The Crusades
... • Why might so many people have taken part in the Crusades, not only knights and soldiers but also ordinary people and even children? ...
... • Why might so many people have taken part in the Crusades, not only knights and soldiers but also ordinary people and even children? ...
The earliest crusaders had honorable motives that
... The story of the Crusades began in 1095 when Pope Urban II called the first crusade to liberate the Holy Land from the rule of the infidel and restore it to Christian control. The Byzantine emperor asked for aid from the West, but the liberation of Jerusalem was only a pretext: what the emperor rea ...
... The story of the Crusades began in 1095 when Pope Urban II called the first crusade to liberate the Holy Land from the rule of the infidel and restore it to Christian control. The Byzantine emperor asked for aid from the West, but the liberation of Jerusalem was only a pretext: what the emperor rea ...
Church History 900-1500
... Children’s Crusade of 1212; pre-teenage children went to Holy Land and were slaughtered or taken as slaves; led by 10 year olds Fifth Crusade, 1228-1229, led by Emperor Fredrick II; briefly retook Jerusalem Sixth and last Crusade, 1248-1254, led by King Louis IX of France (later proclaimed saint) wh ...
... Children’s Crusade of 1212; pre-teenage children went to Holy Land and were slaughtered or taken as slaves; led by 10 year olds Fifth Crusade, 1228-1229, led by Emperor Fredrick II; briefly retook Jerusalem Sixth and last Crusade, 1248-1254, led by King Louis IX of France (later proclaimed saint) wh ...
Chapter 11: From the Crusades to New Muslim Empires (Teacher
... 6. The Muslims were defeated because they lacked __________________ 7. The Seljuk Empire was breaking apart into ______________________ C. The Second Crusade (1146 – 1148) 1. In 1144, a united Muslim force _____________________________, the capital of the northernmost crusader kingdom 2. The German ...
... 6. The Muslims were defeated because they lacked __________________ 7. The Seljuk Empire was breaking apart into ______________________ C. The Second Crusade (1146 – 1148) 1. In 1144, a united Muslim force _____________________________, the capital of the northernmost crusader kingdom 2. The German ...
Yr 7 – History Knowledge Organiser: The Crusades in Depth
... Richard was born in 1157 to King Henry II of England and Duchess Eleanor of Aquitaine. He was born into the Angevin Dynasty (family) who ruled the kingdom of England after the Normans between 1154-1242. The first Angevin king of England was Henry II who expanded the kingdom’s lands hugely but spent ...
... Richard was born in 1157 to King Henry II of England and Duchess Eleanor of Aquitaine. He was born into the Angevin Dynasty (family) who ruled the kingdom of England after the Normans between 1154-1242. The first Angevin king of England was Henry II who expanded the kingdom’s lands hugely but spent ...
What happened when Crusaders entered Jerusalem during the First
... Finally, our men took possession of the walls and towers, and wonderful sights were to be seen. Some of our men (and this was more merciful) cut off the heads of their enemies; others shot them with arrows, so that they fell from the towers; others tortured them longer by casting them into the flame ...
... Finally, our men took possession of the walls and towers, and wonderful sights were to be seen. Some of our men (and this was more merciful) cut off the heads of their enemies; others shot them with arrows, so that they fell from the towers; others tortured them longer by casting them into the flame ...
Crusades (1096–1291)
... • Children who believed in the idea • Women & nuns who believed in the idea • Knights who wanted something to fight for. ...
... • Children who believed in the idea • Women & nuns who believed in the idea • Knights who wanted something to fight for. ...
Eleanor of Aquitane - Mrs. Tucker`s History Webpage
... to a brutal end. Eleanor gave her sons considerable military support. The revolt failed, and Eleanor was captured while seeking refuge in the kingdom of her first husband, Louis VII. Her semi-imprisonment in England ended only with the death of Henry II in 1189. On her release, Eleanor played a grea ...
... to a brutal end. Eleanor gave her sons considerable military support. The revolt failed, and Eleanor was captured while seeking refuge in the kingdom of her first husband, Louis VII. Her semi-imprisonment in England ended only with the death of Henry II in 1189. On her release, Eleanor played a grea ...
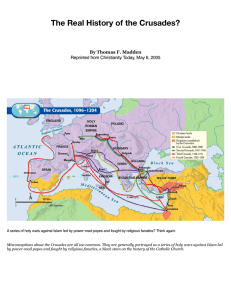
THE CR SAIES C 0 The Crusades were the culminating act f the
... task when two weeks after the great liberation, an Egyptian army came up to Ascalon to reliberate it. Godfrey defeated it, but a year later he died. His less able brother, Baldwin I (1100-18), took the loftier title of king. Under King Fulk, Count Anjou (1131-43), the new state included most of Pale ...
