Ch 16.4 Enzymes and rest
... Lyases: (Add/Remove groups with double bonds Isomerases: rearrange to form isomers (cis/trans) Ligases: connect molecules using ATP (DNA strands in replication) ...
... Lyases: (Add/Remove groups with double bonds Isomerases: rearrange to form isomers (cis/trans) Ligases: connect molecules using ATP (DNA strands in replication) ...
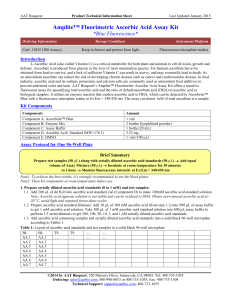
13835_Amplite™ Fluorimetric Ascorbic Acid Assay
... Note: Ascorbic acid aqueous solution is not stable and can be oxidized to DHA. Please store unused ascorbic acid at 20 oC, avoid light and repeated freeze-thaw cycles. 1.2 Prepare ascorbic acid standard dilutions: Add 10 μL of 100 mM ascorbic acid (from step 1.1) into 990 μL of assay buffer to get 1 ...
... Note: Ascorbic acid aqueous solution is not stable and can be oxidized to DHA. Please store unused ascorbic acid at 20 oC, avoid light and repeated freeze-thaw cycles. 1.2 Prepare ascorbic acid standard dilutions: Add 10 μL of 100 mM ascorbic acid (from step 1.1) into 990 μL of assay buffer to get 1 ...
Unit 20C Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... at the first trophic level in a food web (producers) capture solar energy and then store it as chemical energy in the bonds of glucose molecules. This energy is eventually passed to other organisms in the food web. All organisms, including those that carry out photosynthesis, release the energy in g ...
... at the first trophic level in a food web (producers) capture solar energy and then store it as chemical energy in the bonds of glucose molecules. This energy is eventually passed to other organisms in the food web. All organisms, including those that carry out photosynthesis, release the energy in g ...
" Vitamins "
... Vitamins are organic nutrients (molecules), that are required in small quantities for a variety of biochemical functions,(the most prominent ...
... Vitamins are organic nutrients (molecules), that are required in small quantities for a variety of biochemical functions,(the most prominent ...
Enzyme kinetics and its relevance to enzyme assay
... Not all enzymes can be measured quite so simply as lactate dehydrogenase or alkaline phosphatase, and numerous procedures have been devised in which the test reaction is coupled with one or more auxiliary or indicator reactions. Perhaps the best known of these is the spectrophotometric method for se ...
... Not all enzymes can be measured quite so simply as lactate dehydrogenase or alkaline phosphatase, and numerous procedures have been devised in which the test reaction is coupled with one or more auxiliary or indicator reactions. Perhaps the best known of these is the spectrophotometric method for se ...
Generation of adenosine tri-phosphate in Leishmania
... from phoshoenolpyruvate. Evidence also suggests that the activity of these enzymes are comparatively higher in the amastigotes. Such a pathway could provide dicarboxylic acids for biosynthetic processes and also contributed to NADP+ recycling. Amastigote cells continuously excrete relatively large q ...
... from phoshoenolpyruvate. Evidence also suggests that the activity of these enzymes are comparatively higher in the amastigotes. Such a pathway could provide dicarboxylic acids for biosynthetic processes and also contributed to NADP+ recycling. Amastigote cells continuously excrete relatively large q ...
Chapter 6
... Energy from Carbohydrates • When glucose is transported to the liver, it is: • Phosphorylated and metabolized for energy or stored as glycogen • Released into circulation for other cells to use as fuel or stored as glycogen (muscle tissue) • Converted to fatty acids, if glucose exceeds energy needs ...
... Energy from Carbohydrates • When glucose is transported to the liver, it is: • Phosphorylated and metabolized for energy or stored as glycogen • Released into circulation for other cells to use as fuel or stored as glycogen (muscle tissue) • Converted to fatty acids, if glucose exceeds energy needs ...
Structure of ATP-Bound Human ATP:Cobalamin
... cobalamin analogue treatments (13). These inborn errors in vitamin B12 metabolism have been categorized into eight complementation classes, cblABCDEFG and mut (14, 15). Loss of AdoCbl results in methylmalonic aciduria (MMA), a buildup of methylmalonic acid in body fluids, including blood and urine ( ...
... cobalamin analogue treatments (13). These inborn errors in vitamin B12 metabolism have been categorized into eight complementation classes, cblABCDEFG and mut (14, 15). Loss of AdoCbl results in methylmalonic aciduria (MMA), a buildup of methylmalonic acid in body fluids, including blood and urine ( ...
