Enzymes
... The reaction catalyzed by lysozyme is the hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond of the (NAM-NAG)n heteropolymer that is the backbone of the bacterial cell wall. The enzyme is specific for NAMNAG glycosidic bonds (β-1,4 conformation). ...
... The reaction catalyzed by lysozyme is the hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond of the (NAM-NAG)n heteropolymer that is the backbone of the bacterial cell wall. The enzyme is specific for NAMNAG glycosidic bonds (β-1,4 conformation). ...
BONUS: Which line in the above graph represents G for the reaction
... 6. In which reaction will an increase in total pressure at constant temperature favor formation of the products? ...
... 6. In which reaction will an increase in total pressure at constant temperature favor formation of the products? ...
Pancreas
... 1) fatty acid (18 C) + coenzyme A 2) fatty acid (18 C)-coA 3) fatty acid (16 C) and acetyl-coA Acetyl-CoA used in citric acid cycle This reaction also yields NADH => electron transport chain Excess acetyl-CoA forms ketone bodies ...
... 1) fatty acid (18 C) + coenzyme A 2) fatty acid (18 C)-coA 3) fatty acid (16 C) and acetyl-coA Acetyl-CoA used in citric acid cycle This reaction also yields NADH => electron transport chain Excess acetyl-CoA forms ketone bodies ...
Resume - TILT - Colorado State University
... C-H oxidation at the internal position of terminal olefins was carried out with new category of sulfoxide ligand leading to high selectivity over wacker product or linear product. Varies substrates and carboxylic acids were successfully used leading to 60-85 % yield (of biologically important compou ...
... C-H oxidation at the internal position of terminal olefins was carried out with new category of sulfoxide ligand leading to high selectivity over wacker product or linear product. Varies substrates and carboxylic acids were successfully used leading to 60-85 % yield (of biologically important compou ...
Acids - Beck-Shop
... 2 Add the other solution to a burette, and record the initial burette reading to the nearest 0.05 cm3. 3 Add a few drops of an indicator to the solution in the conical flask. 4 Run the solution in the burette into the solution in the conical flask, swirling the conical flask throughout to mix the ...
... 2 Add the other solution to a burette, and record the initial burette reading to the nearest 0.05 cm3. 3 Add a few drops of an indicator to the solution in the conical flask. 4 Run the solution in the burette into the solution in the conical flask, swirling the conical flask throughout to mix the ...
vitamins ( PPT )
... humans made us unable to make ascorbic acid. So for us, and some closely related primates, it’s a vitamin. Guinea pigs can’t make ascorbic acid, either. Sources of vitamin C are fruit and fresh meat. Vitamin C deficiency causes scurvy, and in human history vitamin C deficiency may have been an imped ...
... humans made us unable to make ascorbic acid. So for us, and some closely related primates, it’s a vitamin. Guinea pigs can’t make ascorbic acid, either. Sources of vitamin C are fruit and fresh meat. Vitamin C deficiency causes scurvy, and in human history vitamin C deficiency may have been an imped ...
Chapter 29 The Organic Chemistry of Metabolic Pathways
... Sugars and fat components are broken down in steps ...
... Sugars and fat components are broken down in steps ...
Properties and Kinetic Analysis of UDP
... noethylcellulose that had been preequilibrated with buffer A. The column was washed with buffer A (50 ml) and then eluted with buffer A containing 200 mM NaCl (50 ml). Active fractions were pooled and concentrated (to 6.7 ml) using Centriprep-10 concentrators and dialyzed against 1 liter of buffer B ...
... noethylcellulose that had been preequilibrated with buffer A. The column was washed with buffer A (50 ml) and then eluted with buffer A containing 200 mM NaCl (50 ml). Active fractions were pooled and concentrated (to 6.7 ml) using Centriprep-10 concentrators and dialyzed against 1 liter of buffer B ...
Chapter 29 The Organic Chemistry of Metabolic Pathways
... Sugars and fat components are broken down in steps ...
... Sugars and fat components are broken down in steps ...
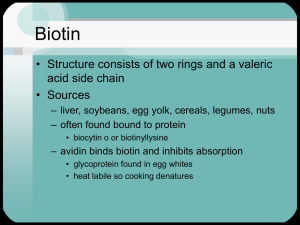
PowerPoint Presentation - Biotin Conclusion and Discussion
... • if surplus of ATP, gluconeogenic pathway • if deficiency of ATP, TCA cycle ...
... • if surplus of ATP, gluconeogenic pathway • if deficiency of ATP, TCA cycle ...
Acid–Base Physiology
... This 21-year-old man with type I diabetes (insulin deficiency) has the clinical manifestations of DKA. The first priorities are always the ABCs: Because the airways and breathing are normal, the focus in this case is on the circulation. Two large-bore IV lines should be placed, and the patient shoul ...
... This 21-year-old man with type I diabetes (insulin deficiency) has the clinical manifestations of DKA. The first priorities are always the ABCs: Because the airways and breathing are normal, the focus in this case is on the circulation. Two large-bore IV lines should be placed, and the patient shoul ...
41 Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism
... acids. These molecules can be synthesized either from scratch, de novo, or salvaged from existing bases. Dietary uptake of purine and pyrimidine bases is low, because most of the ingested nucleic acids are metabolized by the intestinal epithelial cells. The de novo pathway of purine synthesis is com ...
... acids. These molecules can be synthesized either from scratch, de novo, or salvaged from existing bases. Dietary uptake of purine and pyrimidine bases is low, because most of the ingested nucleic acids are metabolized by the intestinal epithelial cells. The de novo pathway of purine synthesis is com ...
