Chapter 9
... Transport Chain • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an ...
... Transport Chain • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an ...
Chapter 9
... Transport Chain • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an ...
... Transport Chain • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an ...
09_Lecture_Presentation
... Transport Chain • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an ...
... Transport Chain • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an ...
Exam 3 Q2 Review Sheet 1/2/11
... numbers for ATP used/made and NADH/FADH2 made for every step. (The following terms MUST be properly included: ETC, chemiosmosis, oxidative phosphorylation, electron carriers, mitochondria, NAD+, NADH, citrate, FAD, FADH2, glycolysis, glucose, cytosol, inner mitochondrial membrane, outer mitochondria ...
... numbers for ATP used/made and NADH/FADH2 made for every step. (The following terms MUST be properly included: ETC, chemiosmosis, oxidative phosphorylation, electron carriers, mitochondria, NAD+, NADH, citrate, FAD, FADH2, glycolysis, glucose, cytosol, inner mitochondrial membrane, outer mitochondria ...
Bis2A 07.1 Glycolysis
... words, these organisms only utilize or extract a small amount of the total potential energy within the glucose molecule. However, for many other organisms, including us humans, the end product pyruvate can be further oxidized by a series of additional reactions, which will be discussed later. In gen ...
... words, these organisms only utilize or extract a small amount of the total potential energy within the glucose molecule. However, for many other organisms, including us humans, the end product pyruvate can be further oxidized by a series of additional reactions, which will be discussed later. In gen ...
Bio1A - Lec 9 slides File
... and O2 and yields ATP • Fermentation is a partial degradation of sugars that occurs without O2 • Anaerobic respiration - similar, but consumes compounds other than O2 ...
... and O2 and yields ATP • Fermentation is a partial degradation of sugars that occurs without O2 • Anaerobic respiration - similar, but consumes compounds other than O2 ...
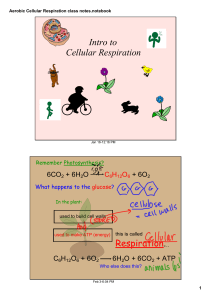
Aerobic Cellular Respiration class notes.notebook
... The Kreb Cycle is the first step in aerobic respiration. If oxygen is present after glycolysis, then some of the products of glycolysis will enter the mitochondria and begin aerobic respiration. ...
... The Kreb Cycle is the first step in aerobic respiration. If oxygen is present after glycolysis, then some of the products of glycolysis will enter the mitochondria and begin aerobic respiration. ...
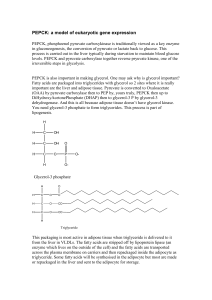
PEPCK: a model of eukaryotic gene expression
... PEPCK, phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase is traditionally viewed as a key enzyme in gluconeogenesis, the conversion of pyruvate or lactate back to glucose. This process is carried out in the liver typically during starvation to maintain blood glucose levels. PEPCK and pyruvate carboxylase together ...
... PEPCK, phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase is traditionally viewed as a key enzyme in gluconeogenesis, the conversion of pyruvate or lactate back to glucose. This process is carried out in the liver typically during starvation to maintain blood glucose levels. PEPCK and pyruvate carboxylase together ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 6: Allosteric regulation of enzymes
... Is there sufficient energy or substrate or reducing power to carry out the synthesis? Where there are parallel catabolic and synthetic pathways, regulation is especially important, because if both are allowed to run concurrently, it wastes energy: Glycolysis: gain 2 ATP and 2 NADH ...
... Is there sufficient energy or substrate or reducing power to carry out the synthesis? Where there are parallel catabolic and synthetic pathways, regulation is especially important, because if both are allowed to run concurrently, it wastes energy: Glycolysis: gain 2 ATP and 2 NADH ...
MLAB 1315-Hematology Fall 2007 Keri Brophy
... Autosomal recessive anemia Red cells are unable to retain water which results in hemolysis, due to cell shrinkage, distortion of shape and increased membrane rigidity Pyruvate kinase is an essential enzyme in the Glycolytic/Embden-Meyerhof pathway ...
... Autosomal recessive anemia Red cells are unable to retain water which results in hemolysis, due to cell shrinkage, distortion of shape and increased membrane rigidity Pyruvate kinase is an essential enzyme in the Glycolytic/Embden-Meyerhof pathway ...
Course Syllabus AG 408 – Nutritional Biochemistry Spring Semester, 2013 MWF 12:00-12:50
... bases and how transcription and translation is accomplished on the cellular level. Student Learning Outcomes: Students will learn the biochemical mechanisms of nutrition and metabolism. Student progress will be evaluated by exams over class content and discussions of current research papers involvin ...