Gellan-related polysaccharides and the genus
... 10 g Bacto tryptone, 5 g Bacto yeast extract and 10 g NaCl per litre of water. All Bacto products were from Difco. YM medium contained 3 g Bacto yeast extract, 3 g Bacto malt extract, 5 g Bacto peptone and 10 g Bacto dextrose per litre of water. M9 medium contained 6 g Na,HPO,, 3 g KH,PO,, 0-5 g NaC ...
... 10 g Bacto tryptone, 5 g Bacto yeast extract and 10 g NaCl per litre of water. All Bacto products were from Difco. YM medium contained 3 g Bacto yeast extract, 3 g Bacto malt extract, 5 g Bacto peptone and 10 g Bacto dextrose per litre of water. M9 medium contained 6 g Na,HPO,, 3 g KH,PO,, 0-5 g NaC ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... The visible spectra of solutions of two transition metal complexes C and D are shown in the diagram below. ...
... The visible spectra of solutions of two transition metal complexes C and D are shown in the diagram below. ...
m5zn_a9c640ccbe96115
... c) Myoglubin . d) Nothing . 51) Alpha helix differ from Beta sheet by……………………… a) H-bond exbend parallel to backbone . b) H-bond exbend vertical to backbone . c) Have only one polypeptide chain . d) A & C . 52) In alpha helix the H-bond performed between the carbonyl oxygen and.. a) Hydrogen of side ...
... c) Myoglubin . d) Nothing . 51) Alpha helix differ from Beta sheet by……………………… a) H-bond exbend parallel to backbone . b) H-bond exbend vertical to backbone . c) Have only one polypeptide chain . d) A & C . 52) In alpha helix the H-bond performed between the carbonyl oxygen and.. a) Hydrogen of side ...
Gellan-related polysaccharides and the genus
... 10 g Bacto tryptone, 5 g Bacto yeast extract and 10 g NaCl per litre of water. All Bacto products were from Difco. YM medium contained 3 g Bacto yeast extract, 3 g Bacto malt extract, 5 g Bacto peptone and 10 g Bacto dextrose per litre of water. M9 medium contained 6 g Na,HPO,, 3 g KH,PO,, 0-5 g NaC ...
... 10 g Bacto tryptone, 5 g Bacto yeast extract and 10 g NaCl per litre of water. All Bacto products were from Difco. YM medium contained 3 g Bacto yeast extract, 3 g Bacto malt extract, 5 g Bacto peptone and 10 g Bacto dextrose per litre of water. M9 medium contained 6 g Na,HPO,, 3 g KH,PO,, 0-5 g NaC ...
my handy vitamin review
... Required for collagen synthesis, and as a cofactor for several enzymes. Also scavenges oxygen radicals. In almost all organisms, ascorbic acid is synthesized from glucose in 4 steps. A relatively recent (40 million years ago) mutation in the ancestor of humans made us unable to make ascorbic acid. S ...
... Required for collagen synthesis, and as a cofactor for several enzymes. Also scavenges oxygen radicals. In almost all organisms, ascorbic acid is synthesized from glucose in 4 steps. A relatively recent (40 million years ago) mutation in the ancestor of humans made us unable to make ascorbic acid. S ...
1063-1069 - Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences
... The study of the lipid fraction of the aerial parts of the B. grandiflora extract resulted in the identification of the unsaponifiable matters as well as fatty acid mixture. The GLC analysis of the unsaponifiable fraction, Table (1) revealed the presence of a mixture of a hydrocarbon fraction rangin ...
... The study of the lipid fraction of the aerial parts of the B. grandiflora extract resulted in the identification of the unsaponifiable matters as well as fatty acid mixture. The GLC analysis of the unsaponifiable fraction, Table (1) revealed the presence of a mixture of a hydrocarbon fraction rangin ...
Amino Acid Catabolism: N
... available a-keto acids, transaminases funnel amino groups from excess dietary amino acids to those amino acids (e.g., glutamate) that can be deaminated. Carbon skeletons of deaminated amino acids can be catabolized for energy, or used to synthesize glucose or fatty acids for energy storage. Only a f ...
... available a-keto acids, transaminases funnel amino groups from excess dietary amino acids to those amino acids (e.g., glutamate) that can be deaminated. Carbon skeletons of deaminated amino acids can be catabolized for energy, or used to synthesize glucose or fatty acids for energy storage. Only a f ...
File
... lowers activation energy: Accept any of the above if clearly explained in a labelled diagram. ...
