OXIDATIVE STRESS IN PLANTS Ever since the introduction of
... ROI play a central role in the defense of plants against pathogens. During this response, ROI are produced by plant cells via the enhanced enzymatic activity of plasma membrane-bound NADPH oxidases, cell wall-bound peroxidases and amine oxidases in the apoplast. H2O2 produced during this response is ...
... ROI play a central role in the defense of plants against pathogens. During this response, ROI are produced by plant cells via the enhanced enzymatic activity of plasma membrane-bound NADPH oxidases, cell wall-bound peroxidases and amine oxidases in the apoplast. H2O2 produced during this response is ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... – Incorrect amino acids change a protein’s structure and function. – Denaturation occurs when a protein A protein is denatured when it loses its shape and ability to function due to heat, a change in pH, or some ...
... – Incorrect amino acids change a protein’s structure and function. – Denaturation occurs when a protein A protein is denatured when it loses its shape and ability to function due to heat, a change in pH, or some ...
Mitochondrial Cytopathies: A Primer
... Threshold expression: All tissues require ATP to survive. Some tissues require a greater flux of ATP production and utilizatioin, and therefore require the integrity of the ox-phos enzyme system. Cellular dysfunction will occur if not enough ATP can be generated. The tissues most affected are those ...
... Threshold expression: All tissues require ATP to survive. Some tissues require a greater flux of ATP production and utilizatioin, and therefore require the integrity of the ox-phos enzyme system. Cellular dysfunction will occur if not enough ATP can be generated. The tissues most affected are those ...
7 Fig. 1. "Double-sieve" (two- step subtrate selection - SPring-8
... ones, such as L-valine, are strictly eliminated at the hydrolytic editing site by the "second, fine sieve." (Fig. 1). In ValRS, amino acids larger than the cognate L-valine are excluded in the first sieve, and smaller (or isosteric) and hydrophilic ones, such as L-threonine, are eliminated in the se ...
... ones, such as L-valine, are strictly eliminated at the hydrolytic editing site by the "second, fine sieve." (Fig. 1). In ValRS, amino acids larger than the cognate L-valine are excluded in the first sieve, and smaller (or isosteric) and hydrophilic ones, such as L-threonine, are eliminated in the se ...
Supplementary Data - American Diabetes Association
... for plasma CRH and Cortisol EIA kit (Cayman, Ann Arbor, MI) for plasma cortisol. Homeostasis model assessment of insulin sensitivity (HOMA-IS) was calculated using the following equations: HOMA-IS = 1/ (plasma insulin (mIU/L) × plasma glucose (mM))(1). Assays of rat plasma Plasma glucose was analyze ...
... for plasma CRH and Cortisol EIA kit (Cayman, Ann Arbor, MI) for plasma cortisol. Homeostasis model assessment of insulin sensitivity (HOMA-IS) was calculated using the following equations: HOMA-IS = 1/ (plasma insulin (mIU/L) × plasma glucose (mM))(1). Assays of rat plasma Plasma glucose was analyze ...
Acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase – an attractive enzyme for biotechnolo
... human cellular homeostasis, which results from differences in genes regulation, proteins activity and product allocation. The cytosolic ACC1 produces malonyl-CoA for FAS and, therefore, both enzyme activity and gene transcription are increased under anabolic conditions. The mitochondria-associated A ...
... human cellular homeostasis, which results from differences in genes regulation, proteins activity and product allocation. The cytosolic ACC1 produces malonyl-CoA for FAS and, therefore, both enzyme activity and gene transcription are increased under anabolic conditions. The mitochondria-associated A ...
Acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase – an attractive enzyme for biotechnolo
... human cellular homeostasis, which results from differences in genes regulation, proteins activity and product allocation. The cytosolic ACC1 produces malonyl-CoA for FAS and, therefore, both enzyme activity and gene transcription are increased under anabolic conditions. The mitochondria-associated A ...
... human cellular homeostasis, which results from differences in genes regulation, proteins activity and product allocation. The cytosolic ACC1 produces malonyl-CoA for FAS and, therefore, both enzyme activity and gene transcription are increased under anabolic conditions. The mitochondria-associated A ...
Fritz Lipmann - Nobel Lecture
... there towards a general concept of transfer of activated groupings by carrier as the fundamental reaction in biosynthesis8,9. Although in the related manner the appearance of acetyl phosphate as a metabolic intermediary first focussed attention to possible mechanisms for the metabolic elaboration of ...
