DNA Replication - Texas Tech University
... Do not bind directly onto DNA Usually too weak to act on their own ...
... Do not bind directly onto DNA Usually too weak to act on their own ...
pptx - WVU School of Medicine
... DNA sequences “upstream” of transcription initiation site. • different σ factors recognize different promoters (σ70 = most genes; σ32 = heat shock proteins; σ28 = flagella & chemotaxis genes). • 2 DNA sequences (-35 & -10) found in most prokaryotic promoters – “upstream” of transcription start site ...
... DNA sequences “upstream” of transcription initiation site. • different σ factors recognize different promoters (σ70 = most genes; σ32 = heat shock proteins; σ28 = flagella & chemotaxis genes). • 2 DNA sequences (-35 & -10) found in most prokaryotic promoters – “upstream” of transcription start site ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene
... SO, how does this occur? • Transcription and translation are linguistic terms, so….. • nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and polypeptides (chain of amino acids linked by peptide bond) Have their own language! What is their language? • A, T, G, C in DNA and A, U, G, C in RNA ...
... SO, how does this occur? • Transcription and translation are linguistic terms, so….. • nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and polypeptides (chain of amino acids linked by peptide bond) Have their own language! What is their language? • A, T, G, C in DNA and A, U, G, C in RNA ...
Anaerobic Respiration - Deans Community High School
... tRNA A second type of RNA is found in the cell’s cytoplasm. This is called ____________ _____ (______). Each molecule of tRNA has an exposed triplet of bases, known as an anticodon. This anticodon corresponds to a particular amino acid. Each tRNA molecule picks up the appropriate amino acid from the ...
... tRNA A second type of RNA is found in the cell’s cytoplasm. This is called ____________ _____ (______). Each molecule of tRNA has an exposed triplet of bases, known as an anticodon. This anticodon corresponds to a particular amino acid. Each tRNA molecule picks up the appropriate amino acid from the ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Congratulations! You have just transcribed and translated DNA into a protein! ...
... Congratulations! You have just transcribed and translated DNA into a protein! ...
Ch. 17: From Gene to Protein
... 3) RNA splicing: exons (expressed sequences) kept introns (intervening sequences) are spliced out forming a spliceosome ...
... 3) RNA splicing: exons (expressed sequences) kept introns (intervening sequences) are spliced out forming a spliceosome ...
Section: Gene Regulation and Structure
... 14. long segment of nucleotides on a eukaryotic gene that has no coding ...
... 14. long segment of nucleotides on a eukaryotic gene that has no coding ...
Multiple choice questions
... Occurs at the ends of coding regions Can be induced by specific RNA stem-loops Is similar in prokaryotes and in the nucleus of eukaryotes Can involve the action of several proteins Is always linked to translation Can be regulated ...
... Occurs at the ends of coding regions Can be induced by specific RNA stem-loops Is similar in prokaryotes and in the nucleus of eukaryotes Can involve the action of several proteins Is always linked to translation Can be regulated ...
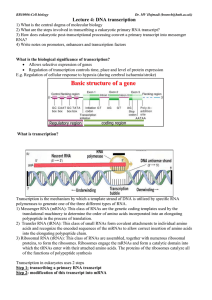
Lecture 4: DNA transcription
... Allows selective expression of genes Regulation of transcription controls time, place and level of protein expression E.g. Regulation of cellular response to hypoxia (during cerebral ischaemia/stroke) ...
... Allows selective expression of genes Regulation of transcription controls time, place and level of protein expression E.g. Regulation of cellular response to hypoxia (during cerebral ischaemia/stroke) ...
Gene Expression
... • Production of enzymes to break down milk sugar • An activator and repressor have roles • Conditions tightly controlled – Lactose must be high, but no other sugar present – [Lactose] and [glucose] ...
... • Production of enzymes to break down milk sugar • An activator and repressor have roles • Conditions tightly controlled – Lactose must be high, but no other sugar present – [Lactose] and [glucose] ...
Matched DNA and RNA sets
... Description: High quality intact total RNA and DNA were isolated simultaneously from a single biomaterial source. The RNA and DNA samples were treated with RNase-free DNase and DNase-free RNase to remove the contaminant DNA and RNA residuals respectively. Content: Each set contains 50µg RNA and 10µg ...
... Description: High quality intact total RNA and DNA were isolated simultaneously from a single biomaterial source. The RNA and DNA samples were treated with RNase-free DNase and DNase-free RNase to remove the contaminant DNA and RNA residuals respectively. Content: Each set contains 50µg RNA and 10µg ...
(Francis Crick, 1958) (Transcription) (Translation)
... Cells have adapter molecules called tRNA with a three nucleotide sequence on one end (anticodon) that is complementary to a codon of the genetic code. • There are different transfer RNAs (tRNAs) with anticodons that are complementary to the codons for each of the twenty amino acids. • Each tRNA int ...
... Cells have adapter molecules called tRNA with a three nucleotide sequence on one end (anticodon) that is complementary to a codon of the genetic code. • There are different transfer RNAs (tRNAs) with anticodons that are complementary to the codons for each of the twenty amino acids. • Each tRNA int ...
TranscriptionTranslation
... tRNA 1. Transferring Agent to bring selected rNTP to rRNA 2. 4 Loops “folded Clover leaf” 3. Amino Acid Binding site 3’ End 4. Anticodon- Determine AA Requested on mRNA 5. Energy Required- Amino Acyl-tRNA Synthetases ...
... tRNA 1. Transferring Agent to bring selected rNTP to rRNA 2. 4 Loops “folded Clover leaf” 3. Amino Acid Binding site 3’ End 4. Anticodon- Determine AA Requested on mRNA 5. Energy Required- Amino Acyl-tRNA Synthetases ...
