Physiological effects of exercise
... inhibition and is sustained by autonomic sympathetic responses and carbon dioxide acting on the medulla. The efficacy of systolic contraction is particularly important in trained athletes who can achieve significant increases in cardiac output as a consequence of hypertrophy of cardiac muscle. Table ...
... inhibition and is sustained by autonomic sympathetic responses and carbon dioxide acting on the medulla. The efficacy of systolic contraction is particularly important in trained athletes who can achieve significant increases in cardiac output as a consequence of hypertrophy of cardiac muscle. Table ...
Summer Assignment
... 5. Hydrogen gas and bromine gas react to form hydrogen bromide gas. a. Write a balanced equation for this reaction. b. 3.2 grams of hydrogen react with 9.5 grams of bromine. Which is the limiting reagent? c. How many grams of hydrogen bromide gas can be produced using the amounts in (b)? d. How many ...
... 5. Hydrogen gas and bromine gas react to form hydrogen bromide gas. a. Write a balanced equation for this reaction. b. 3.2 grams of hydrogen react with 9.5 grams of bromine. Which is the limiting reagent? c. How many grams of hydrogen bromide gas can be produced using the amounts in (b)? d. How many ...
Organic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning
... ribose sugar, an adenine base, and three phosphate groups. ATP releases free energy when its phosphate bonds are broken, and thus supplies ready energy to the cell. ...
... ribose sugar, an adenine base, and three phosphate groups. ATP releases free energy when its phosphate bonds are broken, and thus supplies ready energy to the cell. ...
Glucose homeostasis in the blood (2) – un-storing energy
... be used to maintain those muscles. Therefore even a body builder can’t last a week on their glycogen! After the glycogen stores have been exhausted new glucose still needs to enter the blood stream for Figure 9: In long-term the brain and the red blood cells. The liver will begin to rely more on fas ...
... be used to maintain those muscles. Therefore even a body builder can’t last a week on their glycogen! After the glycogen stores have been exhausted new glucose still needs to enter the blood stream for Figure 9: In long-term the brain and the red blood cells. The liver will begin to rely more on fas ...
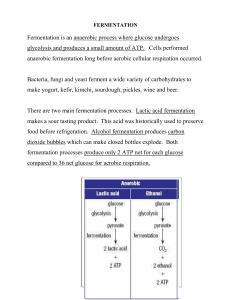
FERMENTATION
... FERMENTATION Fermentation is an __________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________. Cells performed anaerobic fermentation long before aerobic cellular respiration occurred. ...
... FERMENTATION Fermentation is an __________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________. Cells performed anaerobic fermentation long before aerobic cellular respiration occurred. ...
Metabolic Disorders
... Every metabolic disease has several forms that vary in AGE OF ONSET , clinical severity and, often, MODE OF INHERITANCE. ...
... Every metabolic disease has several forms that vary in AGE OF ONSET , clinical severity and, often, MODE OF INHERITANCE. ...
2_3 Slides - Lipids _ Carbs
... • A positive correlation has been found between saturated fatty acid intake and rates of CHD in many studies. • Correlation ≠ causation. Another factor, e.g. dietary fiber could be responsible. • There are populations that do not fit the correlation such as the Masai of Kenya. They have a diet that ...
... • A positive correlation has been found between saturated fatty acid intake and rates of CHD in many studies. • Correlation ≠ causation. Another factor, e.g. dietary fiber could be responsible. • There are populations that do not fit the correlation such as the Masai of Kenya. They have a diet that ...
BC-O5 Wangila Folin-Ciocalteau reagent
... The Folin-Ciocalteu (FC) Assay was developed in 1927 as a colorimetric assay for tyrosine. The FC assay uses a mixture containing sodium molybdate, sodium tungstate, and other reagents. In the presence of phenols, it produces a blue color which absorbs at 765 nm. It is believed that the blue color i ...