... task when two weeks after the great liberation, an Egyptian army came up to Ascalon to reliberate it. Godfrey defeated it, but a year later he died. His less able brother, Baldwin I (1100-18), took the loftier title of king. Under King Fulk, Count Anjou (1131-43), the new state included most of Pale ...
File
... answered their questions calmly and gave them money and supplies even when his own resources were exhausted. Comnena had mixed feelings about the crusades. On one hand, she respected the crusaders because they were, like herself and the Byzantines, Christians. She understood that one of the reasons ...
... answered their questions calmly and gave them money and supplies even when his own resources were exhausted. Comnena had mixed feelings about the crusades. On one hand, she respected the crusaders because they were, like herself and the Byzantines, Christians. She understood that one of the reasons ...
The Crusades
... regularly made pilgrimages to the Holy Land and birthplace of their religion since the 6 th century but after control of Jerusalem was taken by the Seljuk Turks, Christians were forbidden from entering. The Turks also threatened to invade the Byzantine Empire and Constantinople, causing the Emperor ...
... regularly made pilgrimages to the Holy Land and birthplace of their religion since the 6 th century but after control of Jerusalem was taken by the Seljuk Turks, Christians were forbidden from entering. The Turks also threatened to invade the Byzantine Empire and Constantinople, causing the Emperor ...
byzantine, crusades and russia - Lyons-Global
... “Western Europe owed a debt of gratitude to the Empire that for almost a thousand years ensured the survival of Christianity during a time when Europe was too weak to accomplish the task.” Which Empire is referred to in this quotation? ...
... “Western Europe owed a debt of gratitude to the Empire that for almost a thousand years ensured the survival of Christianity during a time when Europe was too weak to accomplish the task.” Which Empire is referred to in this quotation? ...
If YOU were there `~
... Politics in Europe also changed. Some kings increased their power because many nobles and knights had died in the Holy Land. These kings seized lands that were left without clear owners. During the later Crusades, kings also gained influence at the popes' expense. The popes had wanted the church to ...
... Politics in Europe also changed. Some kings increased their power because many nobles and knights had died in the Holy Land. These kings seized lands that were left without clear owners. During the later Crusades, kings also gained influence at the popes' expense. The popes had wanted the church to ...
Document
... so, they killed most Muslims and Jews living in the Holy Land. The Second Crusade: (1147-1149 C.E.) o Fifty years after the First Crusade, the Seljuk Turks conquered parts of Palestine. In response, Pope Eugenius IV called upon another volunteer army to defend the Holy Land. However, the Christians ...
... so, they killed most Muslims and Jews living in the Holy Land. The Second Crusade: (1147-1149 C.E.) o Fifty years after the First Crusade, the Seljuk Turks conquered parts of Palestine. In response, Pope Eugenius IV called upon another volunteer army to defend the Holy Land. However, the Christians ...
A-level History Candidate exemplar Unit 01 (HIS1) - Average
... create a sense of unity within the newly formed country as soon as possible. Bismarck saw a threat to unity from the Catholics, as they saw the Pope as the highest source of authority rather than the German government. The Pope at that time often interfered in the governments of Europe, and this is ...
... create a sense of unity within the newly formed country as soon as possible. Bismarck saw a threat to unity from the Catholics, as they saw the Pope as the highest source of authority rather than the German government. The Pope at that time often interfered in the governments of Europe, and this is ...
THE CRUSADES
... Use your book (14.1) to fill in the blanks and answer the questions about each of the events listed below. ...
... Use your book (14.1) to fill in the blanks and answer the questions about each of the events listed below. ...
Crusades
... → Byzantine emperor, Alexius I, asks Pope Urban II for knights to help him fight Muslim Turks in 1095 …although they have been rivals (Great Schism), Urban agrees → Pope Urban II uses this as an opportunity to reclaim Jerusalem & the Holy Land …not to necessarily aid the Byzantines …calls for all Eu ...
... → Byzantine emperor, Alexius I, asks Pope Urban II for knights to help him fight Muslim Turks in 1095 …although they have been rivals (Great Schism), Urban agrees → Pope Urban II uses this as an opportunity to reclaim Jerusalem & the Holy Land …not to necessarily aid the Byzantines …calls for all Eu ...