The DNA connection - Somerset Academy North Las Vegas
... The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins in an organism’s cells. Proteins help to determine the size, shape, color, and many other traits of an organism. Genes and DNA: recall; chromosomes are mostly DNA. DNA has four different nitrogen basis (A adenine, T thymine, ...
... The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins in an organism’s cells. Proteins help to determine the size, shape, color, and many other traits of an organism. Genes and DNA: recall; chromosomes are mostly DNA. DNA has four different nitrogen basis (A adenine, T thymine, ...
notes File - selu moodle
... Near universal (exceptions in organelles and ciliates (prokaryotes also use Nformylmethionine instead of methionine to initiate translation) 15.3 Prokaryotic Transcription Promoter – sequence within DNA Docking site for RNA polymerase Signifies start of a gene Infers directionality of the gene Elong ...
... Near universal (exceptions in organelles and ciliates (prokaryotes also use Nformylmethionine instead of methionine to initiate translation) 15.3 Prokaryotic Transcription Promoter – sequence within DNA Docking site for RNA polymerase Signifies start of a gene Infers directionality of the gene Elong ...
Mass spectrometry and stable isotope labeling for
... Posttranscriptional modifications provide a unique and often unappreciated way to induce control over RNA structure, metabolism and biological functions. Over the last years, the list of modified RNAs has expanded and increasing numbers of modified sites continue to be found in catalytic, non-coding ...
... Posttranscriptional modifications provide a unique and often unappreciated way to induce control over RNA structure, metabolism and biological functions. Over the last years, the list of modified RNAs has expanded and increasing numbers of modified sites continue to be found in catalytic, non-coding ...
Transcription
... Types Messenger (mRNA) Structure Single strand of RNA nucleotides complementary to a gene on the DNA coding strand. Purpose Carry protein-building instructions to ribosome. ...
... Types Messenger (mRNA) Structure Single strand of RNA nucleotides complementary to a gene on the DNA coding strand. Purpose Carry protein-building instructions to ribosome. ...
Topic 7 The Discovery of DNA & Its Roles
... RNA is similar to DNA except that it is always single-stranded, the sugar has a 2’-OH group, and the nitrogenous bases are A, C, G, & Uracil ...
... RNA is similar to DNA except that it is always single-stranded, the sugar has a 2’-OH group, and the nitrogenous bases are A, C, G, & Uracil ...
Central Dogma WebQuest - Life Science
... Answer each of the questions as you travel to the webpages below. Links can be found here: mvhslifescience.weebly.com → Biology → DNA → WebQuest (bottom of the page) From Gene to Protein: Transcription Complete the tutorial by clicking “Next Concept” and reading each page. Answer the questions and f ...
... Answer each of the questions as you travel to the webpages below. Links can be found here: mvhslifescience.weebly.com → Biology → DNA → WebQuest (bottom of the page) From Gene to Protein: Transcription Complete the tutorial by clicking “Next Concept” and reading each page. Answer the questions and f ...
Genetic Information
... C A T T A G G C A T G (dna) G U A A U C C G U A C (rna) o Transfer RNA (tRNA) Transport rna code from mRNA to the ribosome Acts like a taxi o Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Makes proteins in the ribosome Translation Protein synthesis ...
... C A T T A G G C A T G (dna) G U A A U C C G U A C (rna) o Transfer RNA (tRNA) Transport rna code from mRNA to the ribosome Acts like a taxi o Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Makes proteins in the ribosome Translation Protein synthesis ...
Protein Synthesis
... – Single chain that carries genetic information from DNA in nucleus to the cytosol ...
... – Single chain that carries genetic information from DNA in nucleus to the cytosol ...
Chapter 11 Vocabulary and Objectives
... explain that organisms have systems to fight diseases Lesson 1: How are Molecules of Life Involved in Heredity? I. Objectives: Describe the structure of nucleotides; Explain the structure of a DNA molecule; Explain complementary pairing. II. Vocabulary: sugarphosphate backbone cytosine ( ...
... explain that organisms have systems to fight diseases Lesson 1: How are Molecules of Life Involved in Heredity? I. Objectives: Describe the structure of nucleotides; Explain the structure of a DNA molecule; Explain complementary pairing. II. Vocabulary: sugarphosphate backbone cytosine ( ...
How many phosphate bonds are required to build a protein with 50
... What kind of cancer causing allele is the result of a loss of function mutation? What initiates transcription from the early promoter of the Sxl gene? is the function of amino acyl RNA synthetase? What In recombinant DNA technology what is the name of a carrier of DNA? In the Sanger DNA sequencing m ...
... What kind of cancer causing allele is the result of a loss of function mutation? What initiates transcription from the early promoter of the Sxl gene? is the function of amino acyl RNA synthetase? What In recombinant DNA technology what is the name of a carrier of DNA? In the Sanger DNA sequencing m ...
Clark: Biotechnology, 2nd Edition Chapter 2: DNA, RNA, and Protein
... *e. All of the above are ways to control eukaryotic gene expression. 20. Transcription in eukaryotes and prokaryotes differs in the followings ways EXCEPT: a. Prokaryotic transcription is coupled to translation *b. Eukaryotic DNA has a cap added to the 3’ end. c. Eukaryotic DNA has a poly(A) tail at ...
... *e. All of the above are ways to control eukaryotic gene expression. 20. Transcription in eukaryotes and prokaryotes differs in the followings ways EXCEPT: a. Prokaryotic transcription is coupled to translation *b. Eukaryotic DNA has a cap added to the 3’ end. c. Eukaryotic DNA has a poly(A) tail at ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.