RuBisCO and C4 plants
... As oxygen has been used up and carbon dioxide has been produced, this resembles aerobic respiration, so the process has been called photorespiration (even though ATP is used up, not made). Photorespiration wastes both carbon and energy, reducing the efficiency of photosynthesis. The C3 pathway of ph ...
... As oxygen has been used up and carbon dioxide has been produced, this resembles aerobic respiration, so the process has been called photorespiration (even though ATP is used up, not made). Photorespiration wastes both carbon and energy, reducing the efficiency of photosynthesis. The C3 pathway of ph ...
Slide 1
... hydrophobic, neutral molecule made from reaction of OH group of glycerol and COO- group of fatty acids. Fatty acids are made up of a long hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain (highly reduced) and a carboxylic acid polar group. Different kinds of fatty acids play very important structural (as major componen ...
... hydrophobic, neutral molecule made from reaction of OH group of glycerol and COO- group of fatty acids. Fatty acids are made up of a long hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain (highly reduced) and a carboxylic acid polar group. Different kinds of fatty acids play very important structural (as major componen ...
Midterm_Review
... 5. What is the formal charge of all atoms in ozone, O3? 6. How many resonance forms are there for NO3-? Draw them, with curved arrows showing movement of electrons. ...
... 5. What is the formal charge of all atoms in ozone, O3? 6. How many resonance forms are there for NO3-? Draw them, with curved arrows showing movement of electrons. ...
WJEC Biology / Human Biology BY4 Question
... they are provided with nutrients by the plant and protected from oxygen. Oxygen inhibits the enzyme (nitrogenase) required for nitrogen fixation. Azotobacter are free-living in soil and have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen by converting it to ammonia. Like other nitrogenases, Azotobacter nit ...
... they are provided with nutrients by the plant and protected from oxygen. Oxygen inhibits the enzyme (nitrogenase) required for nitrogen fixation. Azotobacter are free-living in soil and have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen by converting it to ammonia. Like other nitrogenases, Azotobacter nit ...
PROTEIN METABOLISM
... but many liver enzymes turn over in a couple of days. Some regulatory enzymes have half-lives measured in hours or minutes. The majority of the amino acids released during protein degradation are promptly reincorporated into fresh proteins. ...
... but many liver enzymes turn over in a couple of days. Some regulatory enzymes have half-lives measured in hours or minutes. The majority of the amino acids released during protein degradation are promptly reincorporated into fresh proteins. ...
File
... B. The molecule must be stored around his waist before the energy can be used C. The molecule has no energy. It will be used to create energy as he sleeps. D. He will get a fever. Question 10 Which of the following is true about protein molecules? A. The shape and folded structure of a protein molec ...
... B. The molecule must be stored around his waist before the energy can be used C. The molecule has no energy. It will be used to create energy as he sleeps. D. He will get a fever. Question 10 Which of the following is true about protein molecules? A. The shape and folded structure of a protein molec ...
Chapter 16 Section A: Control and Integration of Carbohydrate
... What is the fate of glucose absorbed skeletal muscle during the absorptive phase? In adipocytes, what is the fate of glucose during the absorptive phase? What are the multiple fates of glucose in liver cells (hepatocytes) during the absorptive phase? What are lipoproteins and what is their purpose? ...
... What is the fate of glucose absorbed skeletal muscle during the absorptive phase? In adipocytes, what is the fate of glucose during the absorptive phase? What are the multiple fates of glucose in liver cells (hepatocytes) during the absorptive phase? What are lipoproteins and what is their purpose? ...
The effects of calcium ions on the activites of hexokinase
... enzymes of both glycolysis and the cycle will reflect the maximum rates of these two processes; and therefore maximum activities of x-glycerophosphate oxidase (EC 1.1.2.1) and phosphofructokinase (or hexokinase plus phosphorylase) have been measured in crude muscle extracts. For insect flight muscle ...
... enzymes of both glycolysis and the cycle will reflect the maximum rates of these two processes; and therefore maximum activities of x-glycerophosphate oxidase (EC 1.1.2.1) and phosphofructokinase (or hexokinase plus phosphorylase) have been measured in crude muscle extracts. For insect flight muscle ...
acids and bases - Althea`s Academy
... Acts on subs high in protein and stain them yellow, producing a nitro cmpd known as xanthoprotein Pharmacology of the nitrate ion: 1. It has no specific action in the body 2. Potassium nitrate is a neutral salt but is the most potent diuretic of all the salts it acts by upsetting th eionic balance ...
... Acts on subs high in protein and stain them yellow, producing a nitro cmpd known as xanthoprotein Pharmacology of the nitrate ion: 1. It has no specific action in the body 2. Potassium nitrate is a neutral salt but is the most potent diuretic of all the salts it acts by upsetting th eionic balance ...
1. Describe the properties of the following apical and basolateral
... a. What enzyme complex is involved in this disease and what are its components? What reaction does this complex catalyze? Branched chain keto acid dehydrogenase. Three components can be affected: E1-keto acid decarboxylase (thiamine dependent) either alpha (IA) or beta (IB); E2-dihydrolipoyl acyltr ...
... a. What enzyme complex is involved in this disease and what are its components? What reaction does this complex catalyze? Branched chain keto acid dehydrogenase. Three components can be affected: E1-keto acid decarboxylase (thiamine dependent) either alpha (IA) or beta (IB); E2-dihydrolipoyl acyltr ...
Carbohydrates , lipids, and proteins
... Are the reverse of hydrolysis Condensation reactions occur to re-form larger biochemical molecules Water molecules are products rather than reactants Also requires a different type of enzyme ...
