unit 3: the world in transition
... Henry Tudor - won the War of the Roses in 1485 by defeating King Richard III of York; married a daughter from the House of York &, as King Henry VII, set up a strong monarchy in England ...
... Henry Tudor - won the War of the Roses in 1485 by defeating King Richard III of York; married a daughter from the House of York &, as King Henry VII, set up a strong monarchy in England ...
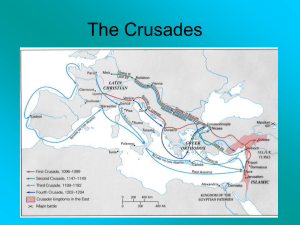
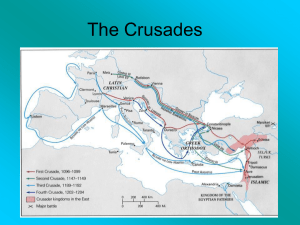
The Crusades
... The Second Crusade, however, was an absolute and total failure and was only called for in response to the fall of the County of Edessa in 1144. ...
... The Second Crusade, however, was an absolute and total failure and was only called for in response to the fall of the County of Edessa in 1144. ...
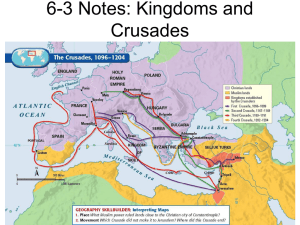
14.3 and 14.4 (Changes in Medieval Europe)
... pick up the fighting where the last one left off, causing the war to be dragged on. † England won most of the battles, but the French continued to fight. † Joan of Arc - A peasant girl from France who took charge of French forces at the battle of Orleans in 1429. † Claimed she heard a message from G ...
... pick up the fighting where the last one left off, causing the war to be dragged on. † England won most of the battles, but the French continued to fight. † Joan of Arc - A peasant girl from France who took charge of French forces at the battle of Orleans in 1429. † Claimed she heard a message from G ...
The Crusades - Hawk History
... forces and started to regain land taken from them during the first crusade 1147 the second crusade began Louis VII of France and Conrad III from Germany united at the city of Damascus and tried to gain back the Holy Land These combined forces failed to recapture the city and in 1149 turned bac ...
... forces and started to regain land taken from them during the first crusade 1147 the second crusade began Louis VII of France and Conrad III from Germany united at the city of Damascus and tried to gain back the Holy Land These combined forces failed to recapture the city and in 1149 turned bac ...
Background on the 1st Crusade: In 1095, Byzantine Emperor
... Jerusalem was taken from the north on the morning of July 15, 1099. The population was put to the sword by the Franks, who pillaged the area for a week. A band of Muslims barricaded themselves into the Tower of David and fought on for several days. They were granted their lives in return for surrend ...
... Jerusalem was taken from the north on the morning of July 15, 1099. The population was put to the sword by the Franks, who pillaged the area for a week. A band of Muslims barricaded themselves into the Tower of David and fought on for several days. They were granted their lives in return for surrend ...
Year 12 to 13 History Crusades Coursework
... Research into Innocent III regarding his aims and objectives for the papacy. Groupwork into key participants on the Fourth Crusade. Identify common motivating factors such as religious devotion, social ties and or economic greed. Debate as to the degree to which motivations had changed and the role ...
... Research into Innocent III regarding his aims and objectives for the papacy. Groupwork into key participants on the Fourth Crusade. Identify common motivating factors such as religious devotion, social ties and or economic greed. Debate as to the degree to which motivations had changed and the role ...
CHAPTER 11: From the Crusades to New Muslim Empires
... Crusades continued for another 100 years ...
... Crusades continued for another 100 years ...
