1. (a) Propan-1ol, C2H5CH2OH can be oxidised to propanoic acid
... X reacts with sodium hydrogencarbonate solution to give a gas which turns lime water milky. It also reacts with a solution of sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid between 0 ºC and 5 ºC to produce a substance which reacts with phenol to give an orange ...
... X reacts with sodium hydrogencarbonate solution to give a gas which turns lime water milky. It also reacts with a solution of sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid between 0 ºC and 5 ºC to produce a substance which reacts with phenol to give an orange ...
Peer-reviewed Article PDF
... The citric acid or the Krebs cycle, [1] comprises a series of chemical reactions utilized by all aerobic organisms to generate its energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins [2]. The final outcome of the cycle releases carbon dioxide and chemical energy in ...
... The citric acid or the Krebs cycle, [1] comprises a series of chemical reactions utilized by all aerobic organisms to generate its energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins [2]. The final outcome of the cycle releases carbon dioxide and chemical energy in ...
Course Objectives
... • What are fatty acids and how do they differ from one another? (P. 343-344) • What are triglycerides and waxes? What are their roles in nature? (P. 345-348) • What are the different types of membrane-forming lipids? (P. 348-350) • What is the role of membrane lipids in blood group determination? (P ...
... • What are fatty acids and how do they differ from one another? (P. 343-344) • What are triglycerides and waxes? What are their roles in nature? (P. 345-348) • What are the different types of membrane-forming lipids? (P. 348-350) • What is the role of membrane lipids in blood group determination? (P ...
Plant biotin-containing carboxylases
... where fatty acids are used either in the assembly of membrane lipids or for the biogenesis of triacylglycerol that is deposited as oil. Consistent with the metabolic demands on the plastidic malonyl-CoA pool, the ACCase subunits and their mRNAs accumulate to high levels in young developing seeds and ...
... where fatty acids are used either in the assembly of membrane lipids or for the biogenesis of triacylglycerol that is deposited as oil. Consistent with the metabolic demands on the plastidic malonyl-CoA pool, the ACCase subunits and their mRNAs accumulate to high levels in young developing seeds and ...
Amino Acids and Proteins Amino Acid Compound
... comparison with the migration of DNP-derivative standards allows for the identification of the N-terminal amino acid. Dansyl chloride: Like DNF, dansyl chloride reacts with the N-terminal residue under alkaline conditions. Analysis of the modified amino acids is carried out similarly to the Sanger ...
... comparison with the migration of DNP-derivative standards allows for the identification of the N-terminal amino acid. Dansyl chloride: Like DNF, dansyl chloride reacts with the N-terminal residue under alkaline conditions. Analysis of the modified amino acids is carried out similarly to the Sanger ...
Assigning and Using Oxidation Numbers in Biochemistry Lecture
... think about this question is that NADH, which is also produced in the conversion of glucose to pyruvate, must be reoxidized to NAD+ for anaerobic metabolism to operate. Pyruvate, which is the product of glycolysis, can be reduced by NADH to lactate or can be decarboxylated to ethanal and CO2 (the et ...
... think about this question is that NADH, which is also produced in the conversion of glucose to pyruvate, must be reoxidized to NAD+ for anaerobic metabolism to operate. Pyruvate, which is the product of glycolysis, can be reduced by NADH to lactate or can be decarboxylated to ethanal and CO2 (the et ...
The Metabolism of Acetate by the Blue-green Algae
... other than carbon dioxide has been noted by many workers. Exceptions to this statement include Tolypothrix tenius, the growth of which is stimulated by glucose (Kiyohara et al. 1960; 1962) and ChlorogZoc.n.fi.itscliii, which has been reported to grow in the dark on sLicrose albeit the growth rate wa ...
... other than carbon dioxide has been noted by many workers. Exceptions to this statement include Tolypothrix tenius, the growth of which is stimulated by glucose (Kiyohara et al. 1960; 1962) and ChlorogZoc.n.fi.itscliii, which has been reported to grow in the dark on sLicrose albeit the growth rate wa ...
