Protein Synthesis Quick Questions
... 5. Each codon on mRNA is read and a tRNA with the matching anti-codon carries the correct amino acid to the ribosome 6. There, the tRNA binds to the ribosome and the amino acid is linked to the previous one by a peptide bond 7. Process continues, amino acids are linked, and the polypeptide chain gro ...
... 5. Each codon on mRNA is read and a tRNA with the matching anti-codon carries the correct amino acid to the ribosome 6. There, the tRNA binds to the ribosome and the amino acid is linked to the previous one by a peptide bond 7. Process continues, amino acids are linked, and the polypeptide chain gro ...
Eukaryotic Gene Control
... 2. The expression of specific genes can be inhibited by the presence of a repressor. (Negative control: repressor protein present which prevents transcription, inducer (usually a small molecule) is needed to allow initiation of transcription) 3. Inducers and repressors are small molecules that inter ...
... 2. The expression of specific genes can be inhibited by the presence of a repressor. (Negative control: repressor protein present which prevents transcription, inducer (usually a small molecule) is needed to allow initiation of transcription) 3. Inducers and repressors are small molecules that inter ...
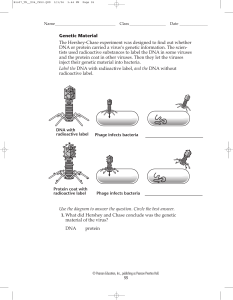
Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to
... 1. What did Hershey and Chase conclude was the genetic material of the virus? DNA ...
... 1. What did Hershey and Chase conclude was the genetic material of the virus? DNA ...
Supplementary Methods and Tables Supplementary Methods ChIP
... matrices within a group of sequences and highlight significant enrichments using a random set of sequences as a control. The main limitations of these methods are that they only explore a defined set of matrices and they require previous manipulations of raw data to identify DNA sequences bound by a ...
... matrices within a group of sequences and highlight significant enrichments using a random set of sequences as a control. The main limitations of these methods are that they only explore a defined set of matrices and they require previous manipulations of raw data to identify DNA sequences bound by a ...
Transcription & Translation
... introns in the coding region of the gene are cut out, producing a shorter mRNA molecule. (Splicing of pre mRNA is carried out by a complex known as splicosome, a complex consisting of RNA and protein) 5. The final mRNA molecule is chemically capped with a a methyl “cap” (AUG) ...
... introns in the coding region of the gene are cut out, producing a shorter mRNA molecule. (Splicing of pre mRNA is carried out by a complex known as splicosome, a complex consisting of RNA and protein) 5. The final mRNA molecule is chemically capped with a a methyl “cap” (AUG) ...
Slide 1
... Some individuals have been found with an XX genotype, but a MALE phenotype. What could account for this? Think-Pair-Share ...
... Some individuals have been found with an XX genotype, but a MALE phenotype. What could account for this? Think-Pair-Share ...
DNA Replication
... – Mutation can occur in a growth-factor gene, causing rapid, uncontrolled cell growth – Error in DNA replication, producing multiple copies of a single-growth factor gene – Change in gene’s location--falls under the control of a different promoter is transcribed more often (producing more growth-fac ...
... – Mutation can occur in a growth-factor gene, causing rapid, uncontrolled cell growth – Error in DNA replication, producing multiple copies of a single-growth factor gene – Change in gene’s location--falls under the control of a different promoter is transcribed more often (producing more growth-fac ...
EXAM 1
... C. (2 points) How might the presence of xenophan influence the expression of R? The presence of xenophan indicates that it is not necessary to synthesize more xenophan, so xenophan may decrease expression of R. Or it may bind to R to change its conformation such that it cannot bind the operator and ...
... C. (2 points) How might the presence of xenophan influence the expression of R? The presence of xenophan indicates that it is not necessary to synthesize more xenophan, so xenophan may decrease expression of R. Or it may bind to R to change its conformation such that it cannot bind the operator and ...
I. Multiple Choice: choose one best answer (2.5 points each, 80 points)
... 18. The failure of chromosomes to separate properly in meiosis or mitosis, leading to aneuploidy is called A. chromosome lagging. B. centromeric fusion. C . Robertsonian fusion. D. nondisjunction. E. unequal crossing over. ...
... 18. The failure of chromosomes to separate properly in meiosis or mitosis, leading to aneuploidy is called A. chromosome lagging. B. centromeric fusion. C . Robertsonian fusion. D. nondisjunction. E. unequal crossing over. ...
Modern methods in biology
... The study of all proteins in a cell, organ or organism under specific conditions ...
... The study of all proteins in a cell, organ or organism under specific conditions ...
Chapter 21: Genomes & Their Evolution 1. Sequencing & Analyzing Genomes
... functions can arise by: 1) Duplication of existing gene followed by mutation producing distinct gene product • the 2 genes will share significant homology however may have very different functions (e.g., lysozyme and -lactalbumin) ...
... functions can arise by: 1) Duplication of existing gene followed by mutation producing distinct gene product • the 2 genes will share significant homology however may have very different functions (e.g., lysozyme and -lactalbumin) ...
Microevolution is a change in a population*s gene pool
... A change in the gene pool of a population due to chance GENETIC DRIFT ALL populations are subject to genetic drift ...
... A change in the gene pool of a population due to chance GENETIC DRIFT ALL populations are subject to genetic drift ...
Biology 102, Lectures 17 and 18 Study Guide
... a. Where along the mRNA molecule does translation begin? (At the beginning? At a starting point determined by a particular base sequence, perhaps?) b. What do the tRNA molecules carry? c. What determines which tRNA molecule will enter the open site on the ribosome? d. What is the function of the cat ...
