What is the most likely path of inheritance?
... retrievers will be produced if a second dominant gene allowing the ability to express pigment is not inherited. Two black Labrador retrievers, heterozygous at both loci, are mated. What is the chance that they will produce yellow offspring? ...
... retrievers will be produced if a second dominant gene allowing the ability to express pigment is not inherited. Two black Labrador retrievers, heterozygous at both loci, are mated. What is the chance that they will produce yellow offspring? ...
Nucleic acid chemistry lecture 3
... template strand of DNA in the nucleus. 5% of total cellular RNA Variable in length Carry genetic codon (a message from DNA) for protein synthesis in the cytoplasm (in ribosomes) The sequence of the bases determines the sequence of the amino acids in the polypeptide chain Each 3 succcessive ...
... template strand of DNA in the nucleus. 5% of total cellular RNA Variable in length Carry genetic codon (a message from DNA) for protein synthesis in the cytoplasm (in ribosomes) The sequence of the bases determines the sequence of the amino acids in the polypeptide chain Each 3 succcessive ...
No Slide Title
... Guo and Kemphues, Cell 81, 611 (1995) observed that sense and antisense strands worked equally at reducing transcript, – in an anti-sense experiment, a gene is constructed so that it produces a complementary strand to an expressed transcript, • the goal is to complement, thus inactivate the mRNA. ...
... Guo and Kemphues, Cell 81, 611 (1995) observed that sense and antisense strands worked equally at reducing transcript, – in an anti-sense experiment, a gene is constructed so that it produces a complementary strand to an expressed transcript, • the goal is to complement, thus inactivate the mRNA. ...
Transcription/Translation Notes Handout
... 2. _____________ strand of DNA serves as a template -Nucleotides pair with one strand of the DNA. -RNA polymerase bonds the nucleotides together. -The DNA helix ___________________ as the gene is transcribed. 3..The RNA strand _____________________________________ from the DNA once the gene is trans ...
... 2. _____________ strand of DNA serves as a template -Nucleotides pair with one strand of the DNA. -RNA polymerase bonds the nucleotides together. -The DNA helix ___________________ as the gene is transcribed. 3..The RNA strand _____________________________________ from the DNA once the gene is trans ...
1DNA - AHSbognasnc4m
... very similar to DNA, but ◦ single stranded ◦ complementary base to adenine is not thymine, as it is in DNA, but rather uracil. ...
... very similar to DNA, but ◦ single stranded ◦ complementary base to adenine is not thymine, as it is in DNA, but rather uracil. ...
Central dogma: from genome to proteins
... Several important differences between the bacterial and eucaryotic RNA polymerases. • .While bacterial RNA polymerase (with s factor as one of its subunits) is able to initiate transcription on a DNA template in vitro without the help of additional proteins, eucaryotic RNA polymerases cannot. They ...
... Several important differences between the bacterial and eucaryotic RNA polymerases. • .While bacterial RNA polymerase (with s factor as one of its subunits) is able to initiate transcription on a DNA template in vitro without the help of additional proteins, eucaryotic RNA polymerases cannot. They ...
Transcription
... • Chemical signals turn gene for a specific protein on. • Enzymes attach to DNA at the gene’s location and unzip only where that gene is on the DNA. – DNA A T C G ...
... • Chemical signals turn gene for a specific protein on. • Enzymes attach to DNA at the gene’s location and unzip only where that gene is on the DNA. – DNA A T C G ...
Slide 1
... small ribosomal subunit, the other larger ribosomal subunit binds as well, forming a complete ribosome during translation, the mRNA threads through the ribosome three nucleotides at a time a new tRNA holding an amino acid to be added enters the ribosome at the A site ...
... small ribosomal subunit, the other larger ribosomal subunit binds as well, forming a complete ribosome during translation, the mRNA threads through the ribosome three nucleotides at a time a new tRNA holding an amino acid to be added enters the ribosome at the A site ...
Energy Unit SG Key
... The structure and function of a protein is determined by the order of the amino acids and their chemical properties. ...
... The structure and function of a protein is determined by the order of the amino acids and their chemical properties. ...
28th Annual San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium—Abstract #310
... recurrence (Paik et al. NEJM [2004]). However, in many studies, limited amounts of FPE tissue are available, for example as 600 µm cores in the form of tissue microarrays (TMA). We conducted a feasibility study to determine first, whether the standard 21 gene Oncotype DX assay can be obtained with s ...
... recurrence (Paik et al. NEJM [2004]). However, in many studies, limited amounts of FPE tissue are available, for example as 600 µm cores in the form of tissue microarrays (TMA). We conducted a feasibility study to determine first, whether the standard 21 gene Oncotype DX assay can be obtained with s ...