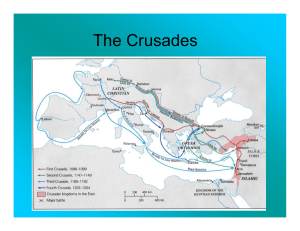
The Crusades
... The Mongol Invasion-- Muslims succeeded in driving the crusaders from the Holy Land. Even as the crusades were taking place, other changes were happening in Muslim lands. By the mid 1200s, Muslims faced a great threat than European crusaders—the Mongols. In the 13th century, Mongols began wars of c ...
... The Mongol Invasion-- Muslims succeeded in driving the crusaders from the Holy Land. Even as the crusades were taking place, other changes were happening in Muslim lands. By the mid 1200s, Muslims faced a great threat than European crusaders—the Mongols. In the 13th century, Mongols began wars of c ...
File
... However, by now even Richard the Lionhearted was suffering. He had a fever and appealed to his enemy Saladin to send him fresh water and fresh fruit. Saladin did just this - sending frozen snow to the Crusaders to be used as water and fresh fruit. Why would Saladin do this? There are two reasons. Fi ...
... However, by now even Richard the Lionhearted was suffering. He had a fever and appealed to his enemy Saladin to send him fresh water and fresh fruit. Saladin did just this - sending frozen snow to the Crusaders to be used as water and fresh fruit. Why would Saladin do this? There are two reasons. Fi ...
Crusades
... • Primary battles to place between 1096 AD through 1204 AD • At this point in history, Palestine is a territory in the Middle East that includes the holy city of Jerusalem. ...
... • Primary battles to place between 1096 AD through 1204 AD • At this point in history, Palestine is a territory in the Middle East that includes the holy city of Jerusalem. ...
(Section I): The Crusades Begin
... Jerusalem and set up another crusader state (surrounded by Muslims though). The first Crusade was successful for Christians, but in winning, they killed many Muslims (even women and children), and Jewish people living in Jerusalem. ...
... Jerusalem and set up another crusader state (surrounded by Muslims though). The first Crusade was successful for Christians, but in winning, they killed many Muslims (even women and children), and Jewish people living in Jerusalem. ...
ROLE OF THE CHURCH System of Organization
... *Monk – a man who separates himself from everyday life to dedicate himself entirely to God, lives in a monastery run by an abbot *Spent lots of time in prayer and physical labor, took a ...
... *Monk – a man who separates himself from everyday life to dedicate himself entirely to God, lives in a monastery run by an abbot *Spent lots of time in prayer and physical labor, took a ...
World History Study Guide Feudal System/Middle Ages/ Black Death
... The garbage and mud in the streets helped spread disease in medieval cities. A manor is a large estate often including a village and farmlands ruled by a lord. Feudalism is a political and military system based on the holding of land. The lands belonging to a medieval lord is known as a mano ...
... The garbage and mud in the streets helped spread disease in medieval cities. A manor is a large estate often including a village and farmlands ruled by a lord. Feudalism is a political and military system based on the holding of land. The lands belonging to a medieval lord is known as a mano ...
The Crusades
... profit from their participation • Merchants also hoped for access to the merchandise available in the Middle East ...
... profit from their participation • Merchants also hoped for access to the merchandise available in the Middle East ...
The Crusades - OnMyCalendar
... profit from their participation • Merchants also hoped for access to the merchandise available in the Middle East ...
... profit from their participation • Merchants also hoped for access to the merchandise available in the Middle East ...
The Crusades
... profit from their participation • Merchants also hoped for access to the merchandise available in the Middle East ...
... profit from their participation • Merchants also hoped for access to the merchandise available in the Middle East ...
Untitled - The Sixth Form College, Colchester
... AS Level: Henry II 1154-1189. Henry II accession to the throne and the Angevin Empire. Relations with his wife, Eleanor of Aquitaine and sons. Henry’s re-assertion of royal control leading to conflict between the Crown and the Church, the murder of Thomas Becket. A Level: Richard and John 1189-1216. ...