... there towards a general concept of transfer of activated groupings by carrier as the fundamental reaction in biosynthesis8,9. Although in the related manner the appearance of acetyl phosphate as a metabolic intermediary first focussed attention to possible mechanisms for the metabolic elaboration of ...
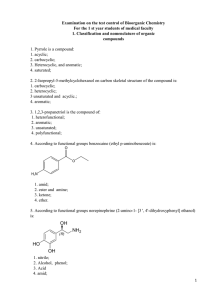
2. 2-Isopropyl-5-methylcyclohexanol on carbon skeletal
... 24. The conformations of 1-chloropropane with a torsion angle of 60˚ and 300˚ are degenerate, because in these conformations the molecule have: 1. same configuration; 2. same chemical structure; 3. different conformational structure; 4. same torsion, Van der Waals and angular stresses; 25. The molec ...
... 24. The conformations of 1-chloropropane with a torsion angle of 60˚ and 300˚ are degenerate, because in these conformations the molecule have: 1. same configuration; 2. same chemical structure; 3. different conformational structure; 4. same torsion, Van der Waals and angular stresses; 25. The molec ...
Organotins-promoted peroxidation of unsaturated fatty acids: A new
... meso-tetraphenylporphyrin (TPPH2 )) has been studied. The monitoring of the unsaturated acid peroxidation level has been performed by the determination of the total concentration of isomeric hydroperoxides as well as of the thiobarbituric acid reactive substances, as markers of carbonyl compounds fo ...
... meso-tetraphenylporphyrin (TPPH2 )) has been studied. The monitoring of the unsaturated acid peroxidation level has been performed by the determination of the total concentration of isomeric hydroperoxides as well as of the thiobarbituric acid reactive substances, as markers of carbonyl compounds fo ...
3 | biological macromolecules
... that a low-carbohydrate diet helps people to lose weight faster. However, carbohydrates have been an important part of the human diet for thousands of years; artifacts from ancient civilizations show the presence of wheat, rice, and corn in our ancestors’ storage areas. Carbohydrates should be suppl ...
... that a low-carbohydrate diet helps people to lose weight faster. However, carbohydrates have been an important part of the human diet for thousands of years; artifacts from ancient civilizations show the presence of wheat, rice, and corn in our ancestors’ storage areas. Carbohydrates should be suppl ...
Enzymes - CEA Workshop Teacher Notes.pptx
... to assist enzyme acJvity • A coenzyme will bind to a protein to form an acJve enzyme • Coenzymes osen help by carrying a group of atoms to the acJve site which are then transferred to the su ...
... to assist enzyme acJvity • A coenzyme will bind to a protein to form an acJve enzyme • Coenzymes osen help by carrying a group of atoms to the acJve site which are then transferred to the su ...
Full text
... to oxidation by free radicals. Dietary supplementation with selenium in animals increased selenium content in several tissues. The antioxidant effect of selenium on lipid peroxidation, enzyme activities and biochemical parameters might be beneficial in antagonizing aluminum toxicity [1]. Oral nutrit ...
... to oxidation by free radicals. Dietary supplementation with selenium in animals increased selenium content in several tissues. The antioxidant effect of selenium on lipid peroxidation, enzyme activities and biochemical parameters might be beneficial in antagonizing aluminum toxicity [1]. Oral nutrit ...
Biological energy
... • NADH, the reduced form of NAD+ – Passes the electrons to the electron transport chain ...
... • NADH, the reduced form of NAD+ – Passes the electrons to the electron transport chain ...
Phytochemistry 24:
... (Omithopus satiuus) nodules [3] it was further shown that both the amide and the a-amino nitrogens of glutamine acted as precursor nitrogen for other amino compounds. In soybean [4] and lupin [5] nodules, most of the GS activity was found in the nodule cytosol, consistent with the idea that most of ...
... (Omithopus satiuus) nodules [3] it was further shown that both the amide and the a-amino nitrogens of glutamine acted as precursor nitrogen for other amino compounds. In soybean [4] and lupin [5] nodules, most of the GS activity was found in the nodule cytosol, consistent with the idea that most of ...
ppt file/carnitine
... Never nowhere fatty acids can enter to mitochondria to be oxidized, therefore: a) always everywhere glucose (and amino acids) are degraded to yield energy, glucose is consumed very fast, causing between meals life threatening hypoglycemia, coma b) in liver, muscle etc. PDHC is not inhibited by acety ...
