Protegrins: leukocyte antimicrobial peptides that combine features of
... Four principal families of cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptides have been recognized in animals during the past few years: tachyplesins [13,21], defensins [4,5], pdefensins [6,12] and insect defensins [22,23]. Plants also produce small cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptides, which differ from those th ...
... Four principal families of cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptides have been recognized in animals during the past few years: tachyplesins [13,21], defensins [4,5], pdefensins [6,12] and insect defensins [22,23]. Plants also produce small cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptides, which differ from those th ...
The Hypothesis that the Genetic Code Originated in Coupled
... mechanisms suggests it was a redox gradient across a membrane. Energy transduction by respiration is an ancient process [33]. In “modern” cells, it is extraordinarily complicated, requiring formation of ion gradients across cell membranes and use of these gradients to drive ATP synthesis. The ion gr ...
... mechanisms suggests it was a redox gradient across a membrane. Energy transduction by respiration is an ancient process [33]. In “modern” cells, it is extraordinarily complicated, requiring formation of ion gradients across cell membranes and use of these gradients to drive ATP synthesis. The ion gr ...
Biology Notes: Test I
... those that were dropped off by ships 3. It was a “little world unto itself” 4. Darwin realized that the species were close to those on South America 5. Note: Most potential colonizers die, but a very few live to spread out 6. The islands were downwind from South America, and therefore could have mor ...
... those that were dropped off by ships 3. It was a “little world unto itself” 4. Darwin realized that the species were close to those on South America 5. Note: Most potential colonizers die, but a very few live to spread out 6. The islands were downwind from South America, and therefore could have mor ...
Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers
... This pH = isoelectric point (pI) How do you calculate pI? 1. Draw out the complete ionization of amino acid 2. Determine net charge on each ionized form 3. Find the structure that has no net charge 4. Take the average of the pKa’s that are around the structure with NO NET CHARGE pI = pKa1 + pKa2 ...
... This pH = isoelectric point (pI) How do you calculate pI? 1. Draw out the complete ionization of amino acid 2. Determine net charge on each ionized form 3. Find the structure that has no net charge 4. Take the average of the pKa’s that are around the structure with NO NET CHARGE pI = pKa1 + pKa2 ...
Free amino acids as phagostimulants in cricket nuptial gifts: support
... benefits (Sakaluk 2000; Vahed 2007). This has been termed the ‘Candymaker’ hypothesis ( Warwick 1999). Relatively few previous studies have examined the chemical composition of nuptial gifts (reviewed in Vahed 2007). One way of increasing the attractiveness of orally ingested gifts might be to incor ...
... benefits (Sakaluk 2000; Vahed 2007). This has been termed the ‘Candymaker’ hypothesis ( Warwick 1999). Relatively few previous studies have examined the chemical composition of nuptial gifts (reviewed in Vahed 2007). One way of increasing the attractiveness of orally ingested gifts might be to incor ...
Abbreviations and Symbols for Chemical Names of Special Interest
... are built up from these units. The standardization of treatment will involve certain unimportant changes in the (as yet partly developed) systems for individual groups. This standardization is desirable for two reasons. a) The work of authors, editors, and readers is made simpler if the same princip ...
... are built up from these units. The standardization of treatment will involve certain unimportant changes in the (as yet partly developed) systems for individual groups. This standardization is desirable for two reasons. a) The work of authors, editors, and readers is made simpler if the same princip ...
Pharos university Faculty of Allied Medical SCIENCE Biochemistry 1
... bonded to an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a fourth group that differs from one amino acid to another and often is referred to as the-R group or the side chain. ...
... bonded to an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a fourth group that differs from one amino acid to another and often is referred to as the-R group or the side chain. ...
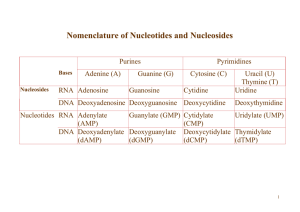
Nomenclature of Nucleotides and Nucleosides
... a. Carbamoyl phosphate is synthesized in the cytosol from glutamine and CO2 by the enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II. b. Carbamoyl phosphate also is synthesized in the liver as an intermediate in urea synthesis, but this synthesis takes place in the mitochondria and is catalyzed by a differen ...
