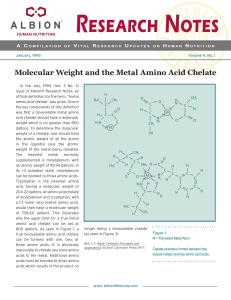
Molecular Weight and the Metal Amino Acid Chelate
... the above example even though the molecular weight of the iron sulfate can be determined, the sulfate in the starting material was included in the total weight of the product formed. The sulfate should not have been counted in the weight of the chelate even though most so-called chelate manufacturer ...
... the above example even though the molecular weight of the iron sulfate can be determined, the sulfate in the starting material was included in the total weight of the product formed. The sulfate should not have been counted in the weight of the chelate even though most so-called chelate manufacturer ...
The Amino Acid Composition of Algal Cell Walls
... found only six amino acids in a saccharomyces wall preparation. These latter results may have been due to incomplete hydrolysis, however, because in later reports from the same laboratory (Korn & Northcote, 1960) 18 to 20 amino acids are reported in yeast walls. Protein was found by Dyke (1964)in na ...
... found only six amino acids in a saccharomyces wall preparation. These latter results may have been due to incomplete hydrolysis, however, because in later reports from the same laboratory (Korn & Northcote, 1960) 18 to 20 amino acids are reported in yeast walls. Protein was found by Dyke (1964)in na ...
Amino Acids - Rose
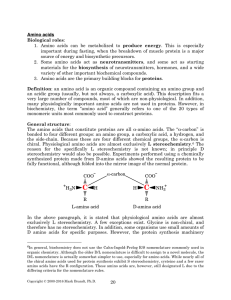
... biochemistry, the term “amino acid” generally refers to one of the 20 types of monomeric units most commonly used to construct proteins. General structure: The amino acids that constitute proteins are all α-amino acids. The “α-carbon” is bonded to four different groups: an amino group, a carboxylic ...
... biochemistry, the term “amino acid” generally refers to one of the 20 types of monomeric units most commonly used to construct proteins. General structure: The amino acids that constitute proteins are all α-amino acids. The “α-carbon” is bonded to four different groups: an amino group, a carboxylic ...
Chapter 5 Notes (Biomolecules)
... • What are the building blocks of Proteins? • What are the 4 main parts of an amino acid? • What part of an amino acid give it it’s identity? • What reaction puts amino acids together? What happens during that reaction? • What special type of bond links amino acids? ...
... • What are the building blocks of Proteins? • What are the 4 main parts of an amino acid? • What part of an amino acid give it it’s identity? • What reaction puts amino acids together? What happens during that reaction? • What special type of bond links amino acids? ...
1-2 (Weigent)
... i. Ketone bodies are good news and bad news. The bad news is that they change the pH of the blood which ultimately could lead to a coma. The good news is that these ketone bodies in some regards spare the muscle (when the body has to have substrate to make glucose, if it doesn’t use these then it’s ...
... i. Ketone bodies are good news and bad news. The bad news is that they change the pH of the blood which ultimately could lead to a coma. The good news is that these ketone bodies in some regards spare the muscle (when the body has to have substrate to make glucose, if it doesn’t use these then it’s ...
Metabolic fuels: regulating fluxes to select mix
... Animals must regulate the fluxes of multiple fuels to support changing metabolic rates that result from variation in physiological circumstances. The aim of fuel selection strategies is to exploit the advantages of individual substrates while minimizing the impact of disadvantages. All exercising ma ...
... Animals must regulate the fluxes of multiple fuels to support changing metabolic rates that result from variation in physiological circumstances. The aim of fuel selection strategies is to exploit the advantages of individual substrates while minimizing the impact of disadvantages. All exercising ma ...
anabolic and catabolic reactions. Energetics of bacterial growth
... years ago, microbiologists have made extraordinary progress in studying this extremely diverse group of living organisms. The processes of energy source degradation, ATP formation, monomer synthesis, macromolecular polymerization, DNA replication, and cell duplication are surprisingly well understoo ...