... The Folin-Ciocalteu (FC) Assay was developed in 1927 as a colorimetric assay for tyrosine. The FC assay uses a mixture containing sodium molybdate, sodium tungstate, and other reagents. In the presence of phenols, it produces a blue color which absorbs at 765 nm. It is believed that the blue color i ...
25., Fatty ocid oxidation
... In Chapter 24 we saw that the carbons of the aceryl CoA produced by the catabolism of glucose can be completely oxidized to carbon dioxide in the citric acid cycle. Each molecule of acetyl CoA oxidized in this fashion yields enough energy to make one molecule of AIB one molecule of FADH2,and three m ...
... In Chapter 24 we saw that the carbons of the aceryl CoA produced by the catabolism of glucose can be completely oxidized to carbon dioxide in the citric acid cycle. Each molecule of acetyl CoA oxidized in this fashion yields enough energy to make one molecule of AIB one molecule of FADH2,and three m ...
Chapter 25 Chapter Topics Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
... • Different “Families” according to distance of last double bond from methyl end: • ω-9 (oleic acid, 9-C18:1 ) • ω-7 (palmitoleic acid, 9-C16:1) • ω-6 (linoleic acid, 9,12-C18:2)—only from plants. • Arachidonic acid made from dietary linoleic acid (Fig 25.15) • ω-3 (alpha-linolenic acid, 9,12,15-C18 ...
... • Different “Families” according to distance of last double bond from methyl end: • ω-9 (oleic acid, 9-C18:1 ) • ω-7 (palmitoleic acid, 9-C16:1) • ω-6 (linoleic acid, 9,12-C18:2)—only from plants. • Arachidonic acid made from dietary linoleic acid (Fig 25.15) • ω-3 (alpha-linolenic acid, 9,12,15-C18 ...
VILLIN MODEL CONSTRUCTION
... The villin model is constructed of in three pieces. The first piece consists of amino acids 1 – 2. The second piece is amino acids 3 –7. The final piece is amino acids 8 – 36. The larger piece presented several problems. The final position that individual amino acid should take had to be marked off ...
... The villin model is constructed of in three pieces. The first piece consists of amino acids 1 – 2. The second piece is amino acids 3 –7. The final piece is amino acids 8 – 36. The larger piece presented several problems. The final position that individual amino acid should take had to be marked off ...
Human Physiology - Orange Coast College
... Pyruvic acid converted to glucose-6phosphate: Intermediate for glycogen. Converted to free glucose. Gluconeogenesis: conversion to noncarbohydrate molecules through pyruvic acid to glucose. ...
... Pyruvic acid converted to glucose-6phosphate: Intermediate for glycogen. Converted to free glucose. Gluconeogenesis: conversion to noncarbohydrate molecules through pyruvic acid to glucose. ...
Chapter 28
... • Thelarche - development of breasts • Pubarche - growth of pubic and axillary hair; apocrine and sebaceous glands ...
... • Thelarche - development of breasts • Pubarche - growth of pubic and axillary hair; apocrine and sebaceous glands ...
introduction
... appropriate nitrogen sources and cofactors. Recently, amino acids are isolated from farm wastes ( Tsuruoka, 1987). Production of Lamino acids by fermentation is now being used in industrial scale and this potentiality of microbes have been exploited commercially in countries like Japan and USA (Dula ...
... appropriate nitrogen sources and cofactors. Recently, amino acids are isolated from farm wastes ( Tsuruoka, 1987). Production of Lamino acids by fermentation is now being used in industrial scale and this potentiality of microbes have been exploited commercially in countries like Japan and USA (Dula ...
2008 exam with answers
... Each yields 2 net ATPs. Glucose because 4 ATPs are produced in glycolysis but 2 ATPs need be invested. 3-phosphoglycerate yields 1 net ATP per mole at the last step of glycolysis, pyruvate would be the excreted end product. and NAD is not involved. 2C. Aerobically, ___ one mole of pyruvate, _X__ one ...
