Unit 4: Genetics Name: Date: Aim #23 Translation: How does DNA
... nucleus, allowing the mRNA strand to leave the nucleus with the genetic message and head for the ribosome to make proteins through another process called translation. What is Translation? Where does translation occur? What are the steps of translation? ...
... nucleus, allowing the mRNA strand to leave the nucleus with the genetic message and head for the ribosome to make proteins through another process called translation. What is Translation? Where does translation occur? What are the steps of translation? ...
10-Genes
... A. All codons specify more than one amino acid. B. Some amino acids are specified by a single codon. C. All amino acids are specified by more than one codon. D. The genetic code is different in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 11. As you know, ribosomes contain both rRNAs and many proteins. Outline the p ...
... A. All codons specify more than one amino acid. B. Some amino acids are specified by a single codon. C. All amino acids are specified by more than one codon. D. The genetic code is different in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 11. As you know, ribosomes contain both rRNAs and many proteins. Outline the p ...
Protein Synthesis - Overview
... tRNA is a small single stranded nucleic acid, resembles a cloverleaf one arm: anticodon (sequence of three bases complementary to mRNA) 3’ end has acceptor site for a particular amino ...
... tRNA is a small single stranded nucleic acid, resembles a cloverleaf one arm: anticodon (sequence of three bases complementary to mRNA) 3’ end has acceptor site for a particular amino ...
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
... All three forms have some features in common -both single strand and double strand forms -ribose for the sugar in the nucleotide instead of deoxyribose -PO4 -nucleic acids or bases, A, G, C and a new player U for uracil which base does U pair with??? -all made from DNA just different areas See Fig. ...
... All three forms have some features in common -both single strand and double strand forms -ribose for the sugar in the nucleotide instead of deoxyribose -PO4 -nucleic acids or bases, A, G, C and a new player U for uracil which base does U pair with??? -all made from DNA just different areas See Fig. ...
Aim 24: How does DNA code for the production of proteins through
... nucleus, allowing the mRNA strand to leave the nucleus with the genetic message and head for the ribosome to make proteins through another process called translation. ...
... nucleus, allowing the mRNA strand to leave the nucleus with the genetic message and head for the ribosome to make proteins through another process called translation. ...
the efficient expression of a eukaryotic gene in a prokaryotic cell free
... t s 236, which contains a mutation i n t h e gene coding f o r t h e P3 p o l y p e p t i d e , was i n v e s t i g a t e d . Synthesis o f t h e HA polypeptide could n o t be detected i n chick embryo f i b r o b l a s t s i n f e c t e d a t the r e s t r i c t i v e temperature. The HA could be d ...
... t s 236, which contains a mutation i n t h e gene coding f o r t h e P3 p o l y p e p t i d e , was i n v e s t i g a t e d . Synthesis o f t h e HA polypeptide could n o t be detected i n chick embryo f i b r o b l a s t s i n f e c t e d a t the r e s t r i c t i v e temperature. The HA could be d ...
Topic 3 The Chemistry of Life - wfs
... 3. The exposed bases of each strand are then paired with an available nucleotide by complementary base pairing. The result is two strands where only one was first present. 4. DNA polymerase is an enzyme that allows the connection between nucleotides lined up by basepairing. 5. This replication is ca ...
... 3. The exposed bases of each strand are then paired with an available nucleotide by complementary base pairing. The result is two strands where only one was first present. 4. DNA polymerase is an enzyme that allows the connection between nucleotides lined up by basepairing. 5. This replication is ca ...
File - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... • mRNA-carries the information from the DNA gene to the cytoplasm. Determines the sequence of amino acids for a protein • tRNA-brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome and mRNA in translation • rRNA-found on ribosomes and used to "connect" the tRNA to the mRNA • snRNA-found on spliceosomes. Use ...
... • mRNA-carries the information from the DNA gene to the cytoplasm. Determines the sequence of amino acids for a protein • tRNA-brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome and mRNA in translation • rRNA-found on ribosomes and used to "connect" the tRNA to the mRNA • snRNA-found on spliceosomes. Use ...
Chapter_17_answers
... the base-pairing rules relax a bit on tRNA molecules; this is known as wobble o ex: U in 3rd position of anticodon can pair with A or G o ex: I (inosine) in 3rd position of anticodon can pair with U, C, or A o aha! This is why 1 amino acid may correspond with multiple codons, only differing in the ...
... the base-pairing rules relax a bit on tRNA molecules; this is known as wobble o ex: U in 3rd position of anticodon can pair with A or G o ex: I (inosine) in 3rd position of anticodon can pair with U, C, or A o aha! This is why 1 amino acid may correspond with multiple codons, only differing in the ...