... years ago, microbiologists have made extraordinary progress in studying this extremely diverse group of living organisms. The processes of energy source degradation, ATP formation, monomer synthesis, macromolecular polymerization, DNA replication, and cell duplication are surprisingly well understoo ...
biochem ch 46 [9-4
... Liver Anatomy Liver receives 75% of blood supply from portal vein (carries blood from small intestine, stomach, pancreas, and spleen) and 25% from hepatic artery o Blood from portal vein and hepatic artery mix contents as they enter liver sinusoids o As blood flows through sinusoids, contents of p ...
... Liver Anatomy Liver receives 75% of blood supply from portal vein (carries blood from small intestine, stomach, pancreas, and spleen) and 25% from hepatic artery o Blood from portal vein and hepatic artery mix contents as they enter liver sinusoids o As blood flows through sinusoids, contents of p ...
File ch 14 ppt1
... Arrhenius Acids and Bases • An Arrhenius acid is a chemical compound that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions, H+, in aqueous solution. • An Arrhenius base is a substance that increases the concentration of hydroxide ions, OH−, in aqueous solution. ...
... Arrhenius Acids and Bases • An Arrhenius acid is a chemical compound that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions, H+, in aqueous solution. • An Arrhenius base is a substance that increases the concentration of hydroxide ions, OH−, in aqueous solution. ...
REGULATION OF KETONE BODY AND COENZYME A
... him for his scientific guidance, support, patience and humor on the 5,000 li road. He is an adviser who not only teaches me critical thinking, but also is always willing to sit and discuss every detail of my experiments, presentations and scientific writings. His guidance gives me enough confidence ...
... him for his scientific guidance, support, patience and humor on the 5,000 li road. He is an adviser who not only teaches me critical thinking, but also is always willing to sit and discuss every detail of my experiments, presentations and scientific writings. His guidance gives me enough confidence ...
Nucleic Acids - Lyndhurst Schools
... messenger between DNA & ribosome & carries out process by which proteins are made from amino acids ...
... messenger between DNA & ribosome & carries out process by which proteins are made from amino acids ...
Nutrition and Metabolism
... • Are absorbed primarily from the digestive tract along with lipids of micelles • Normally diffuse into plasma membranes and lipids in liver and adipose tissue ...
... • Are absorbed primarily from the digestive tract along with lipids of micelles • Normally diffuse into plasma membranes and lipids in liver and adipose tissue ...
Effect of ovarian hormones on mitochondrial enzyme activity in the
... Metabolic testing. Animals remained sedentary during the 14-day treatment period. Rats were fasted for 12 h before the commencement of metabolic testing. On the morning of day 15, animals were effectively suffocated with CO2 (80:20, CO2-O2), rendering them unconscious in ⬍20 s. A midline incision wa ...
... Metabolic testing. Animals remained sedentary during the 14-day treatment period. Rats were fasted for 12 h before the commencement of metabolic testing. On the morning of day 15, animals were effectively suffocated with CO2 (80:20, CO2-O2), rendering them unconscious in ⬍20 s. A midline incision wa ...
Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids
... typically solids at room temperature. • Because they contain charges, carboxylate salts are typically much more soluble in water than the carboxylic acids from which they are derived. ...
... typically solids at room temperature. • Because they contain charges, carboxylate salts are typically much more soluble in water than the carboxylic acids from which they are derived. ...
Chapter 17, Section 17.3
... Polyprotic acid: H2CO3(aq) can donate 2 protons Polyprotic base: CO32‾(aq) can accept 2 protons Amphiprotic entity: HCO3‾(aq) can donate or accept a proton (depending on what it’s reacting with) ...
... Polyprotic acid: H2CO3(aq) can donate 2 protons Polyprotic base: CO32‾(aq) can accept 2 protons Amphiprotic entity: HCO3‾(aq) can donate or accept a proton (depending on what it’s reacting with) ...
