SB2a Build DNA using the Nucleotides Then Print
... 5. Place a hand over each RNA nucleotide to symbolize the enzyme that is making the RNA strand. ...
... 5. Place a hand over each RNA nucleotide to symbolize the enzyme that is making the RNA strand. ...
Microbial Genetics
... Prokaryotes have 70S ribosomes Eukaryotes have 80S ribosomes Because ribosomes do such an important job drugs that inhibit them have drastic effects on the cell (many antibiotics and the toxin ricin inhibit protein synthesis by binding to ribosomes) The genes for ribosomal RNA are often used to meas ...
... Prokaryotes have 70S ribosomes Eukaryotes have 80S ribosomes Because ribosomes do such an important job drugs that inhibit them have drastic effects on the cell (many antibiotics and the toxin ricin inhibit protein synthesis by binding to ribosomes) The genes for ribosomal RNA are often used to meas ...
No Slide Title
... An end goal will be how to relate: – Phenotype (e.g., coronary heart disease) – Sequence (e.g., entire string of AGCT available) ...
... An end goal will be how to relate: – Phenotype (e.g., coronary heart disease) – Sequence (e.g., entire string of AGCT available) ...
Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA
... • Broken into smaller pieces of the cell’s entire genome • Pieces are then spliced into a plasmid or a virus to make a collection of clones • The collection of clones (one clone for each fragment) containing different fragments of DNA from a single organism • Each organism and it’s DNA fragments has ...
... • Broken into smaller pieces of the cell’s entire genome • Pieces are then spliced into a plasmid or a virus to make a collection of clones • The collection of clones (one clone for each fragment) containing different fragments of DNA from a single organism • Each organism and it’s DNA fragments has ...
ibbiochapter3geneticsppt(1)
... sequence 1-valine-histidine a)_________b)________c)_______d)_________-glutamic acid • sequence 2-valine-histidine e)_________f)_________g)_______h)________glutamic acid • use genetic code to solve the above • this will change the structure of resulting protein-mutation ...
... sequence 1-valine-histidine a)_________b)________c)_______d)_________-glutamic acid • sequence 2-valine-histidine e)_________f)_________g)_______h)________glutamic acid • use genetic code to solve the above • this will change the structure of resulting protein-mutation ...
BamHI - Courses
... Nucleases – break DNA polymers by cleaving the phosphodiester bond Ligases – join DNA molecules together End-modifying enzymes – add labels and make compatible ends for further manipulation http://www.neb.com/nebecomm/products/categories.asp ...
... Nucleases – break DNA polymers by cleaving the phosphodiester bond Ligases – join DNA molecules together End-modifying enzymes – add labels and make compatible ends for further manipulation http://www.neb.com/nebecomm/products/categories.asp ...
Biology Test Topics Chapters 11-12 Slideshows
... Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA replication Be able to label any of the diagrams in our DNA packet. Gel electrophoresis: how does it work? What can it be used for? What is the purpose of the electrode? What does the gel do? How do short and long strands of DNA behave differently when moving ...
... Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA replication Be able to label any of the diagrams in our DNA packet. Gel electrophoresis: how does it work? What can it be used for? What is the purpose of the electrode? What does the gel do? How do short and long strands of DNA behave differently when moving ...
Gene Section MCPH1 (microcephalin 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Role of BRIT1 in cell cycle control: MCPH1 has been demonstrated to regulate the expression of BRCA1 and Chk1 and required for activation of intra-S and G2/M cell cycle checkpoint after cellular exposure to ionizing radiation. In the absence of MCPH1, BRCA1 and ChK1 expression is significantly reduc ...
... Role of BRIT1 in cell cycle control: MCPH1 has been demonstrated to regulate the expression of BRCA1 and Chk1 and required for activation of intra-S and G2/M cell cycle checkpoint after cellular exposure to ionizing radiation. In the absence of MCPH1, BRCA1 and ChK1 expression is significantly reduc ...
Test Answers - WordPress.com
... would be affected. Person III-1 is unaffected. All other modes of inheritance can be justified from this (very limited) data. 9. B Since there is no history of syndactyly in his family, person II–1 must have the genotype nn. Person II–5 must have the genotype Nn in order for person III–5 to inherit ...
... would be affected. Person III-1 is unaffected. All other modes of inheritance can be justified from this (very limited) data. 9. B Since there is no history of syndactyly in his family, person II–1 must have the genotype nn. Person II–5 must have the genotype Nn in order for person III–5 to inherit ...
nature v. nurture
... The new research, led by Mario F. Fraga and Manel Esteller of the Spanish National Cancer Center in Madrid, focused on two biological mechanisms that influence gene activity. In one, called DNA methylation, enzymes inside a cell attach a minuscule molecular decoration to a gene, deactivating that ge ...
... The new research, led by Mario F. Fraga and Manel Esteller of the Spanish National Cancer Center in Madrid, focused on two biological mechanisms that influence gene activity. In one, called DNA methylation, enzymes inside a cell attach a minuscule molecular decoration to a gene, deactivating that ge ...