... Are the reverse of hydrolysis Condensation reactions occur to re-form larger biochemical molecules Water molecules are products rather than reactants Also requires a different type of enzyme ...
glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids
... part of a hydrogen atom (H), or a hydride ion (H-) . In stage 3, the citric acid (Krebs, or tricarboxylic acid [TCA] ) cycle oxidizes acetyl- CoA to C02. The energy released in this process is primarily conserved by reducing NAD to NADH or FAD to FADH2. The final stage is oxidative phosphorylati ...
... part of a hydrogen atom (H), or a hydride ion (H-) . In stage 3, the citric acid (Krebs, or tricarboxylic acid [TCA] ) cycle oxidizes acetyl- CoA to C02. The energy released in this process is primarily conserved by reducing NAD to NADH or FAD to FADH2. The final stage is oxidative phosphorylati ...
cellular respiration
... Indicate if each of the following characteristics / descriptions is true of Substratelevel and Oxidative phosphorylation. ______ Produce ATP by adding a phosphate to ADP ______ Involves the direct transfer of a phosphate from an intermediate to ADP ______ Couples the addition of a phosphate to ADP w ...
... Indicate if each of the following characteristics / descriptions is true of Substratelevel and Oxidative phosphorylation. ______ Produce ATP by adding a phosphate to ADP ______ Involves the direct transfer of a phosphate from an intermediate to ADP ______ Couples the addition of a phosphate to ADP w ...
Biology Organic Molecules Notes
... Joined together by peptide bonds Dipeptide: two amino acids Polypeptide: very long chain of amino acids Proteins all have a different shape but are all globular ...
... Joined together by peptide bonds Dipeptide: two amino acids Polypeptide: very long chain of amino acids Proteins all have a different shape but are all globular ...
Molecules of Life
... • Enzymes – Enzymes speed up chemical reactions and bind to specific substrates. – The binding of a substrate with an enzyme causes a change in the enzyme’s shape and reduces the activation energy of the reaction. ...
... • Enzymes – Enzymes speed up chemical reactions and bind to specific substrates. – The binding of a substrate with an enzyme causes a change in the enzyme’s shape and reduces the activation energy of the reaction. ...
BIOANALYTICAL/CLINICAL ANALYSIS
... T3 and T4 Important-Assayed by Immunology,old method RadioImmunoassay,Now Enzyme Immunoassay with Antibodies ...
... T3 and T4 Important-Assayed by Immunology,old method RadioImmunoassay,Now Enzyme Immunoassay with Antibodies ...
Intro to Metabolism II and Glycolysis
... XXIX. Relative changes in [ATP] and [AMP] when ATP is consumed [S29] a. When there is plenty of ATP, glycolysis is inhibited & when ATP goes down, glycolysis is activated. b. Glycolysis does not occur though because of changes in ATP but instead due to the change in concentration of AMP. c. Just a 1 ...
... XXIX. Relative changes in [ATP] and [AMP] when ATP is consumed [S29] a. When there is plenty of ATP, glycolysis is inhibited & when ATP goes down, glycolysis is activated. b. Glycolysis does not occur though because of changes in ATP but instead due to the change in concentration of AMP. c. Just a 1 ...
Study Guide
... conformation, 2,3-BPG, Bohr effect, examples of fibrous structural proteins, microfilaments and microtubules, motor protein mechanisms, enzyme rate enhancement, recognizing 6 classes of enzyme catalyzed reactions, chemical mechanisms of catalysis, covalent catalysis, pH effects on enzymes, binding e ...
... conformation, 2,3-BPG, Bohr effect, examples of fibrous structural proteins, microfilaments and microtubules, motor protein mechanisms, enzyme rate enhancement, recognizing 6 classes of enzyme catalyzed reactions, chemical mechanisms of catalysis, covalent catalysis, pH effects on enzymes, binding e ...
Amino Acids - University of Houston
... The CORN method for L isomers: put the hydrogen towards you and read off CO R N clockwise around the Ca This works for all amino acids. CORN LAW amino acid with L configuration ...
... The CORN method for L isomers: put the hydrogen towards you and read off CO R N clockwise around the Ca This works for all amino acids. CORN LAW amino acid with L configuration ...
Model of Skeletal Muscle Energy Metabolism
... MATERIALS S2: METABOLIC REACTIONS FLUX EXPRESSIONS The flux expressions for the compartmentalized lumped metabolic reactions that convert substrates to products in the two subcellular compartments (cytosol and mitochondria) in coupled with the energy controller pairs ATP-ADP and NADH-NAD+ are writte ...
... MATERIALS S2: METABOLIC REACTIONS FLUX EXPRESSIONS The flux expressions for the compartmentalized lumped metabolic reactions that convert substrates to products in the two subcellular compartments (cytosol and mitochondria) in coupled with the energy controller pairs ATP-ADP and NADH-NAD+ are writte ...
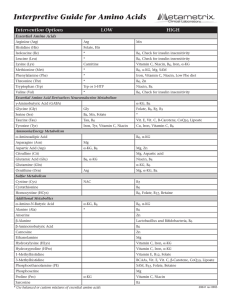
Interpretive Guide for Amino Acids
... α-Amino-N-butyric acid Low - possible increased need for the nutrients which aid in threonine metabolism from which this AA is derived. These include α-KG and B6. High - inadequate utilization of this AA for cellular energy generation. Alpha-ABA is converted to succinyl Co-A for use in the citric ac ...
... α-Amino-N-butyric acid Low - possible increased need for the nutrients which aid in threonine metabolism from which this AA is derived. These include α-KG and B6. High - inadequate utilization of this AA for cellular energy generation. Alpha-ABA is converted to succinyl Co-A for use in the citric ac ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.