Chapter 15 - Advances in Molecular Genetics
... mutation. Give examples of each (not the ones from the book) 27. What is a frameshift mutation? 28. What test is given to every child born in the US at birth? Why? What is the nature of the disorder being tested? 29.Describe three different chromosome arrangements and in the space below, draw repres ...
... mutation. Give examples of each (not the ones from the book) 27. What is a frameshift mutation? 28. What test is given to every child born in the US at birth? Why? What is the nature of the disorder being tested? 29.Describe three different chromosome arrangements and in the space below, draw repres ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Transcription • When RNA molecules are produced by copying part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA into to a complementary sequence of RNA • Transcribe = to write/copy down • When DNA’s instructions are copied by mRNA ...
... Transcription • When RNA molecules are produced by copying part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA into to a complementary sequence of RNA • Transcribe = to write/copy down • When DNA’s instructions are copied by mRNA ...
19. Positional cloning
... one used X-chromosome translocation breakpoint--cloned region adjacent to some rRNA genes one used small deletion from boy with 4 X-linked diseases; then carried out subtractive hybridization vs. normal DNA Which DNA fragments are missing? Southern blot of boys DNAs having deletion in region of ...
... one used X-chromosome translocation breakpoint--cloned region adjacent to some rRNA genes one used small deletion from boy with 4 X-linked diseases; then carried out subtractive hybridization vs. normal DNA Which DNA fragments are missing? Southern blot of boys DNAs having deletion in region of ...
Mapping Life
... Genomics is the use of the information collected in The Human Genome Project and similar projects for other organisms. Once the sequence of DNA that makes a gene is known, the information can be used to repair problems or improve the organism. Plant genes can be changed to make the plant more resist ...
... Genomics is the use of the information collected in The Human Genome Project and similar projects for other organisms. Once the sequence of DNA that makes a gene is known, the information can be used to repair problems or improve the organism. Plant genes can be changed to make the plant more resist ...
Ch 16 Genetics Review
... Structure of DNA • Each DNA molecule is made up of two very long polymers • Double helix: is the shape • Nucleotides: are the building blocks – deoxyribose ( a 5 carbon sugar) – phosphate group – nitrogenous base ...
... Structure of DNA • Each DNA molecule is made up of two very long polymers • Double helix: is the shape • Nucleotides: are the building blocks – deoxyribose ( a 5 carbon sugar) – phosphate group – nitrogenous base ...
2421 _Ch8.ppt
... the new RNA strand has ribonucleotides instead of deoxyribonucleotides & uracil (U) is used in place of thymine (T) to base pair with adenine (A) RNA polymerase binds to a promoter (special start site on DNA), then polymerizes the new chain using complementary bases polymerization stops upon reachin ...
... the new RNA strand has ribonucleotides instead of deoxyribonucleotides & uracil (U) is used in place of thymine (T) to base pair with adenine (A) RNA polymerase binds to a promoter (special start site on DNA), then polymerizes the new chain using complementary bases polymerization stops upon reachin ...
Document
... Translation is the term used to describe this process, as the sequences of DNA nucleotides are transcribed and translated by a various forms of RNA into the specific protein coded for by that gene sequence. By copying the DNA and using the copy to make proteins, it reduces the risk of the original D ...
... Translation is the term used to describe this process, as the sequences of DNA nucleotides are transcribed and translated by a various forms of RNA into the specific protein coded for by that gene sequence. By copying the DNA and using the copy to make proteins, it reduces the risk of the original D ...
Mutations that happen during Transcription and
... • When part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromosome, a ...
... • When part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromosome, a ...
Station #3: DNA structure, replication, protein synthesis, mutation
... Directions: Use the following information to write a conclusion Mike and Kelsey have a male and a female brown mouse with long tails. Question: What will the offspring of two mice who have brown fur and long tails look like? Prediction: If two brown mice mate, their offspring will all be brown with ...
... Directions: Use the following information to write a conclusion Mike and Kelsey have a male and a female brown mouse with long tails. Question: What will the offspring of two mice who have brown fur and long tails look like? Prediction: If two brown mice mate, their offspring will all be brown with ...
Chapter 15
... Is a technique that accomplishes the same end result as asexual reproduction. It is a way of making identical genetic copies. Cloning is done by inserting a nucleus from a “parent” organism’s cell (one that has a complete set of genetic information from that individual) into an egg cell from which t ...
... Is a technique that accomplishes the same end result as asexual reproduction. It is a way of making identical genetic copies. Cloning is done by inserting a nucleus from a “parent” organism’s cell (one that has a complete set of genetic information from that individual) into an egg cell from which t ...
TE content correlates positively with genome size
... •transposition begins with transcription •LTRs (long terminal repeats) are the critical cis-acting sequences (note: these are direct repeats) •element encodes reverse transcriptase and integrase enzymes, plus additional proteins required for replication •RNA copied into double-stranded cDNA in cytop ...
... •transposition begins with transcription •LTRs (long terminal repeats) are the critical cis-acting sequences (note: these are direct repeats) •element encodes reverse transcriptase and integrase enzymes, plus additional proteins required for replication •RNA copied into double-stranded cDNA in cytop ...
