Flux Balance Analysis of Photoautotrophic
... sources of carbon and energy inputs for growth (Figure 1). Thus, the interactions between the carbon substrate and energetic states of the system are expected to be different from those in heterotrophic systems. The major contribution of this work is to extend the linear programming based flux balan ...
... sources of carbon and energy inputs for growth (Figure 1). Thus, the interactions between the carbon substrate and energetic states of the system are expected to be different from those in heterotrophic systems. The major contribution of this work is to extend the linear programming based flux balan ...
Creatinine
... Treatments for a sudden attack or flare-up of gout : Your doctor will recommend that you take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or indomethacin as soon as your symptoms begin Your health care provider may occasionally prescribe strong painkillers such as ...
... Treatments for a sudden attack or flare-up of gout : Your doctor will recommend that you take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, naproxen, or indomethacin as soon as your symptoms begin Your health care provider may occasionally prescribe strong painkillers such as ...
Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 deficiency increases fatty acid oxidation
... Phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) at Ser-79 by AMPK leads to inhibition of ACC activity and decreased malonyl-CoA content. Malonyl-CoA is required for fatty acid biosynthesis and also inhibits the mitochondrial carnityl palmitoyltransferase shuttle system, the rate-limiting step in the ...
... Phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) at Ser-79 by AMPK leads to inhibition of ACC activity and decreased malonyl-CoA content. Malonyl-CoA is required for fatty acid biosynthesis and also inhibits the mitochondrial carnityl palmitoyltransferase shuttle system, the rate-limiting step in the ...
vitamine
... Hormone for Calcium and Phosphate regulation • Nerves and muscles must function properly; calcium is vital for nerve cell transmissions and muscle fiber contractions. • Calcitriol functions in concert with parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcitonin to regulate serum calcium and phosphorous levels by a ...
... Hormone for Calcium and Phosphate regulation • Nerves and muscles must function properly; calcium is vital for nerve cell transmissions and muscle fiber contractions. • Calcitriol functions in concert with parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcitonin to regulate serum calcium and phosphorous levels by a ...
Digital Coding of Amino Acids Based on Hydrophobic Index
... amino-acid index along the primary sequence of the query protein (domain), Bu et al. [14] predicted the protein structural classes and found that most fractions of the amino-acid indices lead to considerably less accuracy than that obtained by using the Oobatake-Ooi index and the hydrophobic index o ...
... amino-acid index along the primary sequence of the query protein (domain), Bu et al. [14] predicted the protein structural classes and found that most fractions of the amino-acid indices lead to considerably less accuracy than that obtained by using the Oobatake-Ooi index and the hydrophobic index o ...
modelling human energy conversion and metabolism
... temperatures caused by exertion rather than fever, and high blood lactate levels caused by physical exertion rather than hypoxia or shock [1]. Physical exercise affects human physiology at multiple scales. The physical work done by athletes is associated with force exertion, temperature changes in t ...
... temperatures caused by exertion rather than fever, and high blood lactate levels caused by physical exertion rather than hypoxia or shock [1]. Physical exercise affects human physiology at multiple scales. The physical work done by athletes is associated with force exertion, temperature changes in t ...
CLN Carbohydrat es part3
... Glucose is the only CHO to be directly use for energy or stored as glycogen. Others have to be broken down then utilized for energy and storage. ...
... Glucose is the only CHO to be directly use for energy or stored as glycogen. Others have to be broken down then utilized for energy and storage. ...
Articulate - WordPress.com
... mitochondia, large blood supply and major fuel source are fats – Fast (2) contract fast, for short periods of time, [predominantly use glycolysis, so fewer mitochondria, smaller blood supply and major fuel is glycogen and creatine phosphate. ...
... mitochondia, large blood supply and major fuel source are fats – Fast (2) contract fast, for short periods of time, [predominantly use glycolysis, so fewer mitochondria, smaller blood supply and major fuel is glycogen and creatine phosphate. ...
General theory of enzyme action, by Leonor Michaelis and Maud
... serine residues, only one, serine 195, was modified, resulting in a total loss of enzyme activity. This chemical modification reaction suggested that this unusually reactive serine residue plays a central role in the catalytic mechanism of chymotrypsin. ...
... serine residues, only one, serine 195, was modified, resulting in a total loss of enzyme activity. This chemical modification reaction suggested that this unusually reactive serine residue plays a central role in the catalytic mechanism of chymotrypsin. ...
Origin of metabolism
... rich sources of functional information and context. While we will find it significant that some module boundaries are recapitulated at many levels, differences between levels will also help to distinguish modularity originating in reaction mechanisms and network topology of the small-molecule metabo ...
... rich sources of functional information and context. While we will find it significant that some module boundaries are recapitulated at many levels, differences between levels will also help to distinguish modularity originating in reaction mechanisms and network topology of the small-molecule metabo ...
biochemistry-lect-4-n-34-amino-acid-and-peptides
... vitamins and biologically important amines like histamine. 3. Peptides have many important biological functions. Some of them are hormones. They are used as anti-biotics and antitumor agents. 4. Some peptides are required for detoxification reactions. Some peptides serve as neurotransmitters. 5. Ami ...
... vitamins and biologically important amines like histamine. 3. Peptides have many important biological functions. Some of them are hormones. They are used as anti-biotics and antitumor agents. 4. Some peptides are required for detoxification reactions. Some peptides serve as neurotransmitters. 5. Ami ...