... Never nowhere fatty acids can enter to mitochondria to be oxidized, therefore: a) always everywhere glucose (and amino acids) are degraded to yield energy, glucose is consumed very fast, causing between meals life threatening hypoglycemia, coma b) in liver, muscle etc. PDHC is not inhibited by acety ...
VCE Biology TSFX REVISION LECTURE UNIT 3 Part 1
... Students are expected to understand that polypeptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids, formed through condensation reactions. They are also expected to understand that the primary structure of a polypeptide or protein is the sequence of amino acids that form the polypeptide or protein, and ...
... Students are expected to understand that polypeptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids, formed through condensation reactions. They are also expected to understand that the primary structure of a polypeptide or protein is the sequence of amino acids that form the polypeptide or protein, and ...
HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONAL - Council for Bile Acid Deficiency
... The enzymes required for bile acid biosynthesis are located in different hepatocyte organelles; C-27 hydroxylation occurs mainly in the mitochondria, whereas further ring structure modification is performed in the cytoplasm. Sidechain modification and conjugation are mainly performed in peroxisomes ...
... The enzymes required for bile acid biosynthesis are located in different hepatocyte organelles; C-27 hydroxylation occurs mainly in the mitochondria, whereas further ring structure modification is performed in the cytoplasm. Sidechain modification and conjugation are mainly performed in peroxisomes ...
gal isomer preferences of siglecs with a sialic acid microarray.
... Sialic acids are the terminal sugars of glycoproteins and glycolipids on cell surfaces that are characterized by a 9-carbon backbone.1 To date, nearly fifty different forms of Sias have been identified. Among them, N-acetylneuraminic acid and its N-glycolyl derivatives are the most prominent.2 Given ...
... Sialic acids are the terminal sugars of glycoproteins and glycolipids on cell surfaces that are characterized by a 9-carbon backbone.1 To date, nearly fifty different forms of Sias have been identified. Among them, N-acetylneuraminic acid and its N-glycolyl derivatives are the most prominent.2 Given ...
2011 Exam 2 Key
... the answer must be clear. The final answer must be reported to the correct number of significant figures and have the correct units. Questions are written on both sides of each page. The last page contains useful information and a periodic table; the last page should be removed and used for scratch ...
... the answer must be clear. The final answer must be reported to the correct number of significant figures and have the correct units. Questions are written on both sides of each page. The last page contains useful information and a periodic table; the last page should be removed and used for scratch ...
L-1 - West Ada
... What is the difference between a cofactor and a coenzyme? (cofactor: can be organic or inorganic; Coenzymes are only organic) L-2 Which 2 organic molecules have C, H And O only? (Carbs and Lipids) L-2 When the products contain more free energy than the reactants, the reaction is known as? (endergoni ...
... What is the difference between a cofactor and a coenzyme? (cofactor: can be organic or inorganic; Coenzymes are only organic) L-2 Which 2 organic molecules have C, H And O only? (Carbs and Lipids) L-2 When the products contain more free energy than the reactants, the reaction is known as? (endergoni ...
Metabolite Markers
... Elevation indicates riboflavin deficiency (vitamin B2), a common factor in moderate urinary increases of glutaric acid. Other possible factors include fatty acid oxidation defects and metabolic effects of valproic acid (Depakene), or celiac disease. The probability of a genetic disease is higher wit ...
... Elevation indicates riboflavin deficiency (vitamin B2), a common factor in moderate urinary increases of glutaric acid. Other possible factors include fatty acid oxidation defects and metabolic effects of valproic acid (Depakene), or celiac disease. The probability of a genetic disease is higher wit ...
Cfe Higher Biology Metabolism and Survival
... complex biochemical reactions that occur in an organism. These reactions are ordered into pathways and controlled at each stage by an enzyme. By means of these metabolic pathways, the cell is able to transform energy, degrade macromolecules and synthesise new organic molecules that are needed for li ...
... complex biochemical reactions that occur in an organism. These reactions are ordered into pathways and controlled at each stage by an enzyme. By means of these metabolic pathways, the cell is able to transform energy, degrade macromolecules and synthesise new organic molecules that are needed for li ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.