Answer Key
... Both proteins recognize the promoter site immediate upstream of a transcription start site—both bind to the ‘TATA box’. They also both function as general transcription factors that do not remain associated with an RNA polymerase after transcription has initiated. These two proteins differ in that ...
... Both proteins recognize the promoter site immediate upstream of a transcription start site—both bind to the ‘TATA box’. They also both function as general transcription factors that do not remain associated with an RNA polymerase after transcription has initiated. These two proteins differ in that ...
PDF - NDSU Agriculture
... process called transcription) from the DNA template in the nucleus (Figure 1f). This mRNA is moved from the nucleus to the cellular ...
... process called transcription) from the DNA template in the nucleus (Figure 1f). This mRNA is moved from the nucleus to the cellular ...
Chapter 2 Genes Encode RNAs and Polypeptides
... • RNA processing – Modifications to RNA transcripts of genes. This may include alterations to the 3′ and 5′ ends and the removal of introns. • pre-mRNA – The nuclear transcript that is processed by modification and splicing to give an mRNA. • exon – Any segment of an interrupted gene that is represe ...
... • RNA processing – Modifications to RNA transcripts of genes. This may include alterations to the 3′ and 5′ ends and the removal of introns. • pre-mRNA – The nuclear transcript that is processed by modification and splicing to give an mRNA. • exon – Any segment of an interrupted gene that is represe ...
Chapter 2 Genes Encode RNAs and Polypeptides
... • RNA processing – Modifications to RNA transcripts of genes. This may include alterations to the 3′ and 5′ ends and the removal of introns. • pre-mRNA – The nuclear transcript that is processed by modification and splicing to give an mRNA. • exon – Any segment of an interrupted gene that is represe ...
... • RNA processing – Modifications to RNA transcripts of genes. This may include alterations to the 3′ and 5′ ends and the removal of introns. • pre-mRNA – The nuclear transcript that is processed by modification and splicing to give an mRNA. • exon – Any segment of an interrupted gene that is represe ...
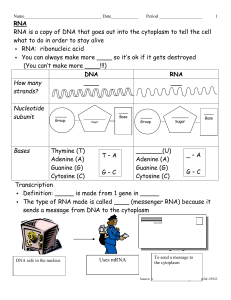
DNA - Gulf Coast State College
... RNA is a copy of DNA that goes out into the cytoplasm to tell the cell what to do in order to stay alive RNA: ribonucleic acid You can always make more ____ so it’s ok if it gets destroyed (You can’t make more ____!!!) DNA RNA How many ____ ___ strands? Nucleotide subunit ...
... RNA is a copy of DNA that goes out into the cytoplasm to tell the cell what to do in order to stay alive RNA: ribonucleic acid You can always make more ____ so it’s ok if it gets destroyed (You can’t make more ____!!!) DNA RNA How many ____ ___ strands? Nucleotide subunit ...
Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false
... 1. A trait is a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another. _________________________ ...
... 1. A trait is a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another. _________________________ ...
Chapter 25: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... a tumor, an abnormal mass of cells. Carcinogenesis, the development of cancer, is a gradual process. Cancer cells lack differentiation, form tumors, undergo angiogenesis and ...
... a tumor, an abnormal mass of cells. Carcinogenesis, the development of cancer, is a gradual process. Cancer cells lack differentiation, form tumors, undergo angiogenesis and ...
Gene Section KIAA1199 (KIAA1199) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Review on KIAA1199, with data on DNA/RNA, on the protein encoded and where the gene is implicated. ...
... Review on KIAA1199, with data on DNA/RNA, on the protein encoded and where the gene is implicated. ...
Advanced Genetics Unit 2: DNA Structure and Processes Quiz Bowl
... 8. Name any double-ringed base. [A, G] 9. A “friend” told me he saw a nucleotide floating around in a cell’s nucleoplasm which was constructed from a ribose sugar AND a T base. You know he was lying to me. How do you know? [Ribose-based nucleotides only used to build RNA. No T bases in RNA.] 10. The ...
... 8. Name any double-ringed base. [A, G] 9. A “friend” told me he saw a nucleotide floating around in a cell’s nucleoplasm which was constructed from a ribose sugar AND a T base. You know he was lying to me. How do you know? [Ribose-based nucleotides only used to build RNA. No T bases in RNA.] 10. The ...
Epigenetics and Inheritance
... or near. The work was coined by Conrad Waddington in the early 1940s to explain “the causal interactions between genes and their products, which bring the phenotype into being”. ...
... or near. The work was coined by Conrad Waddington in the early 1940s to explain “the causal interactions between genes and their products, which bring the phenotype into being”. ...
Hydrophobic: tending to repel and not absorb water
... formed by a combination of smaller molecules. ...
... formed by a combination of smaller molecules. ...
SBI4U: Molecular Genetics Unit Review
... 17. Describe what happens in initiation, elongation, and termination of: ...
... 17. Describe what happens in initiation, elongation, and termination of: ...
Bacterial species
... 2. translational termination is likely. 3. transcriptional termination is likely. 4. tryptophan is inactivating the repressor protein. ...
... 2. translational termination is likely. 3. transcriptional termination is likely. 4. tryptophan is inactivating the repressor protein. ...