... Each yields 2 net ATPs. Glucose because 4 ATPs are produced in glycolysis but 2 ATPs need be invested. 3-phosphoglycerate yields 1 net ATP per mole at the last step of glycolysis, pyruvate would be the excreted end product. and NAD is not involved. 2C. Aerobically, ___ one mole of pyruvate, _X__ one ...
Protein Calorie Malnutrition
... 1-2 kg LBM over first 7 days Lethal depletion after 3 weeks if no adaptation occurs - by the end of 2-3 weeks, decrease muscle protein catabolism to <1/3 of initial (not yet understood) ...
... 1-2 kg LBM over first 7 days Lethal depletion after 3 weeks if no adaptation occurs - by the end of 2-3 weeks, decrease muscle protein catabolism to <1/3 of initial (not yet understood) ...
the Acetyl-Coenzyme A
... media containing ethanol as the sole carbon source, demonstrating that there are alternative pathways leading to acetyl-CoA under these conditions. KEY W O R D S Acetyl-coenzyme ...
... media containing ethanol as the sole carbon source, demonstrating that there are alternative pathways leading to acetyl-CoA under these conditions. KEY W O R D S Acetyl-coenzyme ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide
... the pigment that produces the yellow and orange fall leaf colors these organisms get their energy from food by cellular respiration this is an enzyme assisted anaerobic process that breaks down glucose to pyruvate this are light absorbing substances this is a metabolic process that requires oxygen i ...
... the pigment that produces the yellow and orange fall leaf colors these organisms get their energy from food by cellular respiration this is an enzyme assisted anaerobic process that breaks down glucose to pyruvate this are light absorbing substances this is a metabolic process that requires oxygen i ...
Enzyme Structure and Function
... • An enzyme (and any other protein) is made by linking amino acids together in the correct order (sequence). ...
... • An enzyme (and any other protein) is made by linking amino acids together in the correct order (sequence). ...
Seed Germination and Reserve Mobilization
... 2. the glyoxysome, where the FFA are oxidized, and synthesis of succinate occurs via the glyoxylate cycle; 3. the mitochondrion, in which succinate is converted to malate or oxaloacetate. The latter two are processed further in the cytosol to yield sucrose (Figure 5). Initial TAG hydrolysis (lipolys ...
... 2. the glyoxysome, where the FFA are oxidized, and synthesis of succinate occurs via the glyoxylate cycle; 3. the mitochondrion, in which succinate is converted to malate or oxaloacetate. The latter two are processed further in the cytosol to yield sucrose (Figure 5). Initial TAG hydrolysis (lipolys ...
Biochemical Patterns of Some Heterotrophic Marine
... noted that aspartic acid and glutamic acid were present in large amounts when acetate-C and NH4-Nwere the only nutrients present in the medium. Strain TS/O-~ differed from the others in that histidine and arginine were absent; m/25-1 had the largest number of amino acids in the pool. Biochemical act ...
... noted that aspartic acid and glutamic acid were present in large amounts when acetate-C and NH4-Nwere the only nutrients present in the medium. Strain TS/O-~ differed from the others in that histidine and arginine were absent; m/25-1 had the largest number of amino acids in the pool. Biochemical act ...
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 118, pp. 7646.
... bound to proteins (as sialoglycoproteins), lipids (as gangliosides), or other sialic acids (as polysialic acids linked to other glycoconjugates). Chapter 2 gives a table of 36 naturally occurring sialic acids. This includes many N-acetyl and N-glycolyl derivatives and one deaminated form called Kdn ...
... bound to proteins (as sialoglycoproteins), lipids (as gangliosides), or other sialic acids (as polysialic acids linked to other glycoconjugates). Chapter 2 gives a table of 36 naturally occurring sialic acids. This includes many N-acetyl and N-glycolyl derivatives and one deaminated form called Kdn ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.