The Diversity of Lysine-Acetylated Proteins in Escherichia coli
... kinase, phosphoglycerate mutase and pyruvate dehydrogenase, were lysine-acetylated. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase was shown to be acetylated at 3 different lysine residues. Enzymes involved in the pentose phosphate pathway, transaldolase B and transketolase, were also lysineacetylated, al ...
... kinase, phosphoglycerate mutase and pyruvate dehydrogenase, were lysine-acetylated. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase was shown to be acetylated at 3 different lysine residues. Enzymes involved in the pentose phosphate pathway, transaldolase B and transketolase, were also lysineacetylated, al ...
irm_ch20
... 20.66 –C=O and –N–H 20.67 In a beta-pleated sheet structure, two fully extended protein chain segments are held together by hydrogen bonds. The beta-pleated sheet may be intermolecular when two different peptide chains are aligned parallel to each other, or intramolecular when a single molecule fold ...
... 20.66 –C=O and –N–H 20.67 In a beta-pleated sheet structure, two fully extended protein chain segments are held together by hydrogen bonds. The beta-pleated sheet may be intermolecular when two different peptide chains are aligned parallel to each other, or intramolecular when a single molecule fold ...
Accumulation of Carotenoids and Metabolic Profiling in Different
... medicinal and ornamental purposes around the world. In addition, the nematocidal, fungicidal, and including anti-bacterial, antimicrobial, anti-oxidant, hepatoprotective, wound healing, and larvicidal insecticidal properties of extracts from these species have been demonstrated in several studies [ ...
... medicinal and ornamental purposes around the world. In addition, the nematocidal, fungicidal, and including anti-bacterial, antimicrobial, anti-oxidant, hepatoprotective, wound healing, and larvicidal insecticidal properties of extracts from these species have been demonstrated in several studies [ ...
Lipids
... The balance between these various sphingolipid metabolites may be important for health. For example, within the cell, sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes cellular division (mitosis) as opposed to cell death (apoptosis), which it inhibits in fact. Intracellularly, it also functions to regulate calcium m ...
... The balance between these various sphingolipid metabolites may be important for health. For example, within the cell, sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes cellular division (mitosis) as opposed to cell death (apoptosis), which it inhibits in fact. Intracellularly, it also functions to regulate calcium m ...
Enzymes - Chemistry@Elmhurst
... Enzyme Inhibitors • Regulator or feedback - used to control a sequence of reactions - reaction product may block initial enzyme. ...
... Enzyme Inhibitors • Regulator or feedback - used to control a sequence of reactions - reaction product may block initial enzyme. ...
2_Digestion of CHO_Students
... The sodium is transported from high to low concentration (with concentration gradient) and at the same time causes the carrier to transport glucose against its concentration gradient (from lower to higher concentrations) allowing for greater accumulation of glucose on one side of the membrane than o ...
... The sodium is transported from high to low concentration (with concentration gradient) and at the same time causes the carrier to transport glucose against its concentration gradient (from lower to higher concentrations) allowing for greater accumulation of glucose on one side of the membrane than o ...
Pentose Phosphate Pathway - Berkeley MCB
... Mechanism. The lactone is opened by hydrolysis, the addition of water to cleave a bond, usually a type of amide or ester. In this case, since the lactone (by definition) is intramolecular, then 6-phosphoglucono-δ-lactone is opened up to the acid form, gluconate. ...
... Mechanism. The lactone is opened by hydrolysis, the addition of water to cleave a bond, usually a type of amide or ester. In this case, since the lactone (by definition) is intramolecular, then 6-phosphoglucono-δ-lactone is opened up to the acid form, gluconate. ...
The role of the C8 proton of ATP in the catalysis of shikimate kinase
... making up the “push” mechanism (Figure 1) [2]. Shown are the protein backbone carbonyl associated with the C6-NH2, the Thr associated with the proton transfer from C8-H to the α-PO4 (SK, Thr17; AK1, Thr23), the Arg associated with C8 protonation (SK, Arg110: AK1; Arg128), the Arg coordinated to the ...
... making up the “push” mechanism (Figure 1) [2]. Shown are the protein backbone carbonyl associated with the C6-NH2, the Thr associated with the proton transfer from C8-H to the α-PO4 (SK, Thr17; AK1, Thr23), the Arg associated with C8 protonation (SK, Arg110: AK1; Arg128), the Arg coordinated to the ...
