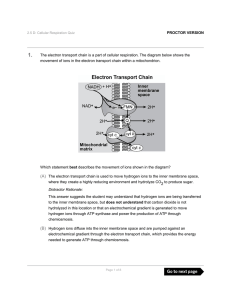
The electron transport chain is a part of cellular respiration. The
... This answer suggests the student may understand that the movement of electrons through the electron transport chain results in water molecules, but does not understand that the electrons are being passed from protein to protein through reduction-oxidation reactions within the membrane, and the elect ...
... This answer suggests the student may understand that the movement of electrons through the electron transport chain results in water molecules, but does not understand that the electrons are being passed from protein to protein through reduction-oxidation reactions within the membrane, and the elect ...
Document
... of the 3rd phase of Glucose Aerobic oxidation • Stage I The acetyl-CoA is completely oxidized into CO2, with electrons collected by NAD and FAD via a cyclic pathway (tricarboxylic acid cycle) • Stage II Electrons of NADH and FADH2 are transferred to O2 via a series carriers, producing H2O and a H+ g ...
... of the 3rd phase of Glucose Aerobic oxidation • Stage I The acetyl-CoA is completely oxidized into CO2, with electrons collected by NAD and FAD via a cyclic pathway (tricarboxylic acid cycle) • Stage II Electrons of NADH and FADH2 are transferred to O2 via a series carriers, producing H2O and a H+ g ...
STARVE-FEED CYCLE 1) WELL-FED STATE (food intake
... • ↑ fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (↑ if insulin is ↑): inhibits fru-1,6-bisphosphatase (= gluconeogenesis), activates 6-PFK-1 (= glycolysis) • ↑ citrate: inhibits 6-PFK-1 (= glycolysis), activates acetyl-CoA carboxylase (= fatty acid synthesis) • ↑ acetyl-CoA: inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase, activates ...
... • ↑ fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (↑ if insulin is ↑): inhibits fru-1,6-bisphosphatase (= gluconeogenesis), activates 6-PFK-1 (= glycolysis) • ↑ citrate: inhibits 6-PFK-1 (= glycolysis), activates acetyl-CoA carboxylase (= fatty acid synthesis) • ↑ acetyl-CoA: inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase, activates ...
Medical Biochemistry Review #2 By
... dehydrogenase and a-KGDH = a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. The GTP generated during the succinate thiokinase (succinyl-CoA synthetase) reaction is equivalent to a mole of ATP by virtue of the presence of nucleoside diphosphokinase. The 3 moles of NADH and 1 mole of FADH2 generated during each round o ...
... dehydrogenase and a-KGDH = a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. The GTP generated during the succinate thiokinase (succinyl-CoA synthetase) reaction is equivalent to a mole of ATP by virtue of the presence of nucleoside diphosphokinase. The 3 moles of NADH and 1 mole of FADH2 generated during each round o ...
Serine Proteases Teaching Exercises
... these two acidic amino acids are hard to distinguish from one another). Notice the distribution of charged amino acids. What significance might this distribution have in terms of function? b. Find examples of asparagine/glutamine, serine/threonine and histidine. Notice the distribution of polar amin ...
... these two acidic amino acids are hard to distinguish from one another). Notice the distribution of charged amino acids. What significance might this distribution have in terms of function? b. Find examples of asparagine/glutamine, serine/threonine and histidine. Notice the distribution of polar amin ...
Untangling the Spirals of Metabolic Disease: Primary Diagnoses and Secondary Effects:
... department by his mother, who reports that he has had a cold and fever for the past 2 days. He has been taking only small amounts of juice and no solid foods. When she tried to arouse him after his nap today, he was lethargic and unresponsive. Results of laboratory studies include a glucose concentr ...
... department by his mother, who reports that he has had a cold and fever for the past 2 days. He has been taking only small amounts of juice and no solid foods. When she tried to arouse him after his nap today, he was lethargic and unresponsive. Results of laboratory studies include a glucose concentr ...
Muscle
... ATP coupling stoichiometry determines the Keq for metabolic sequence • The energy release accompanying ATP hydrolysis is transmitted to the unfavorable reaction so that the overall free energy for the coupled process is negative (favorable) – DG0’ for ATP hydrolysis is a large negative number – ATP ...
... ATP coupling stoichiometry determines the Keq for metabolic sequence • The energy release accompanying ATP hydrolysis is transmitted to the unfavorable reaction so that the overall free energy for the coupled process is negative (favorable) – DG0’ for ATP hydrolysis is a large negative number – ATP ...
SBI4U Formal Lab Outline
... Exergonic reation = large amount of energy is released; would damage cells ...
... Exergonic reation = large amount of energy is released; would damage cells ...
Biochemistry Study Guide NITROGEN METABOLISM
... 2 ATP are required. Basically these are used to "charge" or "activate" ammonia with a highenergy phosphate bond, before we subsequently start urea synthesis. N-Acetylglutamate is absolutely required as a cofactor. This compound also serves a regulatory role in urea synthesis. The rate of carba ...
... 2 ATP are required. Basically these are used to "charge" or "activate" ammonia with a highenergy phosphate bond, before we subsequently start urea synthesis. N-Acetylglutamate is absolutely required as a cofactor. This compound also serves a regulatory role in urea synthesis. The rate of carba ...
Unit 2 Student Guided Notes Introduction Carbon is the basic
... associated with and function with each other. _______________________ is a well-known protein that is actually made up of the asociation of four 3 dimentional shapes around a central heme (iron containing) component. Denature The weaker hydrogen and ionic bonds of the tertiary structure ____________ ...