Urinary Amino Acids Profile of Vegetarians and Non
... common amino acids detected in the young and elderly individuals on vegetarian and non-vegetarian diets were phenylalanine, threonine, arginine and asparagine, while leucine, aspartic acid and alanine were not found in any urine samples in both groups. Isoleucine was not detected in the urine of veg ...
... common amino acids detected in the young and elderly individuals on vegetarian and non-vegetarian diets were phenylalanine, threonine, arginine and asparagine, while leucine, aspartic acid and alanine were not found in any urine samples in both groups. Isoleucine was not detected in the urine of veg ...
Energy - Exercise Sciences!
... membrane transport mechanisms, and changes in substrate availability (a) Enzymes—inactivate rate limiting enzymes (b) Membranes—affect carriers in membrane or permeability of the membrane (c) Substrate—glycogen breakdown to glucose is slowed and fatty acid utilization is decreased. Use of phosphocre ...
... membrane transport mechanisms, and changes in substrate availability (a) Enzymes—inactivate rate limiting enzymes (b) Membranes—affect carriers in membrane or permeability of the membrane (c) Substrate—glycogen breakdown to glucose is slowed and fatty acid utilization is decreased. Use of phosphocre ...
Cerebral Energy Metabolism in Hepatic Encephalopathy and
... Levels of high energy metabolites such as ATP and phosphocreatine were found to decrease in animal models of HE. Hindfelt et al. (1977) reported a moderate fall in phosphocreatine and ATP levels in portacaval-shunted rats infused with ammonia. More recently, decreased phosphocreatine and nucleotide ...
... Levels of high energy metabolites such as ATP and phosphocreatine were found to decrease in animal models of HE. Hindfelt et al. (1977) reported a moderate fall in phosphocreatine and ATP levels in portacaval-shunted rats infused with ammonia. More recently, decreased phosphocreatine and nucleotide ...
Full Text - Harvard University
... were evaluated with paired Student t tests, cluster-based analyses, and multivariable linear regression to examine differences associated with insulin resistance. Of 110 metabolites tested, 91 significantly changed with OGTT (P # 0.0005 for all). Amino acids, b-hydroxybutyrate, and tricarboxylic acid ...
... were evaluated with paired Student t tests, cluster-based analyses, and multivariable linear regression to examine differences associated with insulin resistance. Of 110 metabolites tested, 91 significantly changed with OGTT (P # 0.0005 for all). Amino acids, b-hydroxybutyrate, and tricarboxylic acid ...
Glycogen Storage Disease
... responsible for creating glycogen from glucose, transporting the glycogen to and from storage areas within cells, and extracting glucose from the glycogen as needed. • Both creating and tearing down the glycogen macromolecule are multistep processes requiring a different enzyme at each step. • If on ...
... responsible for creating glycogen from glucose, transporting the glycogen to and from storage areas within cells, and extracting glucose from the glycogen as needed. • Both creating and tearing down the glycogen macromolecule are multistep processes requiring a different enzyme at each step. • If on ...
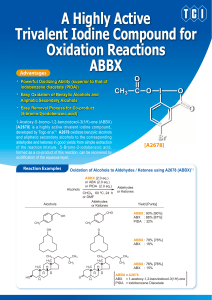
A Highly Active Trivalent Iodine Compound for
... A Highly Active Trivalent Iodine Compound for Oxidation Reactions ABBX ...
... A Highly Active Trivalent Iodine Compound for Oxidation Reactions ABBX ...
- Wiley Online Library
... growth to anaerobic dormancy. What might this physiological role be? Alanine dehydrogenase from M. tuberculosis catalyses the reductive amination of pyruvate at physiological pH [12,13]. To demonstrate that the M. smegmatis enzyme shows similar pH dependence, activity measurements at various pHs (pH ...