Modular Architecture of Metabolic Pathways Revealed by
... Metabolism is the most basic aspect of life. It represents a chemical system generating all necessary chemical substances in living cells through chemical reactions. It also represents a genetic system in the sense that chemical reactions are catalyzed by genome-encoded enzymes. The dual aspect of m ...
... Metabolism is the most basic aspect of life. It represents a chemical system generating all necessary chemical substances in living cells through chemical reactions. It also represents a genetic system in the sense that chemical reactions are catalyzed by genome-encoded enzymes. The dual aspect of m ...
Antioxidant Activity Associated with Lipid and Phenolic Mobilization
... content of the seeds during germination decreased from 46.00 to 18.50% on a dry basis (db). Breakdown of fats stored in oleosomes of seed generally releases relatively large amounts of energy. For seeds, this energy is necessary to drive early seedling development before photosynthesis begins (Salis ...
... content of the seeds during germination decreased from 46.00 to 18.50% on a dry basis (db). Breakdown of fats stored in oleosomes of seed generally releases relatively large amounts of energy. For seeds, this energy is necessary to drive early seedling development before photosynthesis begins (Salis ...
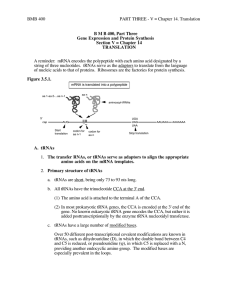
Translation Tutorial
... tyrosine, glycine Just count em up. Methionine, proline, tyrosine, glycine ...
... tyrosine, glycine Just count em up. Methionine, proline, tyrosine, glycine ...
T. TRIOSE PHOSPHATE ISOMERASE Background
... Figure T.2. In the glycolytic pathway, TIM catalyzes the conversion of DHAP to GAP so that the breakdown products of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (F-1,6-P) are two molecules of GAP, which is the substrate of the next enzyme in the pathway, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. The equilibrium const ...
... Figure T.2. In the glycolytic pathway, TIM catalyzes the conversion of DHAP to GAP so that the breakdown products of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (F-1,6-P) are two molecules of GAP, which is the substrate of the next enzyme in the pathway, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. The equilibrium const ...
The Presence and Function of Cytochromes in
... anaerobic bacteria which, like the propionic acid bacteria, form propionate via the succinate pathway (Paynter & Elsden, 1970; Hobson & Summers, 1967; Johns, 1951). V. alcalescens and certain strains of S. ruminantium form nitrite from nitrate, whereas A . lipolytica does not reduce nitrate (Hungate ...
... anaerobic bacteria which, like the propionic acid bacteria, form propionate via the succinate pathway (Paynter & Elsden, 1970; Hobson & Summers, 1967; Johns, 1951). V. alcalescens and certain strains of S. ruminantium form nitrite from nitrate, whereas A . lipolytica does not reduce nitrate (Hungate ...
ppt - 3.LF UK 2015
... • phosphorylated enzyme is either active or inactive (different enzymes are influenced differently) The figure is found at: http://stallion.abac.peachnet.edu/sm/kmccrae/BIOL2050/Ch1-13/JpegArt113/05jpeg/05_jpeg_HTML/index.htm (December 2006) ...
... • phosphorylated enzyme is either active or inactive (different enzymes are influenced differently) The figure is found at: http://stallion.abac.peachnet.edu/sm/kmccrae/BIOL2050/Ch1-13/JpegArt113/05jpeg/05_jpeg_HTML/index.htm (December 2006) ...
The Minimal Nutritional Requirements of Organisms
... with the remaining strains were variable, but followed a definite pattern. When growth occurred it was poor and remained so for one or two subcultures and then either the culture died or growth improved until after five or six subcultures it became as good, or nearly as good, as with the amino acid ...
... with the remaining strains were variable, but followed a definite pattern. When growth occurred it was poor and remained so for one or two subcultures and then either the culture died or growth improved until after five or six subcultures it became as good, or nearly as good, as with the amino acid ...
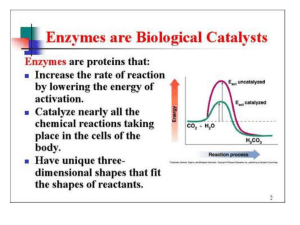
EnzymesLect1 2014
... FIFTH. Allosteric regulation of metabolic pathways. . A. Key enzymes that catalyze rate-limiting steps of metabolic pathways or that are responsible for major cellular processes must be regulated to maintain homeostasis of individual cells and the organism overall. B. Allosteric regulation refers to ...
