chemistry - Canisteo-Greenwood Central School
... produce enough of the enzyme lactase to digest lactose, the sugar found in milk. You will learn what enzymes are and what function they serve in the ...
... produce enough of the enzyme lactase to digest lactose, the sugar found in milk. You will learn what enzymes are and what function they serve in the ...
Unit 4 Notes
... a net gain of ATP and reduced NAD • Pyruvate combines with coenzyme A in the link reaction to produce acetylcoenzyme A • Acetylcoenzyme A is effectively a two carbon molecule that combines with a four carbon molecule to produce a six carbon molecule which enters the Krebs cycle. In a series of oxida ...
... a net gain of ATP and reduced NAD • Pyruvate combines with coenzyme A in the link reaction to produce acetylcoenzyme A • Acetylcoenzyme A is effectively a two carbon molecule that combines with a four carbon molecule to produce a six carbon molecule which enters the Krebs cycle. In a series of oxida ...
Articles Oxidation Numbers in the Study of Metabolism
... of the pyridine ring is more meaningful. The oxidation number of the nitrogen atom, ⫺III, does not change during the NAD⫹ 3 NADH conversion. It is the oxidation number changes on C4 and C6 that are crucial. At C4 the change is from ⫺I in NAD⫹ to ⫺II in NADH and at C6 from I to 0. Hence the reduction ...
... of the pyridine ring is more meaningful. The oxidation number of the nitrogen atom, ⫺III, does not change during the NAD⫹ 3 NADH conversion. It is the oxidation number changes on C4 and C6 that are crucial. At C4 the change is from ⫺I in NAD⫹ to ⫺II in NADH and at C6 from I to 0. Hence the reduction ...
Campbell`s Biology, 9e (Reece et al.) Chapter 8 An
... D) is inhibited by the presence of a coenzyme or a cofactor. Answer: B Topic: Concept 8.4 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 37) According to the induced fit hypothesis of enzyme catalysis, which of the following is correct? A) The binding of the substrate depends on the shape of the active site. B) Som ...
... D) is inhibited by the presence of a coenzyme or a cofactor. Answer: B Topic: Concept 8.4 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 37) According to the induced fit hypothesis of enzyme catalysis, which of the following is correct? A) The binding of the substrate depends on the shape of the active site. B) Som ...
Glycogen Metabolism
... • Glycogenin is an enzyme that catalyzes attachment of a glucose molecule to one of its own tyrosine residues. • Glycogenin is a dimer, and evidence indicates that the 2 copies of the enzyme glucosylate one another. ...
... • Glycogenin is an enzyme that catalyzes attachment of a glucose molecule to one of its own tyrosine residues. • Glycogenin is a dimer, and evidence indicates that the 2 copies of the enzyme glucosylate one another. ...
Enzymes - Dr. Hamad Ali Yaseen
... • active site - a region of an enzyme comprised of different amino acids where catalysis occurs (determined by the tertiary and quaternary structure of each enzyme) • substrate - the molecule being utilized and/or modified by a particular enzyme at its active site • co-factor - organic or inorganic ...
... • active site - a region of an enzyme comprised of different amino acids where catalysis occurs (determined by the tertiary and quaternary structure of each enzyme) • substrate - the molecule being utilized and/or modified by a particular enzyme at its active site • co-factor - organic or inorganic ...
(C) Chronic peripheral neuropathy
... Pyruvic acid is a normal intermediary of carbohydrate metabolism (1, 2). It has been previously demonstrated that thiamin, or more particularly thiamin pyrophosphate (cocarboxylase), is concerned in the normal catabolism of pyruvic acid (1). In Oriental beri-beri (3) and peripheral neuropathy in the ...
... Pyruvic acid is a normal intermediary of carbohydrate metabolism (1, 2). It has been previously demonstrated that thiamin, or more particularly thiamin pyrophosphate (cocarboxylase), is concerned in the normal catabolism of pyruvic acid (1). In Oriental beri-beri (3) and peripheral neuropathy in the ...
Lecture 15, Feb 26
... Since the central carbon atom of an amino acid is asymmetrical, there are 2 enantiomers of each kind of amino acid. Cells use only the "L" enantiomer of each kind of amino acid to construct proteins. The R-group of a few kinds of amino acids carry an amino or a carboxylic acid functional group. Thes ...
... Since the central carbon atom of an amino acid is asymmetrical, there are 2 enantiomers of each kind of amino acid. Cells use only the "L" enantiomer of each kind of amino acid to construct proteins. The R-group of a few kinds of amino acids carry an amino or a carboxylic acid functional group. Thes ...