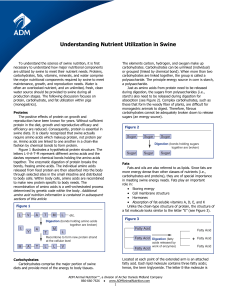
Nutrient Utilization in Swine
... Ten of the 20 amino acids can be synthesized within the pig’s body in sufficient quantities and are referred to as non-essential amino acids. The other ten amino acids that cannot be synthesized or cannot be synthesized at a sufficient rate to enable optimal growth or reproduction must be provided i ...
... Ten of the 20 amino acids can be synthesized within the pig’s body in sufficient quantities and are referred to as non-essential amino acids. The other ten amino acids that cannot be synthesized or cannot be synthesized at a sufficient rate to enable optimal growth or reproduction must be provided i ...
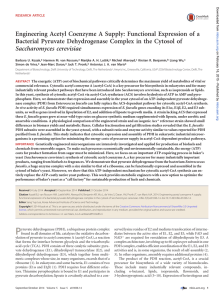
Engineering Acetyl Coenzyme A Supply: Functional Expression of a
... ABSTRACT The energetic (ATP) cost of biochemical pathways critically determines the maximum yield of metabolites of vital or commercial relevance. Cytosolic acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) is a key precursor for biosynthesis in eukaryotes and for many industrially relevant product pathways that have ...
... ABSTRACT The energetic (ATP) cost of biochemical pathways critically determines the maximum yield of metabolites of vital or commercial relevance. Cytosolic acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) is a key precursor for biosynthesis in eukaryotes and for many industrially relevant product pathways that have ...
Electron transport chain…
... PMF drives ATP synthesis • diffusion of protons back across membrane (down gradient) drives formation of ATP • ATP synthase ...
... PMF drives ATP synthesis • diffusion of protons back across membrane (down gradient) drives formation of ATP • ATP synthase ...
Chapter 11
... • Lactate formed in skeletal muscles during exercise is transported to the liver • Liver lactate dehydrogenase can reconvert lactate to pyruvate • Lactic acidosis can result from insufficient oxygen (an increase in lactic acid and decrease in blood pH) Prentice Hall c2002 ...
... • Lactate formed in skeletal muscles during exercise is transported to the liver • Liver lactate dehydrogenase can reconvert lactate to pyruvate • Lactic acidosis can result from insufficient oxygen (an increase in lactic acid and decrease in blood pH) Prentice Hall c2002 ...
amino acid mixture
... acids when presented in the free form), or by glycylglycine, which has been shown to inhibit absorption of several di- and tri-peptides in vitro (Rubino et al., 1971; Addison et al., 1974; Das & Radhakrishnan, 1975), might be explained if these amino acid residues were absorbed by an alternative pep ...
... acids when presented in the free form), or by glycylglycine, which has been shown to inhibit absorption of several di- and tri-peptides in vitro (Rubino et al., 1971; Addison et al., 1974; Das & Radhakrishnan, 1975), might be explained if these amino acid residues were absorbed by an alternative pep ...
Chapter 4
... 3) The oxidation state of oxygen in compounds is -2, except in peroxides, such as H2O2 where it is -1. 4) The oxidation state of hydrogen in compounds is +1, except in metal hydrides, like NaH, where it is -1. ...
... 3) The oxidation state of oxygen in compounds is -2, except in peroxides, such as H2O2 where it is -1. 4) The oxidation state of hydrogen in compounds is +1, except in metal hydrides, like NaH, where it is -1. ...
The pivotal roles of mitochondria in cancer: Warburg and beyond
... may synthesize (under normoxia) approximately 32 ATP molecules per glucose molecule, a highly glycolytic tumor may produce an additional three fourths of this ATP via glycolysis (2 ATP molecules per glucose molecule). Studies by numerous laboratories to date indicate that this extra glucose intake i ...
... may synthesize (under normoxia) approximately 32 ATP molecules per glucose molecule, a highly glycolytic tumor may produce an additional three fourths of this ATP via glycolysis (2 ATP molecules per glucose molecule). Studies by numerous laboratories to date indicate that this extra glucose intake i ...
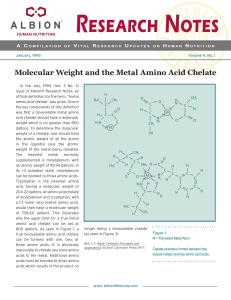
Molecular Weight and the Metal Amino Acid Chelate
... the above example even though the molecular weight of the iron sulfate can be determined, the sulfate in the starting material was included in the total weight of the product formed. The sulfate should not have been counted in the weight of the chelate even though most so-called chelate manufacturer ...
... the above example even though the molecular weight of the iron sulfate can be determined, the sulfate in the starting material was included in the total weight of the product formed. The sulfate should not have been counted in the weight of the chelate even though most so-called chelate manufacturer ...
Energy Metabolism of the Performance Horse. In
... ATP is regenerated from circulating glucose and glycogen stores. In a multiple step pathway, 2 ATP molecules result from the glycolytic pathway per glucose (Table 2). The production of lactate is a possible end stage of this anaerobic pathway. ...
... ATP is regenerated from circulating glucose and glycogen stores. In a multiple step pathway, 2 ATP molecules result from the glycolytic pathway per glucose (Table 2). The production of lactate is a possible end stage of this anaerobic pathway. ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.