5`-cgaucggauccagcuggacgcuagcguaaaaaaaa-3`
... DNA-dependent DNA polymerases (replicate DNA) DNA pol a,b,g,d,e – replication of DNA in eukaryotes (19) DNA pol I, II, III – replication of DNA in prokaryotes Klenow – subunit of E. coli DNA pol I labelling fragments for Southern/Northern blot Taq DNA pol – from Thermus aquaticus PCR ...
... DNA-dependent DNA polymerases (replicate DNA) DNA pol a,b,g,d,e – replication of DNA in eukaryotes (19) DNA pol I, II, III – replication of DNA in prokaryotes Klenow – subunit of E. coli DNA pol I labelling fragments for Southern/Northern blot Taq DNA pol – from Thermus aquaticus PCR ...
Directed Reading B
... GENES AND PROTEINS Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. ...
... GENES AND PROTEINS Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. ...
You Asked for it….. - Mr. Smith’s Science Page
... Steps • DNA Unzips (Hydrogen bonds break) • Each side acts as a template • New DNA nucleotides are added according to base-pairing rules • Two new molecules of DNA result – each with one old and one new strand. Happens in INTERPHASE (before mitosis or meiosis) ...
... Steps • DNA Unzips (Hydrogen bonds break) • Each side acts as a template • New DNA nucleotides are added according to base-pairing rules • Two new molecules of DNA result – each with one old and one new strand. Happens in INTERPHASE (before mitosis or meiosis) ...
MUTATIONS • Mutations are errors made in the DNA sequence that
... Ex/ Chromosome 14 may get a segment from chromosome 8, who gets a segment from chromosome 14 (a form of cancer results). Inversion is when a gene segment is separated then inserted in reverse; no loss in genetic material but the gene may be disrupted or come under transcriptional control. ...
... Ex/ Chromosome 14 may get a segment from chromosome 8, who gets a segment from chromosome 14 (a form of cancer results). Inversion is when a gene segment is separated then inserted in reverse; no loss in genetic material but the gene may be disrupted or come under transcriptional control. ...
Validation of microarray gene expression analysis
... of MAT2B, MARS and MARS2 transcripts in Jurkat vs. lymphoblasts are 1.19 (pvalue=0.28), 1.20 (p-value=0.67) and 1.23 (p-value=0.38), respectively. In all the cases, the statistical significance was evaluated by a two-tailed Pair Wise Fixed Reallocation Randomization Test [1] at a critical alpha valu ...
... of MAT2B, MARS and MARS2 transcripts in Jurkat vs. lymphoblasts are 1.19 (pvalue=0.28), 1.20 (p-value=0.67) and 1.23 (p-value=0.38), respectively. In all the cases, the statistical significance was evaluated by a two-tailed Pair Wise Fixed Reallocation Randomization Test [1] at a critical alpha valu ...
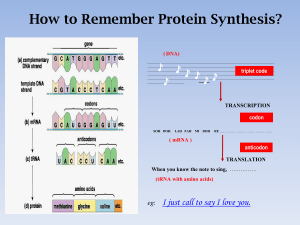
How to remember Protein Synthesis
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
RC 2 Student Notes
... Nucleic acid that uses genetic information from DNA to produce proteins Structure is single stranded Sugar is ribose Proteins Proteins are chains of amino acids Amino acids are determined by codons A codon is a sequence of 3 nucleotides (like AAA or CGG) from the mRNA (which was set from the DNA) ...
... Nucleic acid that uses genetic information from DNA to produce proteins Structure is single stranded Sugar is ribose Proteins Proteins are chains of amino acids Amino acids are determined by codons A codon is a sequence of 3 nucleotides (like AAA or CGG) from the mRNA (which was set from the DNA) ...
GENE REGULATION IN HIGHER ORGANSIMS Although eukaryotes
... globin gene is beside the beta globin gene. These genes are turned on in bone marrow only, which is where all of our blood cells originate. During most of the gestation period, a fetus has fetal hemoglobin or H b - F. Hb-F is a combination of alpha2/gamma2 gene products. There are two gamma genes ju ...
... globin gene is beside the beta globin gene. These genes are turned on in bone marrow only, which is where all of our blood cells originate. During most of the gestation period, a fetus has fetal hemoglobin or H b - F. Hb-F is a combination of alpha2/gamma2 gene products. There are two gamma genes ju ...
Aim: What is the structure of the DNA molecule?
... DNA is a special molecule found in the cells which make up a chromosome. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of a cell. (Therefore DNA is in the nucleus) There are 46 pairs of chromosomes in the human cell. DNA is an instruction manual for all the processes that the organism does. DNA has all the i ...
... DNA is a special molecule found in the cells which make up a chromosome. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of a cell. (Therefore DNA is in the nucleus) There are 46 pairs of chromosomes in the human cell. DNA is an instruction manual for all the processes that the organism does. DNA has all the i ...
Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA
... -usually inducible promoters are used to allow expression of gene independent of host cell gene expression -e.g. Lac Operon: inducible promoter that can be turned on with IPTG -level of expression can be controlled by concentration of inducer -once expressed (transcription ! translation), gene produ ...