Винницкий национальный медицинский университет им
... Answer: Chlorine atom as more electronegative (I-) shifts the electrone density from alkyl grup (I+) therefore on oxygen atom the deficiency of electrons arises. In addition to that Oxygen atom as more electronegative (I-) shifts the electrone density from hydrogen and the atomic mobility increases. ...
... Answer: Chlorine atom as more electronegative (I-) shifts the electrone density from alkyl grup (I+) therefore on oxygen atom the deficiency of electrons arises. In addition to that Oxygen atom as more electronegative (I-) shifts the electrone density from hydrogen and the atomic mobility increases. ...
Availability of amino acids supplied by constant
... solution (Fig. 26). It is tempting to speculate that infusion of an almost tyrosine-free amino acid solution results in a depletion of this amino acid. However, it is difficult to conceive that such a specific depletion could occur within the short infusion period of 4 h as applied in the present st ...
... solution (Fig. 26). It is tempting to speculate that infusion of an almost tyrosine-free amino acid solution results in a depletion of this amino acid. However, it is difficult to conceive that such a specific depletion could occur within the short infusion period of 4 h as applied in the present st ...
Chapt 2-9 Practice Problem Answers
... c. Refer to the summary formula for photosynthesis. If you know the number of molecules or moles of any of the reactants used (or products produced), how would you calculate the number of molecules or moles of all of the other reactants needed and products produced? If the formula is balanced and i ...
... c. Refer to the summary formula for photosynthesis. If you know the number of molecules or moles of any of the reactants used (or products produced), how would you calculate the number of molecules or moles of all of the other reactants needed and products produced? If the formula is balanced and i ...
Microbial production of hyaluronic acid: current state, challenges
... there is a considerable divergence on the impacts of agitation speed and aeration on the microbial HA production. It was observed that HA production was not affected by aeration rate, whereas it decreased with the increase of agitation speed [27]. Hasegawa et al. reported that HA production increase ...
... there is a considerable divergence on the impacts of agitation speed and aeration on the microbial HA production. It was observed that HA production was not affected by aeration rate, whereas it decreased with the increase of agitation speed [27]. Hasegawa et al. reported that HA production increase ...
Two Arabidopsis Genes (IPMS1 and IPMS2
... (Leu) biosynthesis, an aldol-type condensation of acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) and 2-oxoisovalerate yielding isopropylmalate. Most biochemical properties of IPMS1 and IPMS2 are similar: broad pH optimum around pH 8.5, Mg21 as cofactor, feedback inhibition by Leu, Km for 2-oxoisovalerate of approximately ...
... (Leu) biosynthesis, an aldol-type condensation of acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) and 2-oxoisovalerate yielding isopropylmalate. Most biochemical properties of IPMS1 and IPMS2 are similar: broad pH optimum around pH 8.5, Mg21 as cofactor, feedback inhibition by Leu, Km for 2-oxoisovalerate of approximately ...
- Wiley Online Library
... carbon from C1 -compounds [78]. Some metabolic abilities are common to both obligate autotrophs and type I methanotrophs. They use similar cyclic sugar–phosphate pathways for the assimilation of carbon dioxide or reduced C1 -compounds: the ribulose bisphosphate Calvin cycle or the Quayle cycle, resp ...
... carbon from C1 -compounds [78]. Some metabolic abilities are common to both obligate autotrophs and type I methanotrophs. They use similar cyclic sugar–phosphate pathways for the assimilation of carbon dioxide or reduced C1 -compounds: the ribulose bisphosphate Calvin cycle or the Quayle cycle, resp ...
On the mechanism of action of the antifungal agent propionate
... Sodium propionate is widely used as a preservative due to its ability to inhibit fungal growth. Furthermore, this shortchain fatty acid (pion ¼ fat) prevents the biosynthesis of polyketides such as ochratoxin A by Aspergillus sulphureus and Penicillium viridicatum [1]. On the other hand, many fungi ...
... Sodium propionate is widely used as a preservative due to its ability to inhibit fungal growth. Furthermore, this shortchain fatty acid (pion ¼ fat) prevents the biosynthesis of polyketides such as ochratoxin A by Aspergillus sulphureus and Penicillium viridicatum [1]. On the other hand, many fungi ...