Hydrothermal experiments in the system citric acid, H2O-( FeS)
... Abstract—Recent theories have proposed that life arose from primitive hydrothermal environments employing chemical reactions analogous to the reductive citrate cycle (RCC) as the primary pathway for carbon fixation. This chemistry is presumed to have developed as a natural consequence of the intrins ...
... Abstract—Recent theories have proposed that life arose from primitive hydrothermal environments employing chemical reactions analogous to the reductive citrate cycle (RCC) as the primary pathway for carbon fixation. This chemistry is presumed to have developed as a natural consequence of the intrins ...
to the full text - David Moore`s World of Fungi: where
... Cellobiose oxidase is able to oxidise cellobiose to the δ-lactone, which can then be converted to cellobionic acid and then glucose + gluconic acid; cellobiose δ-lactone can also be formed by the enzyme cellobiose: quinone oxidoreductase. Similar cellobiose-oxidizing enzymes, capable of utilizing a ...
... Cellobiose oxidase is able to oxidise cellobiose to the δ-lactone, which can then be converted to cellobionic acid and then glucose + gluconic acid; cellobiose δ-lactone can also be formed by the enzyme cellobiose: quinone oxidoreductase. Similar cellobiose-oxidizing enzymes, capable of utilizing a ...
fulltext
... adenosinediphospho-D-glucose (ADP-D-Glc), cytidinediphospho-D-glucose (CDP-D-Glc), guanidinediphospho-D-glucose (GDPD-Glc), and uridinediphospho-D-glucose (UDP-D-Glc) (Figure 5). The reaction is catalysed by suitable nucleotidylyltransferases that have an important role not only for the initial acti ...
... adenosinediphospho-D-glucose (ADP-D-Glc), cytidinediphospho-D-glucose (CDP-D-Glc), guanidinediphospho-D-glucose (GDPD-Glc), and uridinediphospho-D-glucose (UDP-D-Glc) (Figure 5). The reaction is catalysed by suitable nucleotidylyltransferases that have an important role not only for the initial acti ...
Crude protein and amino acids content in some common
... Furthermore, the optimum dietary protein level for E. malabaricus was ranged from 40% to 50 (Teng et al 1978). In addition, humpback grouper (Cromileptes altivelis (Valenciennes, 1828)) and Malabar grouper (E. malabaricus) required a dietary protein of 51% and 55%, respectively (Usman et al 2005; Tu ...
... Furthermore, the optimum dietary protein level for E. malabaricus was ranged from 40% to 50 (Teng et al 1978). In addition, humpback grouper (Cromileptes altivelis (Valenciennes, 1828)) and Malabar grouper (E. malabaricus) required a dietary protein of 51% and 55%, respectively (Usman et al 2005; Tu ...
Energy Transformation — Cellular Respiration
... 1. The ATP produced during glycolysis is insufficient to sustain life processes. As a result, molecular oxygen has to appear to supply a bulk of ATP (almost 90%) to the body cells. Hence, most cells of multicellular organisms cannot live long without oxygen, especially the human brain cells which ca ...
... 1. The ATP produced during glycolysis is insufficient to sustain life processes. As a result, molecular oxygen has to appear to supply a bulk of ATP (almost 90%) to the body cells. Hence, most cells of multicellular organisms cannot live long without oxygen, especially the human brain cells which ca ...
Cellular Respiration
... 12. What is the yield of ATP molecules from glycolysis? a. 2 b. 4 c. 36 d. None 13. Which statement about anaerobic/fermentation is true? a. A lot of energy is produced. b. Occurs in the presence of O2. c. Lactic acid or alcohol is produced. d. Includes the Citric Acid/Krebs cycle. 14. Why do large ...
... 12. What is the yield of ATP molecules from glycolysis? a. 2 b. 4 c. 36 d. None 13. Which statement about anaerobic/fermentation is true? a. A lot of energy is produced. b. Occurs in the presence of O2. c. Lactic acid or alcohol is produced. d. Includes the Citric Acid/Krebs cycle. 14. Why do large ...
In vivo analysis of straight-chain and branched
... very high level of intact butyrate incorporation is, however, more consistent with the direct utilization of butyryl-CoA for fatty acid biosynthesis using either a Type I or Type II fatty acid synthase (Fig. 1). In contrast, a low level of intact hexanoate incorporation into the straight-chain fatty ...
... very high level of intact butyrate incorporation is, however, more consistent with the direct utilization of butyryl-CoA for fatty acid biosynthesis using either a Type I or Type II fatty acid synthase (Fig. 1). In contrast, a low level of intact hexanoate incorporation into the straight-chain fatty ...
Chapter 4
... metabolism as exercise intensity increases – Due to: • Recruitment of muscle fibers that need fuel quickly • Increasing blood levels of epinephrine that ...
... metabolism as exercise intensity increases – Due to: • Recruitment of muscle fibers that need fuel quickly • Increasing blood levels of epinephrine that ...
Sequence Specific Modeling of E. coli Cell-Free Protein
... (17, 22) and protein structures (GEM-PRO) (23, 24). These expansions have greatly increased the scope of questions these models can explore. Thus, constraint based methods are powerful tools to estimate the performance of metabolic networks with very few adjustable parameters. However, constraint ba ...
... (17, 22) and protein structures (GEM-PRO) (23, 24). These expansions have greatly increased the scope of questions these models can explore. Thus, constraint based methods are powerful tools to estimate the performance of metabolic networks with very few adjustable parameters. However, constraint ba ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.