... a. Carbamoyl phosphate is synthesized in the cytosol from glutamine and CO2 by the enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II. b. Carbamoyl phosphate also is synthesized in the liver as an intermediate in urea synthesis, but this synthesis takes place in the mitochondria and is catalyzed by a differen ...
" Enzymes "
... and alkaloid reagents. - Most enzymes are present in cells at much higher concentrations than in plasma. - Normal plasma levels reflect the balance between the synthesis and release of enzymes during ordinary cell turnover and their clearance from the circulation, therefore, enzymes can be used as m ...
... and alkaloid reagents. - Most enzymes are present in cells at much higher concentrations than in plasma. - Normal plasma levels reflect the balance between the synthesis and release of enzymes during ordinary cell turnover and their clearance from the circulation, therefore, enzymes can be used as m ...
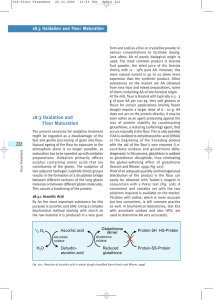
222 18.3 Oxidation and Flour Maturation
... Although it has a very long-lasting effect, this effect starts later than that of AA and allows better processing of the doughs, for bromate clearly oxidizes glutathione only very slowly without the need for an enzyme (cf. ascorbic acid). It results in very good fermentation tolerance and a high vol ...
... Although it has a very long-lasting effect, this effect starts later than that of AA and allows better processing of the doughs, for bromate clearly oxidizes glutathione only very slowly without the need for an enzyme (cf. ascorbic acid). It results in very good fermentation tolerance and a high vol ...
Free fatty acids regulate the uncoupling protein and alternative
... Fig. 1. CN-resistant respiration and LA-induced respiration versus LA concentration. Fully depleted FFA rnitochondria (see Section 2) were incubated with 10 mM succinate, 5 Jam rotenone, 2.5 Jag of oligomycin/mg protein, and 0.17 mM ATP (state 4 respiration). CN-resistant respiration (+1 mM KCN) was ...
... Fig. 1. CN-resistant respiration and LA-induced respiration versus LA concentration. Fully depleted FFA rnitochondria (see Section 2) were incubated with 10 mM succinate, 5 Jam rotenone, 2.5 Jag of oligomycin/mg protein, and 0.17 mM ATP (state 4 respiration). CN-resistant respiration (+1 mM KCN) was ...
Fatty acid and phospholipid metabolism in prokaryotes
... biosynthesis (except acetyl-CoA carboxylase), and does so through interactions with exposed negative residues on ACP with a patch of positive residues on the surfaces of the fab enzymes. The ACP pool in normally growing cells is approximately one-eighth the coenzyme A (CoA) pool, the other acyl grou ...
... biosynthesis (except acetyl-CoA carboxylase), and does so through interactions with exposed negative residues on ACP with a patch of positive residues on the surfaces of the fab enzymes. The ACP pool in normally growing cells is approximately one-eighth the coenzyme A (CoA) pool, the other acyl grou ...
Publication: Amino acid profile of organically grown alternative
... important role in human nutrition. The amino acid content, their proportions and digestibility by humans define protein’s biological value (Joint FAO/WHO/UNU, 1981). Proteins consist of 20 amino acids, but the most important are essential amino acids which the human body needs to gain from food. Acc ...
... important role in human nutrition. The amino acid content, their proportions and digestibility by humans define protein’s biological value (Joint FAO/WHO/UNU, 1981). Proteins consist of 20 amino acids, but the most important are essential amino acids which the human body needs to gain from food. Acc ...
Handout 14, 15 - U of L Class Index
... Proteins equivalent to chaperons and chaperonins have been identified. Eukaryotic folding makes less use of chaperonins, and more depends upon the action of Hsp70 chaperons. ...
... Proteins equivalent to chaperons and chaperonins have been identified. Eukaryotic folding makes less use of chaperonins, and more depends upon the action of Hsp70 chaperons. ...
Phar 722 Pharmacy Practice III
... – In infants there is a characteristic type of convulsions which is reversible when pyridoxine supplements are given. – Deficient infants also show a characteristic electrical encephalogram. (This was "discovered" when infants were fed an infant formula lacking pyridoxine.) ...
... – In infants there is a characteristic type of convulsions which is reversible when pyridoxine supplements are given. – Deficient infants also show a characteristic electrical encephalogram. (This was "discovered" when infants were fed an infant formula lacking pyridoxine.) ...