Carnitine Acetyltransferase and Mitochondrial Acetyl
... novo fatty acid synthesis and elongation. When citrate synthesis exceeds TCA cycle flux, the resulting buildup of mitochondrial citrate can be exported to the cytosol via the citrate carrier. Citrate is then catabolized to oxaloacetate and acetyl-CoA by citrate lysase and may be utilized for lipogen ...
... novo fatty acid synthesis and elongation. When citrate synthesis exceeds TCA cycle flux, the resulting buildup of mitochondrial citrate can be exported to the cytosol via the citrate carrier. Citrate is then catabolized to oxaloacetate and acetyl-CoA by citrate lysase and may be utilized for lipogen ...
- Vijay Education Academy
... (ii) If one of A+ ions from the corner is replaced by a monovalent ion C +, what would be the simplest formula of the resulting compound? 37. Maneesh, a student of class XII, watched a programme on TV where it was being shown how use of polythene bags blocked the sewer system and how sometimes the p ...
... (ii) If one of A+ ions from the corner is replaced by a monovalent ion C +, what would be the simplest formula of the resulting compound? 37. Maneesh, a student of class XII, watched a programme on TV where it was being shown how use of polythene bags blocked the sewer system and how sometimes the p ...
on the potential efficiency of converting solar radiation to phytoenergy
... After briefly considering the spectral properties of solar radiation and how effectively plants can absorb it (the top ‘half’ of Fig. 1a,b), the analysis turns to quantitative biochemistry. This includes summing up the reactions that convert CO2 to photosynthate (i.e. sucrose and starch) to quantify ...
... After briefly considering the spectral properties of solar radiation and how effectively plants can absorb it (the top ‘half’ of Fig. 1a,b), the analysis turns to quantitative biochemistry. This includes summing up the reactions that convert CO2 to photosynthate (i.e. sucrose and starch) to quantify ...
Vitamins and Coenzymes
... carbonyl group of the a-keto acid (i. e. pyruvate or a-KG) followed by protonation forms an activated a-hydroxyacid • The hydroxy acid then undergoes decarboxylation • The positively charged nitrogen of TPP serves as a critical electron sink during the decarboxylation step and contributes to the res ...
... carbonyl group of the a-keto acid (i. e. pyruvate or a-KG) followed by protonation forms an activated a-hydroxyacid • The hydroxy acid then undergoes decarboxylation • The positively charged nitrogen of TPP serves as a critical electron sink during the decarboxylation step and contributes to the res ...
Allessan® CAP - Corden Pharma
... Allessan®CAP as a water scavenger agent: Allessan®CAP is a pH neutral dehydration reagent, similar in strenghth to the highly reactive and hazardous phosphorous pentoxid and polyphosphoric acid, alternative to molecular sieves for water removal from organic solvents and providing Lewis acid catalys ...
... Allessan®CAP as a water scavenger agent: Allessan®CAP is a pH neutral dehydration reagent, similar in strenghth to the highly reactive and hazardous phosphorous pentoxid and polyphosphoric acid, alternative to molecular sieves for water removal from organic solvents and providing Lewis acid catalys ...
Phylogenetic tree construction based on amino acid composition
... number of character states analyzed: 20 amino acids vs. 4 nucleotides. Because comparisons of amino acid or nucleotide gene sequences are based on a large number of characters, phylogenetic tree constructions using these data generally return reasonable results. Amino acid or nucleotide sequences ar ...
... number of character states analyzed: 20 amino acids vs. 4 nucleotides. Because comparisons of amino acid or nucleotide gene sequences are based on a large number of characters, phylogenetic tree constructions using these data generally return reasonable results. Amino acid or nucleotide sequences ar ...
Isotope-Exchange Evidence that Glucose 6
... with the MgATP concentration, at glucose 6-phosphate concentrations above 1 mM. This behaviour does not permit glucose 6-phosphate to act only as a normal product inhibitor. Instead, it seems to require glucose 6-phosphate to act as an allosteric inhibitor and for a second site for binding of MgATP ...
... with the MgATP concentration, at glucose 6-phosphate concentrations above 1 mM. This behaviour does not permit glucose 6-phosphate to act only as a normal product inhibitor. Instead, it seems to require glucose 6-phosphate to act as an allosteric inhibitor and for a second site for binding of MgATP ...
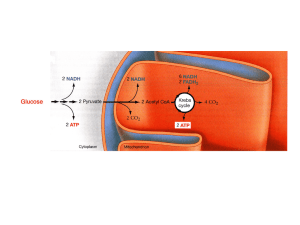
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.