Energy Systems
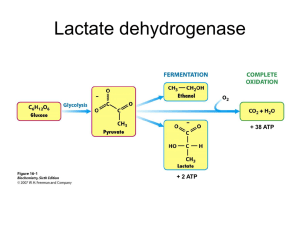
... re-synthesise three molecules of ATP but the process of glycolysis itself requires energy (one molecule) The lactic acid system provides energy for high-intensity activities lasting up to 3 minutes but peaking at 1 minute, for example the 400m ...
... re-synthesise three molecules of ATP but the process of glycolysis itself requires energy (one molecule) The lactic acid system provides energy for high-intensity activities lasting up to 3 minutes but peaking at 1 minute, for example the 400m ...
Photosynthesis
... make 3 carbon sugars from CO2 Used to make more complex sugars or other biochemical molecules ...
... make 3 carbon sugars from CO2 Used to make more complex sugars or other biochemical molecules ...
Oxidative phosphorylation (1)
... Respiratory chain Electron transport chain (ETC) is the final common pathway in aerobic cells by which electrons and hydrogen (NADH & FADH2) derived from foodstuffs are transferred to oxygen to form water and finally produce ATP (energy) ETC is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane & is the fi ...
... Respiratory chain Electron transport chain (ETC) is the final common pathway in aerobic cells by which electrons and hydrogen (NADH & FADH2) derived from foodstuffs are transferred to oxygen to form water and finally produce ATP (energy) ETC is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane & is the fi ...
36. ______ layers of ______ make up the cell membrane.
... 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carb ...
... 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carb ...
C - 鄭智美的Homepage
... NAD+ as an electron shuttle • Electrons from organic compounds – Are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme ...
... NAD+ as an electron shuttle • Electrons from organic compounds – Are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme ...
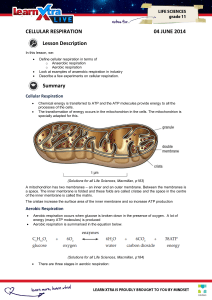
CELLULAR RESPIRATION 04 JUNE 2014 Lesson Description
... Oxidative phosphorylation: takes the energy from the energy-rich hydrogens to make ATP. The energy depleted hydrogens combine with oxygen to make water. This is either breathed out as water vapour or excreted via the kidneys. ...
... Oxidative phosphorylation: takes the energy from the energy-rich hydrogens to make ATP. The energy depleted hydrogens combine with oxygen to make water. This is either breathed out as water vapour or excreted via the kidneys. ...
THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... bacteria, which live under aerobic conditions and oxidize their organic fuels to carbon dioxide and water, glycolysis is but the first stage in the complete oxidation of glucose. Rather than being reduced to lactate, ethanol, or some other fermentation product, the pyruvate produced by glycolysis is ...
... bacteria, which live under aerobic conditions and oxidize their organic fuels to carbon dioxide and water, glycolysis is but the first stage in the complete oxidation of glucose. Rather than being reduced to lactate, ethanol, or some other fermentation product, the pyruvate produced by glycolysis is ...
final-exam-tables-ba..
... The Krebs cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In the Krebs cycle, pyruvate is reacted with coenzyme A (CoA), carbon dioxide is released, hydrogen ions are harvested in NADH and FADH and one ATP is generated per cycle by substrate level phosphorylation. The Electron transport chain ...
... The Krebs cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In the Krebs cycle, pyruvate is reacted with coenzyme A (CoA), carbon dioxide is released, hydrogen ions are harvested in NADH and FADH and one ATP is generated per cycle by substrate level phosphorylation. The Electron transport chain ...
Student________________ Biochemistry I Homework III Due 10/13
... 2). (6 points) The curves below represent the effect of adding a positive allosteric effector or a negative allosteric effector to an enzymatic reaction. a). Identify on the plot which curve represents the effect of a positive allosteric effector and which curve represents the effect of a negative a ...
... 2). (6 points) The curves below represent the effect of adding a positive allosteric effector or a negative allosteric effector to an enzymatic reaction. a). Identify on the plot which curve represents the effect of a positive allosteric effector and which curve represents the effect of a negative a ...
Carbon Compounds in Cells
... Continue.. • When they are part of complex lipids, the fatty acids resemble long flexible tails – Unsaturated fats: fats are liquids (oils) at room temperature because one ore more double bonds between the carbons in the fatty acids permits “kinks” in the tails ...
... Continue.. • When they are part of complex lipids, the fatty acids resemble long flexible tails – Unsaturated fats: fats are liquids (oils) at room temperature because one ore more double bonds between the carbons in the fatty acids permits “kinks” in the tails ...
File
... 2. Compare and contrast photosynthesis and cellular respiration. 3. Describe the relationship between nitrogen fixation and denitrification. 4. Why is nutrient cycling so important in ecosystems? 5. Discuss 3 ways you can reduce carbon emissions. 6. Explain why the sun could be called the ‘engine’ t ...
... 2. Compare and contrast photosynthesis and cellular respiration. 3. Describe the relationship between nitrogen fixation and denitrification. 4. Why is nutrient cycling so important in ecosystems? 5. Discuss 3 ways you can reduce carbon emissions. 6. Explain why the sun could be called the ‘engine’ t ...
Chp 4 Cell Energy
... • Cellular respiration makes ATP by breaking down sugars. • Cellular respiration is aerobic, or requires oxygen. • Aerobic stages take place in mitochondria. ...