Protein Synthesis SG
... 11. What is splicing and it’s purpose? When does it take place? 12. RNA polymerase has no proofreading capacity. How does this affect the error rate in transcription compared with DNA replication? 13. Why do you think it is more important for DNA polymerase than for RNA polymerase to proofread? 14. ...
... 11. What is splicing and it’s purpose? When does it take place? 12. RNA polymerase has no proofreading capacity. How does this affect the error rate in transcription compared with DNA replication? 13. Why do you think it is more important for DNA polymerase than for RNA polymerase to proofread? 14. ...
DNA & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... What Codes For A Protein? A. The genetic code allows for almost an infinite amount of different proteins. B. Every 3 bases of DNA (or mRNA) is referred to as a CODON. - Each codon codes for 1 amino acid. ...
... What Codes For A Protein? A. The genetic code allows for almost an infinite amount of different proteins. B. Every 3 bases of DNA (or mRNA) is referred to as a CODON. - Each codon codes for 1 amino acid. ...
12.3 Transcription and Translation PPT
... strand of RNA. • RNA polymerase binds only to promoters, special DNA regions with specific base sequences that indicate where to start and stop transcription. ...
... strand of RNA. • RNA polymerase binds only to promoters, special DNA regions with specific base sequences that indicate where to start and stop transcription. ...
lecture24_RnaInterfe.. - University of Alberta
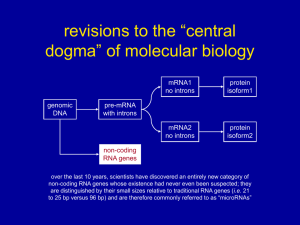
... revisions to the “central dogma” of molecular biology ...
... revisions to the “central dogma” of molecular biology ...
Gene Expression
... mRNA sequence and translates it into the ________ _______ sequence of the protein. The ribosome starts at the sequence _______, and then reads 3 nucleotides at a time. Each 3-nucleotide codon specifies a particular amino __________. The “stop” ________ (UAA, UAG, and UGA) tell the ribosome that the ...
... mRNA sequence and translates it into the ________ _______ sequence of the protein. The ribosome starts at the sequence _______, and then reads 3 nucleotides at a time. Each 3-nucleotide codon specifies a particular amino __________. The “stop” ________ (UAA, UAG, and UGA) tell the ribosome that the ...
Answers
... i Histone coat protecting the DNA double helix in the region of the cistron is stripped away c Hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs of DNA break n Double helix of DNA unwinds f RNA Polymerase binds to single stranded DNA e RNA Nucleotides are attached to the DNA strand according to the ru ...
... i Histone coat protecting the DNA double helix in the region of the cistron is stripped away c Hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs of DNA break n Double helix of DNA unwinds f RNA Polymerase binds to single stranded DNA e RNA Nucleotides are attached to the DNA strand according to the ru ...
11/11/15 - cloudfront.net
... If you need to make up a quiz due to an absence… come see me Tues or Thurs during PLC Flip it over when you are finished and hang on to it ...
... If you need to make up a quiz due to an absence… come see me Tues or Thurs during PLC Flip it over when you are finished and hang on to it ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... 1. when there are high levels of tryptophan in the medium, transcription of the trp operon occurs at high levels. 2. when there is no tryptophan in the medium, transcription of the trp operon occurs at high levels. 3. when there are high levels of tryptophan in the medium, transcription of CAP occur ...
... 1. when there are high levels of tryptophan in the medium, transcription of the trp operon occurs at high levels. 2. when there is no tryptophan in the medium, transcription of the trp operon occurs at high levels. 3. when there are high levels of tryptophan in the medium, transcription of CAP occur ...
PowerPoint
... Micro-RNAs (e.g., so-called stRNAs) are also involved in endogenous gene regulation ...
... Micro-RNAs (e.g., so-called stRNAs) are also involved in endogenous gene regulation ...
17-Gene to Protein
... Processing of RNA • Three types of RNA: mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA • eukaryotes have three polymerases • RNA polymerase II responsible for mRNA synthesis • Transcription subdivided into three stages: Initiation, elongation and termination • RNA must be processed before it can function ...
... Processing of RNA • Three types of RNA: mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA • eukaryotes have three polymerases • RNA polymerase II responsible for mRNA synthesis • Transcription subdivided into three stages: Initiation, elongation and termination • RNA must be processed before it can function ...
Transcription lesson
... Each gene of double stranded DNA has a sense strand and an antisense strand. The sense strand contains the “instructions” for protein synthesis. On the sense strand is a nucleotide sequence (called a promoter sequence) where RNA polymerase can bind. (RNA polymerase makes RNA) ...
... Each gene of double stranded DNA has a sense strand and an antisense strand. The sense strand contains the “instructions” for protein synthesis. On the sense strand is a nucleotide sequence (called a promoter sequence) where RNA polymerase can bind. (RNA polymerase makes RNA) ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.