... AS Level: Henry II 1154-1189. Henry II accession to the throne and the Angevin Empire. Relations with his wife, Eleanor of Aquitaine and sons. Henry’s re-assertion of royal control leading to conflict between the Crown and the Church, the murder of Thomas Becket. A Level: Richard and John 1189-1216. ...
the crusades - Cobb Learning
... •Led by French and Norman nobles •Captured Antioch and Jerusalem • the Crusaders had won a narrow strip of land. It stretched about 650 miles from Edessa in the north to Jerusalem in the south. •Christians win! ...
... •Led by French and Norman nobles •Captured Antioch and Jerusalem • the Crusaders had won a narrow strip of land. It stretched about 650 miles from Edessa in the north to Jerusalem in the south. •Christians win! ...
Welcome to the Middle ages
... Turkish Muslims – Block the pilgrimage routes that Christians used to visit the Holy Land Emperor of the Byzantine Empire in Constantinople (Alexius I) – Needs help from the Roman Catholic Church to defend the Byzantine Empire Pope of the Catholic Church (Pope Urban II) – Believes that it is God’s w ...
... Turkish Muslims – Block the pilgrimage routes that Christians used to visit the Holy Land Emperor of the Byzantine Empire in Constantinople (Alexius I) – Needs help from the Roman Catholic Church to defend the Byzantine Empire Pope of the Catholic Church (Pope Urban II) – Believes that it is God’s w ...
File - HistoryRocks
... • 50 years after the first (1147) • Brought on by the Muslims attacking the Crusader States and the fall of Edessa • Led by Louis VII • Overall had little success ...
... • 50 years after the first (1147) • Brought on by the Muslims attacking the Crusader States and the fall of Edessa • Led by Louis VII • Overall had little success ...
6-3 Kings and Crusades Notes
... 1098 ACE - 1st Crusade conquered Antioch in Syria 1099 - Crusaders conquered Jerusalem after a bloody fight killing Jews, Muslims, and Christians alike Crusaders created four crusader states: Kingdom of Jerusalem, county of Edessa, principality of Antioch, and the county of Tripoli The states were s ...
... 1098 ACE - 1st Crusade conquered Antioch in Syria 1099 - Crusaders conquered Jerusalem after a bloody fight killing Jews, Muslims, and Christians alike Crusaders created four crusader states: Kingdom of Jerusalem, county of Edessa, principality of Antioch, and the county of Tripoli The states were s ...
Second Crusade

The Second Crusade (1145–1149) was the second major crusade launched from Europe. The Second Crusade was started in response to the fall of the County of Edessa the previous year to the forces of Zengi. The county had been founded during the First Crusade (1096–1099) by Baldwin of Boulogne in 1098. While it was the first Crusader state to be founded, it was also the first to fall.The Second Crusade was announced by Pope Eugene III, and was the first of the crusades to be led by European kings, namely Louis VII of France and Conrad III of Germany, with help from a number of other European nobles. The armies of the two kings marched separately across Europe. After crossing Byzantine territory into Anatolia, both armies were separately defeated by the Seljuq Turks. The main Western Christian source, Odo of Deuil, and Syriac Christian sources claim that the Byzantine emperor Manuel I Komnenos secretly hindered the crusaders' progress, particularly in Anatolia where he is alleged to have deliberately ordered Turks to attack them. Louis and Conrad and the remnants of their armies reached Jerusalem and, in 1148, participated in an ill-advised attack on Damascus. The crusade in the east was a failure for the crusaders and a great victory for the Muslims. It would ultimately have a key influence on the fall of Jerusalem and give rise to the Third Crusade at the end of the 12th century.The only Christian success of the Second Crusade came to a combined force of 13,000 Flemish, Frisian, Norman, English, Scottish, and German crusaders in 1147. Travelling from England, by ship, to the Holy Land, the army stopped and helped the smaller (7,000) Portuguese army in the capture of Lisbon, expelling its Moorish occupants.