... • Cellular respiration makes ATP by breaking down sugars. • Cellular respiration is aerobic, or requires oxygen. • Aerobic stages take place in mitochondria. ...
High Energy compounds
... • Phosphocreatine can anaerobically donate a phosphate group to ADP to form ATP during the first 2 to 7 seconds following an intense muscular or neuronal effort. • On the converse, excess ATP can be used during a period of low effort to convert creatine to phosphocreatine. • is catalyzed by several ...
... • Phosphocreatine can anaerobically donate a phosphate group to ADP to form ATP during the first 2 to 7 seconds following an intense muscular or neuronal effort. • On the converse, excess ATP can be used during a period of low effort to convert creatine to phosphocreatine. • is catalyzed by several ...
General Biology (BIO 10)
... Chemiosmosis (know how it works & that it is important in photosynthesis & cellular resp.) Photorespiration C3, C4 and CAM photosynthesis Chapter 7: Reactants & products of cellular respiration (equation) Know the parts of cellular respiration (glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain) Wher ...
... Chemiosmosis (know how it works & that it is important in photosynthesis & cellular resp.) Photorespiration C3, C4 and CAM photosynthesis Chapter 7: Reactants & products of cellular respiration (equation) Know the parts of cellular respiration (glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain) Wher ...
Evolution & organisation of metabolic Pathways
... building blocks energy substrate Transformations: 1 Oxaloacetate + Acetyl CoA + H2O = Citrate + HSCoA 2 Citrate = cis-Aconitrate + H2O 3 cis-Aconitrate + H2O = Isocitrate 4 Isocitrate + NAD+ = α-Ketoglutarate + CO2 + NADH + H+ 5 α-Ketoglutarate + NAD+ + HSCoA = Succinyl CoA + CO2 + NADH + H+ 6 Suc ...
... building blocks energy substrate Transformations: 1 Oxaloacetate + Acetyl CoA + H2O = Citrate + HSCoA 2 Citrate = cis-Aconitrate + H2O 3 cis-Aconitrate + H2O = Isocitrate 4 Isocitrate + NAD+ = α-Ketoglutarate + CO2 + NADH + H+ 5 α-Ketoglutarate + NAD+ + HSCoA = Succinyl CoA + CO2 + NADH + H+ 6 Suc ...
PEP 535 - Exercise Biochemistry
... Enzymes function to do several things. 1) They increase reaction velocities so that there are meaningful rates of product formation. 2) They can operate in both directions so that reaction bioenergetics dictates directionality. 3) Some enzymes can be regulated by activators and inhibitors, allowing ...
... Enzymes function to do several things. 1) They increase reaction velocities so that there are meaningful rates of product formation. 2) They can operate in both directions so that reaction bioenergetics dictates directionality. 3) Some enzymes can be regulated by activators and inhibitors, allowing ...
Unit 2 - OCCC.edu
... Pyruvate is chemically ____________________ for the citric acid cycle A large, multienzyme complex catalyzes three reactions in the mitochondrial matrix A carbon atom is ________________ from pyruvate and released in ___________ The remaining two-carbon compound is _______________________, and a mo ...
... Pyruvate is chemically ____________________ for the citric acid cycle A large, multienzyme complex catalyzes three reactions in the mitochondrial matrix A carbon atom is ________________ from pyruvate and released in ___________ The remaining two-carbon compound is _______________________, and a mo ...
BSU Reading Guide Chapter 7 Respiration
... that is, a circle of reactions. In each turn of the cycle, a new acetyl group replaces the two CO 2 molecules lost, and more electrons are extracted. Note that a single glucose molecule produces two turns of the cycle, one for each of the two pyruvate molecules generated by glycolysis. ...
... that is, a circle of reactions. In each turn of the cycle, a new acetyl group replaces the two CO 2 molecules lost, and more electrons are extracted. Note that a single glucose molecule produces two turns of the cycle, one for each of the two pyruvate molecules generated by glycolysis. ...
De niet-covalente interacties
... • Association of apolar groups/molecules in water results in the release of water molecules that surround the apolar surface in a stiff, ice-like structure. • The released water molecules have more possibilities to interact with other water molecules in solution. • This results in an increase of the ...
... • Association of apolar groups/molecules in water results in the release of water molecules that surround the apolar surface in a stiff, ice-like structure. • The released water molecules have more possibilities to interact with other water molecules in solution. • This results in an increase of the ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... 2 Pyruvates (go to next step) 4 ATP (2 are gained) 2 NADH (go to ETC) ...
... 2 Pyruvates (go to next step) 4 ATP (2 are gained) 2 NADH (go to ETC) ...
AP Midterm Study Guide
... This is where majority of the ATP is created. There is a rotator protein in the between the intermembrane space and the Mitochondrial Matrix. Here the Hydrogen ions move back into the mitochondrial space. They go through the rotator protein which has 1 ADP and 1 phosphate group ready to join. The hy ...
... This is where majority of the ATP is created. There is a rotator protein in the between the intermembrane space and the Mitochondrial Matrix. Here the Hydrogen ions move back into the mitochondrial space. They go through the rotator protein which has 1 ADP and 1 phosphate group ready to join. The hy ...
Biology Content Standards
... Concept: Chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life. 1.1 Recognize that biological organisms are composed primarily of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, #, O, P, S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of ...
... Concept: Chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life. 1.1 Recognize that biological organisms are composed primarily of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, #, O, P, S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.