CG7b-PSSM
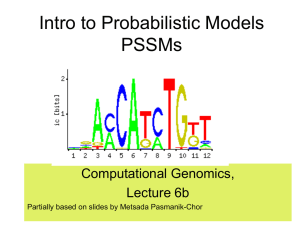
... Computational Genomics, Lecture 6b Partially based on slides by Metsada Pasmanik-Chor ...
... Computational Genomics, Lecture 6b Partially based on slides by Metsada Pasmanik-Chor ...
NGS library facility request form
... __________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... __________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Slide 1
... 13.4 Turning Genes Off and On • Eukaryotic genes have special sequences, called enhancers, that help guide RNA polymerase to the promoter at the beginning of the gene even if this regulatory sequence is located far away from the gene it influences, the enhancer can have an effect because the DNA ...
... 13.4 Turning Genes Off and On • Eukaryotic genes have special sequences, called enhancers, that help guide RNA polymerase to the promoter at the beginning of the gene even if this regulatory sequence is located far away from the gene it influences, the enhancer can have an effect because the DNA ...
13Johnson
... 13.4 Turning Genes Off and On • Eukaryotic genes have special sequences, called enhancers, that help guide RNA polymerase to the promoter at the beginning of the gene even if this regulatory sequence is located far away from the gene it influences, the enhancer can have an effect because the DNA ...
... 13.4 Turning Genes Off and On • Eukaryotic genes have special sequences, called enhancers, that help guide RNA polymerase to the promoter at the beginning of the gene even if this regulatory sequence is located far away from the gene it influences, the enhancer can have an effect because the DNA ...
DNA - Gulf Coast State College
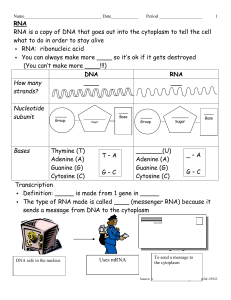
... Definition: _____ is made from 1 gene in _____ The type of RNA made is called ____ (messenger RNA) because it sends a message from DNA to the cytoplasm ...
... Definition: _____ is made from 1 gene in _____ The type of RNA made is called ____ (messenger RNA) because it sends a message from DNA to the cytoplasm ...
Protein Synthesis Quick Questions
... – Sugar is ribose not deoxyribose (less stable, takes less energy to make) ...
... – Sugar is ribose not deoxyribose (less stable, takes less energy to make) ...
From DNA to Protein
... Tay Sachs – One wrong letter - from PBS Cracking the Code of Life – 9:38 and 57:00 ...
... Tay Sachs – One wrong letter - from PBS Cracking the Code of Life – 9:38 and 57:00 ...
Non-coding RNAs
... (foreign nucleic acids). In recent years, a defense mechanism has been discovered, which turns out to be conserved among eukaryotes. The system can be compared to the immune system in several ways: It has specificity against foreign elements and the ability to amplify and raise a massive response ag ...
... (foreign nucleic acids). In recent years, a defense mechanism has been discovered, which turns out to be conserved among eukaryotes. The system can be compared to the immune system in several ways: It has specificity against foreign elements and the ability to amplify and raise a massive response ag ...
DNA - hdueck
... code of mRNA. Compact 3-D structure mRNA: single strand, provides complementary code from DNA for protein - Single strand may fold back on itself to form ...
... code of mRNA. Compact 3-D structure mRNA: single strand, provides complementary code from DNA for protein - Single strand may fold back on itself to form ...
DNA Transcription & Protein Translation
... three bases: A, C and G). When forming base pairs, C links with G, but A links with U (no T) ...
... three bases: A, C and G). When forming base pairs, C links with G, but A links with U (no T) ...
Extraction of RNA File
... 5) The second step include activation or loading the amino acid by some enzyme and contact the active amino acid with the tRNA that special with it, after that the 6) t RNA transport to ribosomes and contact with m RNA the anti codon that found on the tRNA. 7) The m RNA contain the nucleotides calle ...
... 5) The second step include activation or loading the amino acid by some enzyme and contact the active amino acid with the tRNA that special with it, after that the 6) t RNA transport to ribosomes and contact with m RNA the anti codon that found on the tRNA. 7) The m RNA contain the nucleotides calle ...
Molecular Genetics
... – 5’ cap (methylated G) – added and a poly-A tail added to the 3’ end – (Note: cap and tail are protection from degradation and recognition by ribosome) – Spliced out introns (non-coding segments; the coding segments are called exons) ...
... – 5’ cap (methylated G) – added and a poly-A tail added to the 3’ end – (Note: cap and tail are protection from degradation and recognition by ribosome) – Spliced out introns (non-coding segments; the coding segments are called exons) ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
... Protein Folding and Function As the amino acid chain grows, it folds into a three-dimensional (3-D) structure, which depends on both the chemical nature and order of the different amino acids. The 3-D structure determines the function of the protein. When there is a change in one or more amino acid ...