Biotechnology Notes HONORS
... modified by connecting DNA fragments from multiple sources (in vitro) • Host organism you are obtaining the gene from • Vector organism such as a bacteria, you are going to use to put the recombinant DNA into the organism you are trying to change • Plasmid DNA or “chromosome” of a bacteria • Rest ...
... modified by connecting DNA fragments from multiple sources (in vitro) • Host organism you are obtaining the gene from • Vector organism such as a bacteria, you are going to use to put the recombinant DNA into the organism you are trying to change • Plasmid DNA or “chromosome” of a bacteria • Rest ...
Please pass last week`s warm up to the aisle. HW # 63: Read and
... • The material inside the nucleus of cells that carries geneOc informaOon. • The scienOfic name for DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. ...
... • The material inside the nucleus of cells that carries geneOc informaOon. • The scienOfic name for DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. ...
Powerpoint File
... describe gene products in terms of their associated biological processes, cellular components and molecular functions in a species-independent manner (www.geneontology.org) ...
... describe gene products in terms of their associated biological processes, cellular components and molecular functions in a species-independent manner (www.geneontology.org) ...
Introductory to Biology
... establish current genetic theories G. Organisms that has genes from two or more separate species H. The accumulation of mutations I. When genes separate during meiosis, they have no influence on each other J. The total genetic makeup of an organism Match the terms of DNA transcription and translatio ...
... establish current genetic theories G. Organisms that has genes from two or more separate species H. The accumulation of mutations I. When genes separate during meiosis, they have no influence on each other J. The total genetic makeup of an organism Match the terms of DNA transcription and translatio ...
CHAPTER 12
... “transcriptionally silent” genes that initiate transcription but do not transition to elongation. – These polymerases are ready for transcription but are poised by inhibitory factors. – Gene transcription at the level of elongation may be important in activation of genes. ...
... “transcriptionally silent” genes that initiate transcription but do not transition to elongation. – These polymerases are ready for transcription but are poised by inhibitory factors. – Gene transcription at the level of elongation may be important in activation of genes. ...
Transgenic Organisms
... 2. Whatever gene is taken up is then expressed by the plant cell 3. What are some advantages and disadvantages of this technology? ...
... 2. Whatever gene is taken up is then expressed by the plant cell 3. What are some advantages and disadvantages of this technology? ...
student worksheet
... a good description? Why or why not? In living things, the detailed directions for cells to make the proteins that control and compose the organism must be very precise. The code found in DNA is the basis for forming proteins. In this activity you will see how the proteins are formed through an amazi ...
... a good description? Why or why not? In living things, the detailed directions for cells to make the proteins that control and compose the organism must be very precise. The code found in DNA is the basis for forming proteins. In this activity you will see how the proteins are formed through an amazi ...
June-2015-Biology-Final-Exam-Review
... 35. Draw and label the three parts of a nucleotide. (197) 36. The part of DNA for which it is named is the _________________. (197) 37. Name the two scientists credited with discovering the structure of DNA. (196) 38. What did Watson and Crick call the double stranded structure of DNA? (196) 39. Des ...
... 35. Draw and label the three parts of a nucleotide. (197) 36. The part of DNA for which it is named is the _________________. (197) 37. Name the two scientists credited with discovering the structure of DNA. (196) 38. What did Watson and Crick call the double stranded structure of DNA? (196) 39. Des ...
DNA Typing
... Identifying the gene associated with a specific disease requires years of work. The first step is to identify the region of the chromosome the gene is in (pedigree analysis, identifying breaks in chromosomes which cause the disease, etc.) Once the gene has been localized to a region of a chromosome, ...
... Identifying the gene associated with a specific disease requires years of work. The first step is to identify the region of the chromosome the gene is in (pedigree analysis, identifying breaks in chromosomes which cause the disease, etc.) Once the gene has been localized to a region of a chromosome, ...
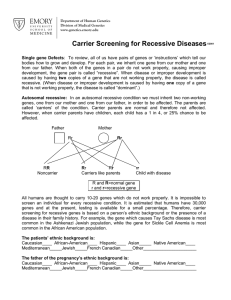
Carrier Screening for Recessive Diseases
... bodies how to grow and develop. For each pair, we inherit one gene from our mother and one from our father. When both of the genes in a pair do not work properly, causing improper development, the gene pair is called “recessive”. When disease or improper development is caused by having two copies of ...
... bodies how to grow and develop. For each pair, we inherit one gene from our mother and one from our father. When both of the genes in a pair do not work properly, causing improper development, the gene pair is called “recessive”. When disease or improper development is caused by having two copies of ...
Transcription PPT
... 5’ cap, poly-A tail, introns, exons, premRNA, mature mRNA, template strand, spliceosome, snRNPs, terminator, promoter, RNA Polymerase. Bonus, properly use transcription factors, TATA Box, ribozymes ...
... 5’ cap, poly-A tail, introns, exons, premRNA, mature mRNA, template strand, spliceosome, snRNPs, terminator, promoter, RNA Polymerase. Bonus, properly use transcription factors, TATA Box, ribozymes ...