Replication/ Transcription/Translation Review
... 4. Describe the different types of RNA, their names and their roles in transcription & translation. mRNA: Messenger RNA: Contains the code transcribed from the DNA. It is used as the code to make the amino acid chains of a protein rRNA: Ribosomal RNA: A component of the ribosome. Ribosomes read the ...
... 4. Describe the different types of RNA, their names and their roles in transcription & translation. mRNA: Messenger RNA: Contains the code transcribed from the DNA. It is used as the code to make the amino acid chains of a protein rRNA: Ribosomal RNA: A component of the ribosome. Ribosomes read the ...
chap12studyguide
... In eukaryotes, DNA RNA contains the sugar Which RNA molecule carries amino acids? What is produced during transcription? What does Figure 12-6 show? ...
... In eukaryotes, DNA RNA contains the sugar Which RNA molecule carries amino acids? What is produced during transcription? What does Figure 12-6 show? ...
Replication, Transcription, Translation
... 2. Know the meaning o, and understand the process for the following words: replication, transcription, translation. 3. Know the respective sugars and nitrogenous bases that DNA and RNA contain. 4. Be able to name each of the 3 types of RNA and be able to explain what each does. 5. Know the types of ...
... 2. Know the meaning o, and understand the process for the following words: replication, transcription, translation. 3. Know the respective sugars and nitrogenous bases that DNA and RNA contain. 4. Be able to name each of the 3 types of RNA and be able to explain what each does. 5. Know the types of ...
Chapter 17: Transcription, RNA Processing, and Translation
... 4.) What is the significance of the -35 box, -10 box, and +1 box? In bacteria, what component of the RNA Polymerase holoenzyme interacts with the DNA initially during transcription initiation? Where does the component bind and how is this assisting the RNA Pol core enzyme? 5.) Once the holoenzyme is ...
... 4.) What is the significance of the -35 box, -10 box, and +1 box? In bacteria, what component of the RNA Polymerase holoenzyme interacts with the DNA initially during transcription initiation? Where does the component bind and how is this assisting the RNA Pol core enzyme? 5.) Once the holoenzyme is ...
12.3 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... called exons because they are expressed in protein synthesis. ...
... called exons because they are expressed in protein synthesis. ...
aa + aa + aa + aa aa – aa – aa – aa
... As you view the lecture presented by your teacher fill out the lecture guide below. 1. The many Functions of proteins ...
... As you view the lecture presented by your teacher fill out the lecture guide below. 1. The many Functions of proteins ...
Replication, Transcription, and Translation
... The important idea is that an exact duplication of the DNA message is required, so that each new cell in the body has the same set of genetic instructions as the cells that preceded it. This also insures that every new generation of individuals has the same ...
... The important idea is that an exact duplication of the DNA message is required, so that each new cell in the body has the same set of genetic instructions as the cells that preceded it. This also insures that every new generation of individuals has the same ...
Chapter 17: Transcription, RNA Processing, and Translation
... 4.) What is the significance of the -35 box, -10 box, and +1 box? In bacteria, what component of the RNA Polymerase holoenzyme interacts with the DNA initially during transcription initiation? Where does the component bind and how is this assisting the RNA Pol core enzyme? 5.) Once the holoenzyme is ...
... 4.) What is the significance of the -35 box, -10 box, and +1 box? In bacteria, what component of the RNA Polymerase holoenzyme interacts with the DNA initially during transcription initiation? Where does the component bind and how is this assisting the RNA Pol core enzyme? 5.) Once the holoenzyme is ...
Protein Synthesis
... • RNA is read three Nitrogen bases at a time by a molecule to code for one amino acid. • The three-nucleotide sequence of RNA is called a codon. • Each 3-nucleotide codon codes for a specific amino acid. • A codon chart is used to find what amino acid each codon codes for. ...
... • RNA is read three Nitrogen bases at a time by a molecule to code for one amino acid. • The three-nucleotide sequence of RNA is called a codon. • Each 3-nucleotide codon codes for a specific amino acid. • A codon chart is used to find what amino acid each codon codes for. ...
3.4: Transcription and Translation
... sugar is deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA; DNA is double stranded and RNA is single stranded; DNA has a (double) helix; DNA has thymine while RNA has uracil; (require full names written out) both contain four nitrogenous bases / A, G, C, T for DNA and A, G, C, U for RNA; [4 max] ...