... Protein Folding and Function As the amino acid chain grows, it folds into a three-dimensional (3-D) structure, which depends on both the chemical nature and order of the different amino acids. The 3-D structure determines the function of the protein. When there is a change in one or more amino acid ...
13.3 RNA and Gene Expression
... the instructions for making proteins from the DNA (in the nucleus) to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm of the cell. Ribosomal (rRNA) – helps to assemble amino acids to make proteins on the ribosomes. ...
... the instructions for making proteins from the DNA (in the nucleus) to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm of the cell. Ribosomal (rRNA) – helps to assemble amino acids to make proteins on the ribosomes. ...
Gene expression
... • nucleotide sequence encoded by a gene that remains present within the final mature RNA product of that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. • This is the expressed genetic material… the light is turned on. ...
... • nucleotide sequence encoded by a gene that remains present within the final mature RNA product of that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. • This is the expressed genetic material… the light is turned on. ...
Bacterial Genetics Summary
... (3) other strand of DNA is inactive (4) transcription begins at promoter (5) complementary ribonucleotides brought in (a) hydrogen bond to complementary base (b) covalent bond to adjacent nucleotide in growing RNA molecule (6) when terminator sequence is reached one gene has been copied into RNA (7) ...
... (3) other strand of DNA is inactive (4) transcription begins at promoter (5) complementary ribonucleotides brought in (a) hydrogen bond to complementary base (b) covalent bond to adjacent nucleotide in growing RNA molecule (6) when terminator sequence is reached one gene has been copied into RNA (7) ...
Chapter 17: Gene Expression Gene Expression DNA houses all
... Introns (interrupt transcript) – long regions of noncoding RNA segments Exons (expressed transcript) – RNA that will be expressed by translation Spliceosome – cut introns, splice exons Large protein plus… snRNP (aka ‘Snurps’) Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins 150 nucleotides (snRNA) + p ...
... Introns (interrupt transcript) – long regions of noncoding RNA segments Exons (expressed transcript) – RNA that will be expressed by translation Spliceosome – cut introns, splice exons Large protein plus… snRNP (aka ‘Snurps’) Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins 150 nucleotides (snRNA) + p ...
HOW SAGE WORKS (Reference http://www
... are called nucleotides. The alphabet of nucleotides is very small (with only four letters), but it suffices to spell out the unique, long words that make up the genetic code. Cells and viruses contain molecular tools that can transform DNA into RNA. Researchers use a method called "sequencing" to re ...
... are called nucleotides. The alphabet of nucleotides is very small (with only four letters), but it suffices to spell out the unique, long words that make up the genetic code. Cells and viruses contain molecular tools that can transform DNA into RNA. Researchers use a method called "sequencing" to re ...
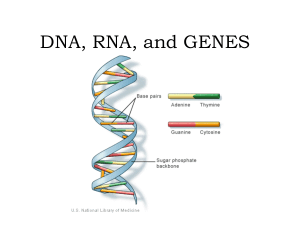
DNA, RNA, and GENES
... molecules. • the rungs of the ladder are made up of nitrogen bases. The bonding of these bases is • Adenine bonds with Thymine • Cytosine bonds with Guanine • A to T and C to G ...
... molecules. • the rungs of the ladder are made up of nitrogen bases. The bonding of these bases is • Adenine bonds with Thymine • Cytosine bonds with Guanine • A to T and C to G ...
The DNA Song
... so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA is single stranded. ...
... so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA is single stranded. ...
SI Worksheet 11
... e. ACU 7. A sequence of pictures of polypeptides synthesis shows a ribosome holding two transfer RNAs. One tRNA has a polypeptide chain attached to it, the other tRNA has a single amino acid attaches to it. What does the next picture show? a. the polypeptide chain moves over and bonds to the single ...
... e. ACU 7. A sequence of pictures of polypeptides synthesis shows a ribosome holding two transfer RNAs. One tRNA has a polypeptide chain attached to it, the other tRNA has a single amino acid attaches to it. What does the next picture show? a. the polypeptide chain moves over and bonds to the single ...
1 BIOL 213 Fourth Exam All atoms, chemical bonding and structures
... Predict the possible results if this mutation occurred within the open reading frame nucleotide sequence of the gene. ...
... Predict the possible results if this mutation occurred within the open reading frame nucleotide sequence of the gene. ...
BIO 101: Transcription and Translation
... Theory: one gene codes for one polypeptide Some proteins are composed of a number of polypeptide chains. In this theory each chain has its own gene. However, eukaryotic genes are much more complex and this is not always the case! • Some genes control the expression of other genes • Some genes code f ...
... Theory: one gene codes for one polypeptide Some proteins are composed of a number of polypeptide chains. In this theory each chain has its own gene. However, eukaryotic genes are much more complex and this is not always the case! • Some genes control the expression of other genes • Some genes code f ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.