... a. Where along the mRNA molecule does translation begin? (At the beginning? At a starting point determined by a particular base sequence, perhaps?) b. What do the tRNA molecules carry? c. What determines which tRNA molecule will enter the open site on the ribosome? d. What is the function of the cat ...
ANSWERS - midterm study guide
... 12. What is a carrier? ______________________________________ Give an example of the genotype of a carrier.___ 13. What disease does someone have if they have Trisomy 21. ______________________________________________ What causes it? (Think about meiosis.) ___________________________________________ ...
... 12. What is a carrier? ______________________________________ Give an example of the genotype of a carrier.___ 13. What disease does someone have if they have Trisomy 21. ______________________________________________ What causes it? (Think about meiosis.) ___________________________________________ ...
Proximal promoter
... the proximal sequence upstream of the gene that tends to contain primary regulatory elements – Approximately -250 – Specific transcription factor binding sites ...
... the proximal sequence upstream of the gene that tends to contain primary regulatory elements – Approximately -250 – Specific transcription factor binding sites ...
overview
... medium lacking leucine, which allows growth of all transformants. Each transformant expresses one of the yeast ORFs expressed as a fusion to the Gal4 activation domain. b, Two-hybrid positives from a screen of the array with a Gal4 DNA-binding domain fusion of the Pcf11 protein, a component of the p ...
... medium lacking leucine, which allows growth of all transformants. Each transformant expresses one of the yeast ORFs expressed as a fusion to the Gal4 activation domain. b, Two-hybrid positives from a screen of the array with a Gal4 DNA-binding domain fusion of the Pcf11 protein, a component of the p ...
Population Genetics
... Aim: What are population genetics and how do they affect evolution? I. Population Genetics – Genetics today is concerned with inheritance in large groups of sexually reproducing animals. The study of these organisms as a reproducing group is known as population genetics. A. Key Terms 1. Species – a ...
... Aim: What are population genetics and how do they affect evolution? I. Population Genetics – Genetics today is concerned with inheritance in large groups of sexually reproducing animals. The study of these organisms as a reproducing group is known as population genetics. A. Key Terms 1. Species – a ...
Genetic code molecule
... Smooth coated pneumonia bacteria kills mice. Rough coated pneumoniad bacteria- mice live! Heat-killed smooth pneumonia bacteria-mice live Heat-killed smooth + safe rough bacteria together –mice die! What did this experiment show? Genetic material can be transferred from one bacteria to another (= tr ...
... Smooth coated pneumonia bacteria kills mice. Rough coated pneumoniad bacteria- mice live! Heat-killed smooth pneumonia bacteria-mice live Heat-killed smooth + safe rough bacteria together –mice die! What did this experiment show? Genetic material can be transferred from one bacteria to another (= tr ...
Gene Expression
... quickly. Many proteins, especially regulatory signaling proteins, are degraded by ubiquitinmediated proteolysis. Ubiquitin is a small protein that is highly conserved in evolution. In this system, multiple copies of ubiquitin are covalently attached to the target protein in long chains. The complex ...
... quickly. Many proteins, especially regulatory signaling proteins, are degraded by ubiquitinmediated proteolysis. Ubiquitin is a small protein that is highly conserved in evolution. In this system, multiple copies of ubiquitin are covalently attached to the target protein in long chains. The complex ...
Daily TAKS Connection: DNA
... The assembly of a messenger RNA strand that normally begins with UAC has been changed so that the newly assembled messenger RNA strand begins with UAG. Which of the following will most likely occur? A The protein will be missing the first amino acid. B The amino acids that make up the protein will a ...
... The assembly of a messenger RNA strand that normally begins with UAC has been changed so that the newly assembled messenger RNA strand begins with UAG. Which of the following will most likely occur? A The protein will be missing the first amino acid. B The amino acids that make up the protein will a ...
Document
... one gene locus and the centromere. • Identify first-division segregation (may or may not be most common group) from second-division segregation. • D = 1/2(second-division segregant asci)/total. • For example, if there are 65 first-division asci and 70 second-division asci, then D = 1/2(70/135) = 0.2 ...
... one gene locus and the centromere. • Identify first-division segregation (may or may not be most common group) from second-division segregation. • D = 1/2(second-division segregant asci)/total. • For example, if there are 65 first-division asci and 70 second-division asci, then D = 1/2(70/135) = 0.2 ...
CHAPTER18-20test
... b. Viruses have capsids composed of protein while viroids have no capsids. c. Viruses contain introns while viroids have only exons. d. Viruses have genomes composed of DNA while viroids have genomes composed of RNA. e. Viruses cannot pass through plasmodesmata while viroids can. 18. In which of the ...
... b. Viruses have capsids composed of protein while viroids have no capsids. c. Viruses contain introns while viroids have only exons. d. Viruses have genomes composed of DNA while viroids have genomes composed of RNA. e. Viruses cannot pass through plasmodesmata while viroids can. 18. In which of the ...
Molecular Genetics - Lake Travis Independent School District
... The “language” of mRNA is sometimes called the genetic code. The genetic code is read 3 letters (or bases) at a time, called codons. A codon is made up of 3 nucleotides that specify for a single amino acid Amino acids are strung together to form proteins (polypeptides) ...
... The “language” of mRNA is sometimes called the genetic code. The genetic code is read 3 letters (or bases) at a time, called codons. A codon is made up of 3 nucleotides that specify for a single amino acid Amino acids are strung together to form proteins (polypeptides) ...