... lowers activation energy: Accept any of the above if clearly explained in a labelled diagram. ...
Slide 1
... Carbon enters the biota through photosynthesis and then returned by respiration or fire ...
... Carbon enters the biota through photosynthesis and then returned by respiration or fire ...
Endoproteinase pro-C-catalyzed peptide bond
... With the exception of H-Pro-NH2 which was not accepted at all, the aromatic amino acid amides and H-ArgNH2, freezing the reaction mixture resulted in significantly higher peptide yields. The yield-enhancing effect of freezing has been attributed to the concentration of the reactants in the unfrozen ...
... With the exception of H-Pro-NH2 which was not accepted at all, the aromatic amino acid amides and H-ArgNH2, freezing the reaction mixture resulted in significantly higher peptide yields. The yield-enhancing effect of freezing has been attributed to the concentration of the reactants in the unfrozen ...
A Strongly Inwardly Rectifying K+ Channel that Is Sensitive to ATP
... Of the five known types of ATP-sensitive channels (reviewed by Ashcroft and Ashcroft, 1990), Types l-3 are Kf-selective. Type 1 ATP-sensitive K+ channels (Noma, 1983), such as the ATPsensitive K+ channels found in pancreas, heart, and skeletal muscle, appear to be members of the family of inwardly r ...
... Of the five known types of ATP-sensitive channels (reviewed by Ashcroft and Ashcroft, 1990), Types l-3 are Kf-selective. Type 1 ATP-sensitive K+ channels (Noma, 1983), such as the ATPsensitive K+ channels found in pancreas, heart, and skeletal muscle, appear to be members of the family of inwardly r ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... coenzyme (19.7) an organic group required by some enzymes; generally a donor or acceptor of electrons or functional groups in a reaction. cofactor (19.7) metal ions, organic compounds, or organometallic compounds that must be bound to an apoenzyme to maintain the correct configuration of the active ...
... coenzyme (19.7) an organic group required by some enzymes; generally a donor or acceptor of electrons or functional groups in a reaction. cofactor (19.7) metal ions, organic compounds, or organometallic compounds that must be bound to an apoenzyme to maintain the correct configuration of the active ...
Branched chain aldehydes: production and breakdown pathways
... Bockelmann et al. 2006). The increase of amino acids in cheese curd, obtained by the application of peptidase overproducing starter cultures, not only leads to increased flavour perception due to the flavour of the amino acids themselves but also to increased levels of amino acid derived flavour com ...
... Bockelmann et al. 2006). The increase of amino acids in cheese curd, obtained by the application of peptidase overproducing starter cultures, not only leads to increased flavour perception due to the flavour of the amino acids themselves but also to increased levels of amino acid derived flavour com ...
Regeneration of Cofactors for Enzyme Biocatalysis
... in the cell-free system will eventually inhibit protein synthesis and uncoupled enzymes in the cell extracts would degrade the phosphoryl regeneration substrates (Kim & Swartz 2001). This novel ATP regeneration approach takes advantage of the enzymes normally present in cell extracts, and rather tha ...
... in the cell-free system will eventually inhibit protein synthesis and uncoupled enzymes in the cell extracts would degrade the phosphoryl regeneration substrates (Kim & Swartz 2001). This novel ATP regeneration approach takes advantage of the enzymes normally present in cell extracts, and rather tha ...
A SOLUBLE RIBONUCLEIC ACID INTERMEDIATE IN PROTEIN
... The cell-free rat liver system in which Cl*-amino acids are incorporated irreversibly into cY-peptide linkage in protein has been used in our laboratories for a number of years as a measure of protein synthesis. The essential components of this system are the microsomal ribonucleoprotein particles, ...
... The cell-free rat liver system in which Cl*-amino acids are incorporated irreversibly into cY-peptide linkage in protein has been used in our laboratories for a number of years as a measure of protein synthesis. The essential components of this system are the microsomal ribonucleoprotein particles, ...
eprint_1_29837_493
... a. do not alter the reaction equilibrium b. not consumed in overall reaction c. required only in very small quantities. 3. They have enormous power for catalysis . 4. Enzymes are highly specific for their substrate . 5. Enzymes possess active sites at which interaction with substrate takes place . 6 ...
... a. do not alter the reaction equilibrium b. not consumed in overall reaction c. required only in very small quantities. 3. They have enormous power for catalysis . 4. Enzymes are highly specific for their substrate . 5. Enzymes possess active sites at which interaction with substrate takes place . 6 ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.