... -usually inducible promoters are used to allow expression of gene independent of host cell gene expression -e.g. Lac Operon: inducible promoter that can be turned on with IPTG -level of expression can be controlled by concentration of inducer -once expressed (transcription ! translation), gene produ ...
Title of Unit: DNA, Genetics and Biotechnology Course and Grade
... replication square to predict the Outline the flow of genetic information results of test crosses and summarize the steps involved ...
... replication square to predict the Outline the flow of genetic information results of test crosses and summarize the steps involved ...
Nucleic Acids, the Genetic Code, and the Synthesis of
... Both DNA and RNA chains are produced by copying of template DNA strands Nucleic acid strands (poly-nucleotides) grow by the addition of one nucleotide at a time, and always in the 5’ -> 3’ direction RNA polymerases can initiate strand growth but DNA polymerases require a primer strand The primary po ...
... Both DNA and RNA chains are produced by copying of template DNA strands Nucleic acid strands (poly-nucleotides) grow by the addition of one nucleotide at a time, and always in the 5’ -> 3’ direction RNA polymerases can initiate strand growth but DNA polymerases require a primer strand The primary po ...
JF lect 5 12
... (1) Evidence that Genes are located on Chromosomes 1902 – McClung – a particular chromosome (X) determines sex in insects (XO = male; XX = female) 1903 – Sutton and Boveri – chromosomes behave just like the ‘unit factors’ described by Mendel 1910 – Morgan – the “white” eye color gene of Drosophila i ...
... (1) Evidence that Genes are located on Chromosomes 1902 – McClung – a particular chromosome (X) determines sex in insects (XO = male; XX = female) 1903 – Sutton and Boveri – chromosomes behave just like the ‘unit factors’ described by Mendel 1910 – Morgan – the “white” eye color gene of Drosophila i ...
Chromosomes and DNA Packaging
... chromatin is reconstituted. Implication? Very highly conserved in eukaryotes in both ...
... chromatin is reconstituted. Implication? Very highly conserved in eukaryotes in both ...
GENETICS EXAM 3 FALL 2004 Student Name
... b) Of those that were able to ligate to the vector, which, if any, would you definitely be able to separate away from the vector by cutting with SfoI? ...
... b) Of those that were able to ligate to the vector, which, if any, would you definitely be able to separate away from the vector by cutting with SfoI? ...
DNA is the hereditary material that transfers info btwn bacterial cells
... code for traits and proteins • Genetic engineering= use of genes to create or modify the genome • DNA fingerprinting = The repeating sequences in noncoding DNA (introns) vary between individuals & thus be used to identify an ...
... code for traits and proteins • Genetic engineering= use of genes to create or modify the genome • DNA fingerprinting = The repeating sequences in noncoding DNA (introns) vary between individuals & thus be used to identify an ...
Gene Section BCL7B (B-cell CLL/lymphoma 7B) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... BCL7B shares 90% sequence homology in the aminoterminal 51 amino acids with human BCL7A from the same gene family. ...
... BCL7B shares 90% sequence homology in the aminoterminal 51 amino acids with human BCL7A from the same gene family. ...
Heredity and Genetics Vocabulary
... 1. Cut the chart apart completely by cutting on all lines. 2. Have your child mix up the cards and try to match the correct definition with the correct vocabulary term. (A second chart can be printed to act as a key) ...
... 1. Cut the chart apart completely by cutting on all lines. 2. Have your child mix up the cards and try to match the correct definition with the correct vocabulary term. (A second chart can be printed to act as a key) ...
Biology Lecture 2 – Genes
... o Intron splicing: snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) cleave out introns, leaving behind exons which are spliced together to form final transcript o Variation in this process can make different proteins for same transcript Translation • 4 different bases, 3 base sequence codes for each amino ...
... o Intron splicing: snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) cleave out introns, leaving behind exons which are spliced together to form final transcript o Variation in this process can make different proteins for same transcript Translation • 4 different bases, 3 base sequence codes for each amino ...
Haploid (__)
... Errors in the genes occur 1 for every ____________ nucleotides read Causes of ERRORS ...
... Errors in the genes occur 1 for every ____________ nucleotides read Causes of ERRORS ...
Human Genome Project and Gene Therapy Overview
... project. You can also google “Exploring Our Molecular Selves Human Genome Project.” Answer the following questions as you watch. ...
... project. You can also google “Exploring Our Molecular Selves Human Genome Project.” Answer the following questions as you watch. ...
Bacteria Power Point File
... B) Assimilated foreign DNA may be integrated into the bacterial chromosome by recombination C) Progeny of the recipient bacterium will carry a new combination of genes D) Many bacteria have surface proteins that recognize and import naked DNA from closely related bacteria species ...
... B) Assimilated foreign DNA may be integrated into the bacterial chromosome by recombination C) Progeny of the recipient bacterium will carry a new combination of genes D) Many bacteria have surface proteins that recognize and import naked DNA from closely related bacteria species ...