The Crusades were a series of wars during the Middle Ages where
... adventures in the east in a rather unique fashion. The narrative of his journeys and almost two decades in Mongol service takes up only the fifteen-page-long prologue. The rest of the text offers detailed descriptions of the people and places he come across, organized geographically from west to eas ...
... adventures in the east in a rather unique fashion. The narrative of his journeys and almost two decades in Mongol service takes up only the fifteen-page-long prologue. The rest of the text offers detailed descriptions of the people and places he come across, organized geographically from west to eas ...
History of the Crusades
... By any reckoning, the First Crusade was a long shot. There was no leader, no chain of command, no supply lines, no detailed strategy. It was simply thousands of warriors marching deep into enemy territory, committed to a common cause. Many of them died, either in battle or through disease or starvat ...
... By any reckoning, the First Crusade was a long shot. There was no leader, no chain of command, no supply lines, no detailed strategy. It was simply thousands of warriors marching deep into enemy territory, committed to a common cause. Many of them died, either in battle or through disease or starvat ...
And on … DON`T WRITE!
... 1. Pope Urban II believed this would increase his power. 2. Christians believed they would go to heaven. ...
... 1. Pope Urban II believed this would increase his power. 2. Christians believed they would go to heaven. ...
Islamic Empires - Brookdale Community College
... dynasty at a dinner of peace, a few of them escaped, fled to Spain, and established Cordoba as their capital. The Great Mosque of Cordoba, begun in 786, contains all of the usual features of a mosque, but it is best known for its interior double set of horseshoe-shaped arches, one above the other, w ...
... dynasty at a dinner of peace, a few of them escaped, fled to Spain, and established Cordoba as their capital. The Great Mosque of Cordoba, begun in 786, contains all of the usual features of a mosque, but it is best known for its interior double set of horseshoe-shaped arches, one above the other, w ...
The Cathars - Kirkwood Community College
... he willing ‘to eliminate such harmful filth’, as Innocent put it, when called upon directly in 1207 . . . Those who did actually participate took the matter very seriously, making careful arrangements for their dependents and appropriate grants either to local monasteries or to important foundations ...
... he willing ‘to eliminate such harmful filth’, as Innocent put it, when called upon directly in 1207 . . . Those who did actually participate took the matter very seriously, making careful arrangements for their dependents and appropriate grants either to local monasteries or to important foundations ...
Chapter 18, Section 2: Crusades Objective: Describe what the
... area Jesus lived, preached and died. ...
... area Jesus lived, preached and died. ...
Why the Crusades Failed? NarratiNg the episode aFter the Fall oF
... Philip Augustus at the siege of Acre on June 8, 1191. “For joy at his coming”, says Bahā al-Dīn, “the Franks broke forth into public rejoicing, and lit mighty fires in their camps all night long. And seeing that the King of England was old in war and wise in council.”13 After four days of the first ...
... Philip Augustus at the siege of Acre on June 8, 1191. “For joy at his coming”, says Bahā al-Dīn, “the Franks broke forth into public rejoicing, and lit mighty fires in their camps all night long. And seeing that the King of England was old in war and wise in council.”13 After four days of the first ...
Second Crusade

The Second Crusade (1145–1149) was the second major crusade launched from Europe. The Second Crusade was started in response to the fall of the County of Edessa the previous year to the forces of Zengi. The county had been founded during the First Crusade (1096–1099) by Baldwin of Boulogne in 1098. While it was the first Crusader state to be founded, it was also the first to fall.The Second Crusade was announced by Pope Eugene III, and was the first of the crusades to be led by European kings, namely Louis VII of France and Conrad III of Germany, with help from a number of other European nobles. The armies of the two kings marched separately across Europe. After crossing Byzantine territory into Anatolia, both armies were separately defeated by the Seljuq Turks. The main Western Christian source, Odo of Deuil, and Syriac Christian sources claim that the Byzantine emperor Manuel I Komnenos secretly hindered the crusaders' progress, particularly in Anatolia where he is alleged to have deliberately ordered Turks to attack them. Louis and Conrad and the remnants of their armies reached Jerusalem and, in 1148, participated in an ill-advised attack on Damascus. The crusade in the east was a failure for the crusaders and a great victory for the Muslims. It would ultimately have a key influence on the fall of Jerusalem and give rise to the Third Crusade at the end of the 12th century.The only Christian success of the Second Crusade came to a combined force of 13,000 Flemish, Frisian, Norman, English, Scottish, and German crusaders in 1147. Travelling from England, by ship, to the Holy Land, the army stopped and helped the smaller (7,000) Portuguese army in the capture of Lisbon, expelling its Moorish occupants.