... FIFTH. Allosteric regulation of metabolic pathways. . A. Key enzymes that catalyze rate-limiting steps of metabolic pathways or that are responsible for major cellular processes must be regulated to maintain homeostasis of individual cells and the organism overall. B. Allosteric regulation refers to ...
Decreased Complete Oxidation Capacity of Fatty Acid in the Liver of
... (Carlson et al., 2007) and how the TCA cycle (complete oxidation pathway) is affected is unknown. So, the enhanced pathways of VLDL synthesis and secretion and NEFA esterification in liver do not relieve NEB. In our previous research using comparative proteomic techniques, we observed that the expre ...
... (Carlson et al., 2007) and how the TCA cycle (complete oxidation pathway) is affected is unknown. So, the enhanced pathways of VLDL synthesis and secretion and NEFA esterification in liver do not relieve NEB. In our previous research using comparative proteomic techniques, we observed that the expre ...
pdf
... PART THREE - V = Chapter 14. Translation The two classes of enzymes do not resemble each other much at all, in either sequence or 3-D structure, leading to the suggestion that they have evolved separately. If so, this would imply that an early form of life may have evolved using the ten amino acids ...
... PART THREE - V = Chapter 14. Translation The two classes of enzymes do not resemble each other much at all, in either sequence or 3-D structure, leading to the suggestion that they have evolved separately. If so, this would imply that an early form of life may have evolved using the ten amino acids ...
The origin of the RNA world: Co-evolution of genes and metabolism
... The nucleotide synthesis module necessary to generate the precursors for RNA is simpler that might be supposed. We now consider how a system of ever more complex catalysts might have led to a situation in which certain components of the network—i.e., RNA molecules—could have been replicated in a tem ...
... The nucleotide synthesis module necessary to generate the precursors for RNA is simpler that might be supposed. We now consider how a system of ever more complex catalysts might have led to a situation in which certain components of the network—i.e., RNA molecules—could have been replicated in a tem ...
in Graminaceous Plants
... detected in the non-binding fraction. In addition, the specific enzyme activity of the NAAT in this fraction (nonbound fraction of DEAE in Table II) was increased by the NA-affinity chromatography step with various ligands more efficiently than the binding fraction (Table II). Therefore, we assumed ...
... detected in the non-binding fraction. In addition, the specific enzyme activity of the NAAT in this fraction (nonbound fraction of DEAE in Table II) was increased by the NA-affinity chromatography step with various ligands more efficiently than the binding fraction (Table II). Therefore, we assumed ...
INDUCIBLE INOS)
... Validation of docking method Prior to dock of asiatic acid into target, the re-docking of L-arginin as a substrate of iNOS (PDB: 1NSI), and naproxen as an inhibitor to COX-2 (PDB: 3NT1) were conducted to ensure whether the method is valid. The amino acid residues that bind compounds produced by the ...
... Validation of docking method Prior to dock of asiatic acid into target, the re-docking of L-arginin as a substrate of iNOS (PDB: 1NSI), and naproxen as an inhibitor to COX-2 (PDB: 3NT1) were conducted to ensure whether the method is valid. The amino acid residues that bind compounds produced by the ...
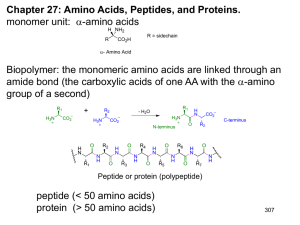
ppt - Vanderbilt University
... 27.10: Partial Hydrolysis of Peptides. Acidic hydrolysis of peptides cleave the amide bonds indiscriminately. Proteases (peptidases): Enzymes that catalyzed the hydrolysis of the amide bonds of peptides and proteins. Enzymatic cleavage of peptides and proteins at defined sites: • trypsin: cleaves a ...
... 27.10: Partial Hydrolysis of Peptides. Acidic hydrolysis of peptides cleave the amide bonds indiscriminately. Proteases (peptidases): Enzymes that catalyzed the hydrolysis of the amide bonds of peptides and proteins. Enzymatic cleavage of peptides and proteins at defined sites: • trypsin: cleaves a ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.