Athena, Jen and Natalie`s Powerpt
... Binds one amino acid to the tRNA tRNA also has an anticodon This complements the mRNA codon If the codon transcribed was AUG The anticodon would be UAC Methionine tRNA is in the P site A second tRNA enters the A site The 2 amino acids then peptide bind To begin the formation of a polypeptide The fir ...
... Binds one amino acid to the tRNA tRNA also has an anticodon This complements the mRNA codon If the codon transcribed was AUG The anticodon would be UAC Methionine tRNA is in the P site A second tRNA enters the A site The 2 amino acids then peptide bind To begin the formation of a polypeptide The fir ...
1) Lecture notes: mechanisms of gene activation
... Sequence to be copied into RNA If there is a protein transcription factor to bind to the RED DNA SEQUENCE, then the GREEN SEQUENCE will uses as a template for a primary RNA transcript. THE STRANDS SEPARATE BEFORE RNA IS MADE! ...
... Sequence to be copied into RNA If there is a protein transcription factor to bind to the RED DNA SEQUENCE, then the GREEN SEQUENCE will uses as a template for a primary RNA transcript. THE STRANDS SEPARATE BEFORE RNA IS MADE! ...
Chapter 14
... Finishing Touches on mRNA Transcripts • New formed mRNA is an unfinished molecule, not yet ready for use • mRNA transcripts are modified before leaving the nucleus – The 5’ end is capped with a special nucleotide that may serve as a “start” signal for translation – Noncoding portions (introns) are ...
... Finishing Touches on mRNA Transcripts • New formed mRNA is an unfinished molecule, not yet ready for use • mRNA transcripts are modified before leaving the nucleus – The 5’ end is capped with a special nucleotide that may serve as a “start” signal for translation – Noncoding portions (introns) are ...
Document
... F. In prokaryotes there is only one type of RNA polymerase, but in eukaryotes there are three types of RNA polymerase. ...
... F. In prokaryotes there is only one type of RNA polymerase, but in eukaryotes there are three types of RNA polymerase. ...
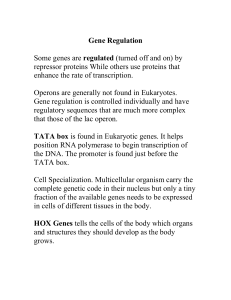
Gene Regulation
... Some genes are regulated (turned off and on) by repressor proteins While others use proteins that enhance the rate of transcription. Operons are generally not found in Eukaryotes. Gene regulation is controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex that those of the la ...
... Some genes are regulated (turned off and on) by repressor proteins While others use proteins that enhance the rate of transcription. Operons are generally not found in Eukaryotes. Gene regulation is controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex that those of the la ...
DNA Test Review
... 1. What are the four nucleotides in DNA? Which goes with which? 2. Describe the Central Dogma of molecular biology. 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. ...
... 1. What are the four nucleotides in DNA? Which goes with which? 2. Describe the Central Dogma of molecular biology. 3. If a DNA molecule has the sequence TACGAACCC, what would be the complimentary mRNA sequence? 4. The process by which a DNA molecule is copied is called _____. 5. What is a codon? 6. ...
Slide 1
... The genetic “bit” information to encode a specific amino acid is contained in a gene’s Codon. A Codon is a 3-base (3-nucleotide) sub-sequence that defines the amino acid to be incorporated into the protein. All proteins start with the Codon ATG (DNA notation) or AUG (RNA), which encodes for the amin ...
... The genetic “bit” information to encode a specific amino acid is contained in a gene’s Codon. A Codon is a 3-base (3-nucleotide) sub-sequence that defines the amino acid to be incorporated into the protein. All proteins start with the Codon ATG (DNA notation) or AUG (RNA), which encodes for the amin ...
protein synthesis (simplified)
... It is the Sequence of bases that act like a code The sequence (order) of bases tells the cell what proteins to make. The sequence of bases dictates the sequence of amino acids, which determines the shape of a protein. ...
... It is the Sequence of bases that act like a code The sequence (order) of bases tells the cell what proteins to make. The sequence of bases dictates the sequence of amino acids, which determines the shape of a protein. ...
Protein Synthesis PowerPoint
... rRNA puts the amino acids together to build the amino acid chain = PROTEIN ...
... rRNA puts the amino acids together to build the amino acid chain = PROTEIN ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein
... • RNA polymerase binds to DNA promoter • DNA strands unwind & separate • RNA polymerase adds free RNA nucleotides to complement 1 strand of DNA bases. ...
... • RNA polymerase binds to DNA promoter • DNA strands unwind & separate • RNA polymerase adds free RNA nucleotides to complement 1 strand of DNA bases. ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.