... sugar is deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA; DNA is double stranded and RNA is single stranded; DNA has a (double) helix; DNA has thymine while RNA has uracil; (require full names written out) both contain four nitrogenous bases / A, G, C, T for DNA and A, G, C, U for RNA; [4 max] ...
Protein Synthesis - Building Directory
... 30 – 200 adenine nucleotides Protects the ends from being degraded by enzymes in the cytoplasm ...
... 30 – 200 adenine nucleotides Protects the ends from being degraded by enzymes in the cytoplasm ...
RNA STRUCTURE - mbbsclub.com
... A chain of 40–200 adenine nucleotides attached to the 3′-end .This poly-A tail is not transcribed from the DNA, but is added after transcription. These tails help stabilize the mRNA and facilitate their exit from the nucleus. After the mRNA enters the cytosol, the poly-A tail is gradually shorten ...
... A chain of 40–200 adenine nucleotides attached to the 3′-end .This poly-A tail is not transcribed from the DNA, but is added after transcription. These tails help stabilize the mRNA and facilitate their exit from the nucleus. After the mRNA enters the cytosol, the poly-A tail is gradually shorten ...
P310 Trypanosoma brucei PUF RNA binding proteins Katelyn Fenn
... which is developmentally regulated. Previous studies revealed that these genes were regulated via signals in the mRNA 3’ untranslated regions (UTRs). In yeast, COX gene expression is regulated by a PUF RNA binding protein. PUF proteins are present in most eukaryotic organisms and have been shown to ...
... which is developmentally regulated. Previous studies revealed that these genes were regulated via signals in the mRNA 3’ untranslated regions (UTRs). In yeast, COX gene expression is regulated by a PUF RNA binding protein. PUF proteins are present in most eukaryotic organisms and have been shown to ...
18. Gene Expression
... • Transcription termination sites are often inverted repeat sequences which can form hairpin loops in RNA C. Eukaryotic Gene Structure • In many eukaryotic genes, the coding regions are interrupted by noncoding segments = “split genes” • Coding regions = exons • Noncoding regions = introns • Primary ...
... • Transcription termination sites are often inverted repeat sequences which can form hairpin loops in RNA C. Eukaryotic Gene Structure • In many eukaryotic genes, the coding regions are interrupted by noncoding segments = “split genes” • Coding regions = exons • Noncoding regions = introns • Primary ...
Regulating Protein Synthesis
... Regulation of protein synthesis is necessary in all cells, but much more complex in eukaryotes, because both the cells and the organism they form are more complex. Uncoiling of chromatin: DNA, histone ...
... Regulation of protein synthesis is necessary in all cells, but much more complex in eukaryotes, because both the cells and the organism they form are more complex. Uncoiling of chromatin: DNA, histone ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... What Codes For A Protein? A. The genetic code allows for almost an infinite amount of different proteins. B. Every 3 bases of DNA (or mRNA) is referred to as a CODON. - Each codon codes for 1 amino acid. ...
... What Codes For A Protein? A. The genetic code allows for almost an infinite amount of different proteins. B. Every 3 bases of DNA (or mRNA) is referred to as a CODON. - Each codon codes for 1 amino acid. ...
Document
... Groups of structural genes with related functions + DNA responsible for controlling ...
... Groups of structural genes with related functions + DNA responsible for controlling ...
1 Biology 20 Protein Synthesis DNA: How is this linear information
... Sugar: Nitrogenous bases: Strands: Genetic code: (p. 194; Fig. 10.8A) ...
... Sugar: Nitrogenous bases: Strands: Genetic code: (p. 194; Fig. 10.8A) ...
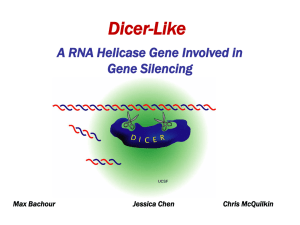
Dicer-Like
... RNA interference • Dicer and Dicer-Like (DCL) enzymes are involved in RNA interference (RNAi) • Nontranslated RNA fragments bind to mRNA and prevent translation into a protein ...
... RNA interference • Dicer and Dicer-Like (DCL) enzymes are involved in RNA interference (RNAi) • Nontranslated RNA fragments bind to mRNA and prevent translation into a protein ...
Here are the answers
... Diagrams should show tRNA molecules moving to a ribosome while carrying amino acids. As each amino acid bonds, the tRNA moves away to bring another amino acid. ...
... Diagrams should show tRNA molecules moving to a ribosome while carrying amino acids. As each amino acid bonds, the tRNA moves away to bring another amino acid. ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.