... associated with and function with each other. _______________________ is a well-known protein that is actually made up of the asociation of four 3 dimentional shapes around a central heme (iron containing) component. Denature The weaker hydrogen and ionic bonds of the tertiary structure ____________ ...
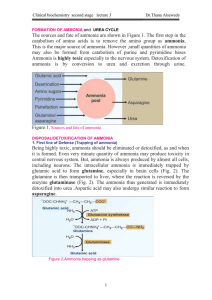
FORMATION OF AMMONIA
... ATPs.The urea cycle consumes 4 high energy phosphatebonds. However, fumarate formed in the4th step may be converted to malate. Malate when oxidised to oxaloacetate produces 1 NADH equivalent to 2.5 ATP. So net energy expenditureis only 1.5 high energy phosphates. The ureacycle and TCA cycle are inte ...
... ATPs.The urea cycle consumes 4 high energy phosphatebonds. However, fumarate formed in the4th step may be converted to malate. Malate when oxidised to oxaloacetate produces 1 NADH equivalent to 2.5 ATP. So net energy expenditureis only 1.5 high energy phosphates. The ureacycle and TCA cycle are inte ...
- humans ingest more proteins than needed for replacement of
... - any amino acid that can be degraded to pyruvate or citric acid cycle intermediate can serve as precursor in liver for synthesis of glucose (glycogenic or gluconeogenic) - some amino acids (try, phe) only part of their carbon skeleton can be used to synthesize glucose because the remainder is conve ...
... - any amino acid that can be degraded to pyruvate or citric acid cycle intermediate can serve as precursor in liver for synthesis of glucose (glycogenic or gluconeogenic) - some amino acids (try, phe) only part of their carbon skeleton can be used to synthesize glucose because the remainder is conve ...
electron transport chain
... producing hydrogen ions which are recombined with oxygen to produce water 2. Electrons produced from the split of NADH and FADH provide the energy for the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP 3. One molecule of glycogen can generate up to 37-39 molecules of ATP ...
... producing hydrogen ions which are recombined with oxygen to produce water 2. Electrons produced from the split of NADH and FADH provide the energy for the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP 3. One molecule of glycogen can generate up to 37-39 molecules of ATP ...
3. What are macromolecules? LARGE ORGANIC
... steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats are made of a glycerol (alcohol) and three fatty acid chains. This subunit is called a triglyceride. Color the glycerol molecule using the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as you did before. The fatty acid chain ...
... steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats are made of a glycerol (alcohol) and three fatty acid chains. This subunit is called a triglyceride. Color the glycerol molecule using the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as you did before. The fatty acid chain ...
Synthetic biology for engineering acetyl coenzyme a
... limit the transport of the end product out of the cell to pass through only a single membrane structure. As illustrated in Fig. 1 however, acetyl-CoA metabolism in yeast is quite complex, as acetyl-CoA is being synthesized in four different compartments (5). Furthermore, production in the cytosol go ...
... limit the transport of the end product out of the cell to pass through only a single membrane structure. As illustrated in Fig. 1 however, acetyl-CoA metabolism in yeast is quite complex, as acetyl-CoA is being synthesized in four different compartments (5). Furthermore, production in the cytosol go ...
MASTERY 2.01 ______ 2.04 ______ Biology I Name: Unit 2
... A. Enzymes and synthesis B. Amino acids and glucose C. Antigens and immunity D. Enzymes and ribosomes 43. Catalase is an enzyme that causes the following reaction: Hydrogen peroxide + Catalase Water + Oxygen + Catalase ...
... A. Enzymes and synthesis B. Amino acids and glucose C. Antigens and immunity D. Enzymes and ribosomes 43. Catalase is an enzyme that causes the following reaction: Hydrogen peroxide + Catalase Water + Oxygen + Catalase ...
Chapter 24 Fatty Acids as Energy Source Fatty Acids as Energy
... phytol in ruminant animals and thus appears in dairy products. ...
... phytol in ruminant animals and thus appears in dairy products. ...
... bilayer is +60 kJ/M. The standard free energy for the transfer of the sidechain of Cysteine to a nonpolar environment is –3 kJ/mol. You add large amounts of phospholipid to a 1 mM solution of Cys20 and allow the system to come to equilibrium. What is the concentration of Cys20 free in aqueous soluti ...
Lecture 36
... acid metabolism which converts free fatty acids in the cytosol into fatty acylCoA using the energy available from ATP and PPi hydrolysis. Carnitine acyltransferase I - catalyzes the commitment step in fatty acid oxidation which links fatty acyl-CoA molecules to the hydroxyl group of carnitine. The a ...
... acid metabolism which converts free fatty acids in the cytosol into fatty acylCoA using the energy available from ATP and PPi hydrolysis. Carnitine acyltransferase I - catalyzes the commitment step in fatty acid oxidation which links fatty acyl-CoA molecules to the hydroxyl group of carnitine. The a ...
Method S1.
... sonication (five 30 s pulses with intermitted one-min-cooling periods in Soniprep 150, UK) in 50 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM NaCl (pH 7.4; 900 µl), and cell debris was removed by centrifugation (30 min at 10000 g). Reaction was initiated adding 2.8 U of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase (type II, 40 U mg ...
... sonication (five 30 s pulses with intermitted one-min-cooling periods in Soniprep 150, UK) in 50 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM NaCl (pH 7.4; 900 µl), and cell debris was removed by centrifugation (30 min at 10000 g). Reaction was initiated adding 2.8 U of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase (type II, 40 U mg ...
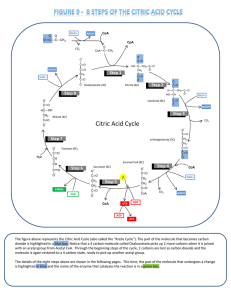
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.