... bases and how transcription and translation is accomplished on the cellular level. Student Learning Outcomes: Students will learn the biochemical mechanisms of nutrition and metabolism. Student progress will be evaluated by exams over class content and discussions of current research papers involvin ...
Protein mteabolism
... Creatine is present in blood in the free form, while in muscles it is gained phosphate group from ATP by creatine kinase (CK) to give creatine phosphate (creatine ~ p) or called phospho creatine (PCr.) and ATP is converted into ADP. creatine ~ p is the main storage form of energy in muscles and use ...
... Creatine is present in blood in the free form, while in muscles it is gained phosphate group from ATP by creatine kinase (CK) to give creatine phosphate (creatine ~ p) or called phospho creatine (PCr.) and ATP is converted into ADP. creatine ~ p is the main storage form of energy in muscles and use ...
Fate of Carbon Skeleton
... The last 3 steps occur in cytoplasm It utilizes 3 ATP and 4 high energy bonds It is catalyzed by five enzymes Any defect in one of these enzymes leads to ammonia intoxication ...
... The last 3 steps occur in cytoplasm It utilizes 3 ATP and 4 high energy bonds It is catalyzed by five enzymes Any defect in one of these enzymes leads to ammonia intoxication ...
Chapter 9
... B) His cells cannot move NADH from glycolysis into the mitochondria. C) His cells contain something that inhibits oxygen use in his mitochondria. D) His cells lack the enzyme in glycolysis that forms pyruvate. E) His cells have a defective electron transport chain, so glucose goes to lactate instead ...
... B) His cells cannot move NADH from glycolysis into the mitochondria. C) His cells contain something that inhibits oxygen use in his mitochondria. D) His cells lack the enzyme in glycolysis that forms pyruvate. E) His cells have a defective electron transport chain, so glucose goes to lactate instead ...
Chapter 3
... • Water helps regulate temperature. • All water taken in by an organism is eventually returned to the environment. ...
... • Water helps regulate temperature. • All water taken in by an organism is eventually returned to the environment. ...
NUTRICALM A Formula Designed to Calm and Sooth NutriCalm
... NUTRICALM A Formula Designed to Calm and Sooth NutriCalm features pharmaceutical grade L-tryptophan, an essential amino acid which is converted to serotonin in the brain. In addition, the herbs ashwaganda, theanine and valerian root help soothe and relax naturally, effectively and safely. 1 Capsule ...
... NUTRICALM A Formula Designed to Calm and Sooth NutriCalm features pharmaceutical grade L-tryptophan, an essential amino acid which is converted to serotonin in the brain. In addition, the herbs ashwaganda, theanine and valerian root help soothe and relax naturally, effectively and safely. 1 Capsule ...
Document
... activation energy to break chemical bonds and begin the reaction. Enzymes lower the barriers that normally prevent chemical reactions from occurring by decreasing the required activation energy. ...
... activation energy to break chemical bonds and begin the reaction. Enzymes lower the barriers that normally prevent chemical reactions from occurring by decreasing the required activation energy. ...
Biomolecules
... activation energy to break chemical bonds and begin the reaction. Enzymes lower the barriers that normally prevent chemical reactions from occurring by decreasing the required activation energy. ...
... activation energy to break chemical bonds and begin the reaction. Enzymes lower the barriers that normally prevent chemical reactions from occurring by decreasing the required activation energy. ...
The Chemical & Physical Basis of Life
... Decomposition reactions break large molecules into their constituent components. Biological molecules are generally broken down by addition of water molecules. This type of reaction is called hydrolysis. ...
... Decomposition reactions break large molecules into their constituent components. Biological molecules are generally broken down by addition of water molecules. This type of reaction is called hydrolysis. ...
Spring 97, Exam 1
... You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded under any circumstances. Some information which may be useful is provided on the bottom half of the next page. Explanations should be concise, a couple of sentences. You will need a calculator for this e ...
... You have 80 minutes for this exam. Exams written in pencil or erasable ink will not be re-graded under any circumstances. Some information which may be useful is provided on the bottom half of the next page. Explanations should be concise, a couple of sentences. You will need a calculator for this e ...
Vitamin-similar substances
... variety of formulas) as an anti-aging ingredient that replaces some of the natural antioxidant produced by the body, whether ingested or applied topically. When applied topically, Ubiquinone is thought to penetrate the skin easily, and reduce free radical damage via its antioxidant properties. • Ubi ...
... variety of formulas) as an anti-aging ingredient that replaces some of the natural antioxidant produced by the body, whether ingested or applied topically. When applied topically, Ubiquinone is thought to penetrate the skin easily, and reduce free radical damage via its antioxidant properties. • Ubi ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.