the chemical structures of the amino acid R groups shown in figure 1.5b of chapter 1 of Bioinformatics (which you should by now have obtained electronically). Wha ...
... portions that correspond to transcription and translation and indicate what enzymes are responsible for those important steps. 3. Examine the chemical structures of the amino acid R groups shown in figure 1.5b of chapter 1 of Bioinformatics (which you should by now have obtained electronically). Wha ...
Study Guide: The Cell
... 2. What are the three types of RNA are and their functions? 3. Differentiate between transcription and translation? ...
... 2. What are the three types of RNA are and their functions? 3. Differentiate between transcription and translation? ...
Chapter 10 Structure and Function of DNA
... Why do chromosomes get shorter and shorter every round of replication? What are telomeres? What is telomerase? What happens if there is a mistake? What is the role of single-stranded binding proteins Protein Synthesis Central Dogma DNA -> mRNA -> protein -> trait RNA vs DNA Single stranded Uracil Ri ...
... Why do chromosomes get shorter and shorter every round of replication? What are telomeres? What is telomerase? What happens if there is a mistake? What is the role of single-stranded binding proteins Protein Synthesis Central Dogma DNA -> mRNA -> protein -> trait RNA vs DNA Single stranded Uracil Ri ...
Transcription and Translation
... Usually double stranded Stores the code (like the master blueprint) ...
... Usually double stranded Stores the code (like the master blueprint) ...
Previously in Bio308
... How does RNA polymerase work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? How does a ribosome work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? If the DNA in every cell in your body is the ...
... How does RNA polymerase work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? How does a ribosome work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? If the DNA in every cell in your body is the ...
doc 3.4.2 protein synthesis checklist
... Translation as the production of polypeptides from the sequence of codons carried by mRNA. The roles of ribosomes, tRNA and ATP. ...
... Translation as the production of polypeptides from the sequence of codons carried by mRNA. The roles of ribosomes, tRNA and ATP. ...
Protein Synthesis - science4warriors
... with in the cell. • The first thing that needs to happen is for DNA to be copied into RNA. (transcription) • Now the RNA contains the coded information for making proteins. ...
... with in the cell. • The first thing that needs to happen is for DNA to be copied into RNA. (transcription) • Now the RNA contains the coded information for making proteins. ...
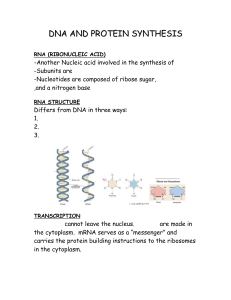
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
... the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
From Gene to Protein Protein Synthesis
... http://wwwclass.unl.edu/biochem/gp2/m_biology/animation/ge ne/gene_a2.html ...
... http://wwwclass.unl.edu/biochem/gp2/m_biology/animation/ge ne/gene_a2.html ...
Chapter 17 Powerpoint
... • RNA splicing – Initial RNA sequence is approximately 8,000 nucleotides – Generally, only approx. 1,200 are needed, though. – Noncoding areas are found in between coding areas ...
... • RNA splicing – Initial RNA sequence is approximately 8,000 nucleotides – Generally, only approx. 1,200 are needed, though. – Noncoding areas are found in between coding areas ...
Chapter 3 Section 4
... THE GENETIC CODE The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that specifies what type of p ...
... THE GENETIC CODE The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins. Proteins help determine the size, shape and other traits of organisms. Nitrogen bases form “rungs” of DNA ladder. The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene form a genetic code that specifies what type of p ...
Reviewing Key Concepts Chapter 12 DNA and RNA Section Review 12-3
... 5. Each tRNA molecule contains three unpaired bases, called the , which ensure that amino acids are added in the correct sequence. ...
... 5. Each tRNA molecule contains three unpaired bases, called the , which ensure that amino acids are added in the correct sequence. ...
Powerpoint
... GENE is a section of a DNA molecule that contains the information to code for one complete protein PROTEINS are made up of a chain of amino acids Proteins determine many of the traits in an ...
... GENE is a section of a DNA molecule that contains the information to code for one complete protein PROTEINS are made up of a chain of amino acids Proteins determine many of the traits in an ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.