Amino acid profile of organically grown alternative agricultural
... important role in human nutrition. The amino acid content, their proportions and digestibility by humans define protein’s biological value (Joint FAO/WHO/UNU, 1981). Proteins consist of 20 amino acids, but the most important are essential amino acids which the human body needs to gain from food. Acc ...
... important role in human nutrition. The amino acid content, their proportions and digestibility by humans define protein’s biological value (Joint FAO/WHO/UNU, 1981). Proteins consist of 20 amino acids, but the most important are essential amino acids which the human body needs to gain from food. Acc ...
FIGURE 21–6 Part 1
... tissue and liver may be quite low when other fuels are available and the release of fatty acids from adipose tissue is limited, but as noted above, the proportion of released fatty acids that are reesterified remains roughly constant ...
... tissue and liver may be quite low when other fuels are available and the release of fatty acids from adipose tissue is limited, but as noted above, the proportion of released fatty acids that are reesterified remains roughly constant ...
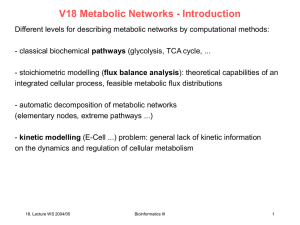
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... network of cellular constituents and reactions. A systematic comparative mathematical analysis of the metabolic networks of 43 organisms representing all 3 domains of life showed that, despite significant variation in their individual constituents and pathways, these metabolic networks have the same ...
... network of cellular constituents and reactions. A systematic comparative mathematical analysis of the metabolic networks of 43 organisms representing all 3 domains of life showed that, despite significant variation in their individual constituents and pathways, these metabolic networks have the same ...
Enzymes - Best Friends of Flours The Miller`s Little Helpers
... atmospheric oxygen, but the slight souring that occurs in the process is negligible; its other effect is to transform water into hydrogen peroxide (Fig. 7). This oxidizing agent acts on the thiol groups of the gluten, either directly or via several pathways, inducing formation of disulphide bonds an ...
... atmospheric oxygen, but the slight souring that occurs in the process is negligible; its other effect is to transform water into hydrogen peroxide (Fig. 7). This oxidizing agent acts on the thiol groups of the gluten, either directly or via several pathways, inducing formation of disulphide bonds an ...
Intermolecular interaction studies in some amino acids with aqueous
... possibility of hydrogen bond formation between water, NaOH and amino acid molecules. When NaOH is dissolved in water, the sodium ion (Na+) has a stucture breaking effect, would first disrupt the water structure.This could be followed by structural reorganization leaving the molecules in closely fitt ...
... possibility of hydrogen bond formation between water, NaOH and amino acid molecules. When NaOH is dissolved in water, the sodium ion (Na+) has a stucture breaking effect, would first disrupt the water structure.This could be followed by structural reorganization leaving the molecules in closely fitt ...
Planta
... species inactivate both the plant and animal enzymes and induce RNA-binding activity in animal cells (Drapier et al. 1994; Navarre et al. 2000). The assembly of the iron–sulfur cluster required for cytosolic aconitase activity is dependent on the activity of the mitochondrial ATP-binding cassette tr ...
... species inactivate both the plant and animal enzymes and induce RNA-binding activity in animal cells (Drapier et al. 1994; Navarre et al. 2000). The assembly of the iron–sulfur cluster required for cytosolic aconitase activity is dependent on the activity of the mitochondrial ATP-binding cassette tr ...
©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies
... One more interesting factoid about cellulose is that insects use a form of it to create chitin; this is a major component of the exoskeleton of arthropods. ...
... One more interesting factoid about cellulose is that insects use a form of it to create chitin; this is a major component of the exoskeleton of arthropods. ...
9-1 PowerPoint
... Our familiar Calorie is actually a kilocalorie (1000 calories) Generally 1 gram of carbohydrates and protein store 4 Calories, while lipids (fats) store 9 Calories. Food is not broken down into energy until it is needed to make ATP. Cellular respiration is the process that releases energy form food ...
... Our familiar Calorie is actually a kilocalorie (1000 calories) Generally 1 gram of carbohydrates and protein store 4 Calories, while lipids (fats) store 9 Calories. Food is not broken down into energy until it is needed to make ATP. Cellular respiration is the process that releases energy form food ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.