Molecular Cloning, Characterization, and mRNA Expression of
... internal water filled cavity. Due to this protein specially found in mature enterocytes, I-FABP was thought to be crucial in fatty acids trafficking, and targeting ligands to specific organelle for metabolic process. Even so, the specific function of I-FABP in animal intestine remains elusive. LCFAs ...
... internal water filled cavity. Due to this protein specially found in mature enterocytes, I-FABP was thought to be crucial in fatty acids trafficking, and targeting ligands to specific organelle for metabolic process. Even so, the specific function of I-FABP in animal intestine remains elusive. LCFAs ...
The Effect of Detergents on Amino Acid Liberation by
... quantity and types of amino acids liberated. MYRJ 52 caused a substantial increase in amino acid liberation and MYRJ 45 induced the liberation of tryptophan. This amino acid is only required in small quantities in the cell and is undetectable as a free-pool amino acid by the methods employed in this ...
... quantity and types of amino acids liberated. MYRJ 52 caused a substantial increase in amino acid liberation and MYRJ 45 induced the liberation of tryptophan. This amino acid is only required in small quantities in the cell and is undetectable as a free-pool amino acid by the methods employed in this ...
Vitamins B6 and B12 (Final).
... Reminder: Essential amino acids are those that are "essential" in the diet. In ...
... Reminder: Essential amino acids are those that are "essential" in the diet. In ...
Biocatalysis - School of Chemical Sciences
... conditions, are also very attractive in commercial applications. The characteristics of limited operating regions, substrate or product inhibition, and reactions in aqueous solutions have often been considered as the most serious drawbacks of biocatalysts. Many of these drawbacks, however, turn out ...
... conditions, are also very attractive in commercial applications. The characteristics of limited operating regions, substrate or product inhibition, and reactions in aqueous solutions have often been considered as the most serious drawbacks of biocatalysts. Many of these drawbacks, however, turn out ...
heme
... • reaction is catalyzed by enzyme ferrochelatase Figure was assumed from http://www.porphyrin.net/mediporph/_netbiochem/synthesis/ ferrochelatase.html ...
... • reaction is catalyzed by enzyme ferrochelatase Figure was assumed from http://www.porphyrin.net/mediporph/_netbiochem/synthesis/ ferrochelatase.html ...
amino acids
... yields without the bitter β-form byproduct. • may hydrolyze into its constituent amino acids under conditions of elevated temperature or high pH. At room temperature, it is most stable at pH 4.3, where its half-life is nearly 300 days. At pH 7, however, its half-life is only a few days ...
... yields without the bitter β-form byproduct. • may hydrolyze into its constituent amino acids under conditions of elevated temperature or high pH. At room temperature, it is most stable at pH 4.3, where its half-life is nearly 300 days. At pH 7, however, its half-life is only a few days ...
A New Type of a Multifunctional ß
... acetyl-CoA yielding thiolytic cleavage of the 3-ketoacyl-CoA esters formed in the dehydrogenation process. Because the fatty acid chains are reduced by only two carbon atoms in the course of these successive reactions, the reaction sequence has to be repeated until the fatty acids have been complete ...
... acetyl-CoA yielding thiolytic cleavage of the 3-ketoacyl-CoA esters formed in the dehydrogenation process. Because the fatty acid chains are reduced by only two carbon atoms in the course of these successive reactions, the reaction sequence has to be repeated until the fatty acids have been complete ...
Lb. curvatus
... This defect on the surfaces of cheese does not pose any health hazards, but may be mistaken by consumers as mold, resulting in economic loss to the industry. It is postulated that certain non-starter lactic acid bacteria (NSLAB) that grow in cheese are responsible. The conversion of pyruvate to L(+) ...
... This defect on the surfaces of cheese does not pose any health hazards, but may be mistaken by consumers as mold, resulting in economic loss to the industry. It is postulated that certain non-starter lactic acid bacteria (NSLAB) that grow in cheese are responsible. The conversion of pyruvate to L(+) ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.