... growth to anaerobic dormancy. What might this physiological role be? Alanine dehydrogenase from M. tuberculosis catalyses the reductive amination of pyruvate at physiological pH [12,13]. To demonstrate that the M. smegmatis enzyme shows similar pH dependence, activity measurements at various pHs (pH ...
studies in the dielectric constants of fatty acids
... physical properties have been reported in Iiterature. ' Fatty acids offer a promising field for the study of the correlation between structure and the dielectric constant. Polar liquids are known to form association complexes by dipolar interaction. A precise knowledge of the nature and the extent o ...
... physical properties have been reported in Iiterature. ' Fatty acids offer a promising field for the study of the correlation between structure and the dielectric constant. Polar liquids are known to form association complexes by dipolar interaction. A precise knowledge of the nature and the extent o ...
Solution - gearju.com
... A 0.5662-g sample of an ionic compound containing chloride ions and an unknown metal is dissolved in water and treated with an excess of AgNO3. If 1.0882 g of AgCl precipitate forms, what is the percent by mass of Cl in the original compound? ...
... A 0.5662-g sample of an ionic compound containing chloride ions and an unknown metal is dissolved in water and treated with an excess of AgNO3. If 1.0882 g of AgCl precipitate forms, what is the percent by mass of Cl in the original compound? ...
A new simple fluorimetric method to assay cytosolic ATP content
... seedlings (Petrussa et al. 2001; Chiandussi et al. 2002; Casolo et al. 2003; Petrussa et al. 2004), soybean cell cultures (Casolo et al. 2005), embryogenic cultures of Picea abies (L.) Karst., Abies cephalonica Loud (Petrussa et al. 2008a), Abies alba Mill. (Petrussa et al. 2009), and Arum spadix an ...
... seedlings (Petrussa et al. 2001; Chiandussi et al. 2002; Casolo et al. 2003; Petrussa et al. 2004), soybean cell cultures (Casolo et al. 2005), embryogenic cultures of Picea abies (L.) Karst., Abies cephalonica Loud (Petrussa et al. 2008a), Abies alba Mill. (Petrussa et al. 2009), and Arum spadix an ...
Oxidation and Synthesis of Fatty Acids in Soluble Enzyme Systems
... The fatty acyl CoA is oxidized by a flavoprotein enzyme to the corresponding a-fl unsaturated acyl CoA derivative (25). In turn this unsaturated derivative is hydrated to form the L configurational fi-hydroxyacyl CoA (32). Then a second oxidation takes place at the fl-carbon atom leading to the form ...
... The fatty acyl CoA is oxidized by a flavoprotein enzyme to the corresponding a-fl unsaturated acyl CoA derivative (25). In turn this unsaturated derivative is hydrated to form the L configurational fi-hydroxyacyl CoA (32). Then a second oxidation takes place at the fl-carbon atom leading to the form ...
CERTIFICATE OF HIGHER EDUCATION IN COSMETIC SCIENCE
... droplet on the surface of the substrate. In your answer make consideration of the relevance of the contact angle to the removal of the oil droplet from the substrate. What conditions must be met in order for the oily soil to detach from the substrate? ( 8 Marks) d) Although non-ionic surfactants are ...
... droplet on the surface of the substrate. In your answer make consideration of the relevance of the contact angle to the removal of the oil droplet from the substrate. What conditions must be met in order for the oily soil to detach from the substrate? ( 8 Marks) d) Although non-ionic surfactants are ...
The Inherited Metabolic Disorders News
... PDCD is a rare disorder. Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) is an essential and important enzyme in the mitochondrial metabolism. The effects of this deficiency are serious as there is a lack of energy production and build up of lactic acid. PDH catalyzes the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA (Fig 1). W ...
... PDCD is a rare disorder. Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) is an essential and important enzyme in the mitochondrial metabolism. The effects of this deficiency are serious as there is a lack of energy production and build up of lactic acid. PDH catalyzes the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA (Fig 1). W ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.