Chemistry Spell check on
... 1 Check that the answer sheet provided is for Chemistry Intermediate 2 (Section A). 2 For this section of the examination you must use an HB pencil and, where necessary, an eraser. 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number ...
... 1 Check that the answer sheet provided is for Chemistry Intermediate 2 (Section A). 2 For this section of the examination you must use an HB pencil and, where necessary, an eraser. 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish Candidate Number ...
CH2 Organic Chem notes only OrganicChem13
... Albinism: lack of pigment in skin (can be caused by many problems) One type is caused by lack of enzyme that metabolizes tyrosine. Cannot make pigment melanin. Hypercholesterolemia: reduced ability to remove cholesterol from the blood. Galactosemia: lack of enzyme that catalyzes the conversion o ...
... Albinism: lack of pigment in skin (can be caused by many problems) One type is caused by lack of enzyme that metabolizes tyrosine. Cannot make pigment melanin. Hypercholesterolemia: reduced ability to remove cholesterol from the blood. Galactosemia: lack of enzyme that catalyzes the conversion o ...
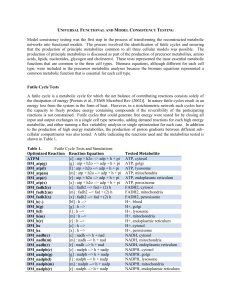
Universal Functional and Model Consistency Testing
... Validation of the myocyte network included simulating the ATP production from one mole of octadecenoate (C18:1), palmitate (C16:0) and pentadecanoate (C15:0) (Table 2). To demonstrate how each of these fatty acids could be catabolized to produce energy, the influx of all other carbon sources includ ...
... Validation of the myocyte network included simulating the ATP production from one mole of octadecenoate (C18:1), palmitate (C16:0) and pentadecanoate (C15:0) (Table 2). To demonstrate how each of these fatty acids could be catabolized to produce energy, the influx of all other carbon sources includ ...
Qualitative Analysis of Biomolecules
... each amino acid. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, though other elements are found in the side-chains of certain amino acids. Proteins are biological macromolecules that are built up of proteinogenic amino acids linked by peptide bounds. Most of the protei ...
... each amino acid. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, though other elements are found in the side-chains of certain amino acids. Proteins are biological macromolecules that are built up of proteinogenic amino acids linked by peptide bounds. Most of the protei ...
Biological Molecules: Structure and Methods of Analysis
... a substance changes form a solid to a liquid. Molecules in a solid state are packed together in an orderly fashion with very much movement, while molecules in a liquid state are moving around in a random pattern termed Brownian motion. Therefore, the melting point is affected by anything that affect ...
... a substance changes form a solid to a liquid. Molecules in a solid state are packed together in an orderly fashion with very much movement, while molecules in a liquid state are moving around in a random pattern termed Brownian motion. Therefore, the melting point is affected by anything that affect ...
Ch. 5 - Macromolecules
... • The structure of phospholipids – Results in a bilayer arrangement found in cell membranes ...
... • The structure of phospholipids – Results in a bilayer arrangement found in cell membranes ...
BI25M1
... HCl denatures proteins and makes them accessible to degradative enzymes. The zymogen pepsinogen is cleaved to pepsin autocatalytically, and, later, by pepsin itself. Pepsin cleaves proteins to small polypeptides. ...
... HCl denatures proteins and makes them accessible to degradative enzymes. The zymogen pepsinogen is cleaved to pepsin autocatalytically, and, later, by pepsin itself. Pepsin cleaves proteins to small polypeptides. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 08. The dipeptide contains one peptide bond. 09. Saturated fatty acids contain double bond. 10. IUB refers to International Union of Biochemistry. III. Complete the following ...
... 08. The dipeptide contains one peptide bond. 09. Saturated fatty acids contain double bond. 10. IUB refers to International Union of Biochemistry. III. Complete the following ...
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper – 2015
... affinity towards oxygen and so cannot be reduced by carbon. (Note: Error in the question. Zinc oxide can be reduced to zinc metal by using carbon, but aluminium oxide cannot be reduced by a reducing agent.) (ii) Carbon tetrachloride is made of individual covalently bonded molecules, CCl 4. In additi ...
... affinity towards oxygen and so cannot be reduced by carbon. (Note: Error in the question. Zinc oxide can be reduced to zinc metal by using carbon, but aluminium oxide cannot be reduced by a reducing agent.) (ii) Carbon tetrachloride is made of individual covalently bonded molecules, CCl 4. In additi ...
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Phosphatase Deficiency
... and although the lactate t o pyruvate ratio was abnorn~allyhigh, there was no apparent hypoxia. The absence of hypoglycemia at any point during the course of the patient's disease suggested that the lactic acidosis was not due to a primary block in the gluconeogenic pathway such as is seen in pyruva ...
... and although the lactate t o pyruvate ratio was abnorn~allyhigh, there was no apparent hypoxia. The absence of hypoglycemia at any point during the course of the patient's disease suggested that the lactic acidosis was not due to a primary block in the gluconeogenic pathway such as is seen in pyruva ...
5 The structure and function of large biological molecules
... It has 4 valence electrons It can form up to 4 covalent bonds These can be single, double, or triple cov. Bonds It can form large molecules. These molecules and be chains, ring-shaped, or branched ...
... It has 4 valence electrons It can form up to 4 covalent bonds These can be single, double, or triple cov. Bonds It can form large molecules. These molecules and be chains, ring-shaped, or branched ...
amino acids properties
... the amino acids and is in many cases contributed by its α-amino and αcarboxyl group . Amino acids can posses other specific properties dictated ...
... the amino acids and is in many cases contributed by its α-amino and αcarboxyl group . Amino acids can posses other specific properties dictated ...
Chapter 2 - Saladin
... Ions, Electrolytes, and Free Radicals • Anion—atom that gains electrons (net negative charge) • Cation—atom that loses an electron (net positive charge) • Ions with opposite charges are attracted to each other Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or displ ...
... Ions, Electrolytes, and Free Radicals • Anion—atom that gains electrons (net negative charge) • Cation—atom that loses an electron (net positive charge) • Ions with opposite charges are attracted to each other Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or displ ...
CBSE/12th Class/2010/CHEMISTRY
... (i) State one use each of DDT and iodoform. (ii) Which compound in the following couples will react faster in SN2 displacement and why? (a) 1-Bromopentane or 2-bromopentane (b) 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane or 2-bromo-2methylbutane. ...
... (i) State one use each of DDT and iodoform. (ii) Which compound in the following couples will react faster in SN2 displacement and why? (a) 1-Bromopentane or 2-bromopentane (b) 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane or 2-bromo-2methylbutane. ...
This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy
... an easy phase separation. In the subsequent step, Section 3 including reactions (9) and (10), the separation of HI from L − 2, the heavier iodine/iodide–water phase, is the most critical scenario of the cycle [4] and believed to be the most expensive and energy-consuming step [5]. After establishing ...
... an easy phase separation. In the subsequent step, Section 3 including reactions (9) and (10), the separation of HI from L − 2, the heavier iodine/iodide–water phase, is the most critical scenario of the cycle [4] and believed to be the most expensive and energy-consuming step [5]. After establishing ...
RESEARCH NOTES
... sensitive to the presence of certain omino acids and vitamins. The mutont strains used were Hb146 (FGSC#492) ond H3791 ...
... sensitive to the presence of certain omino acids and vitamins. The mutont strains used were Hb146 (FGSC#492) ond H3791 ...
Biol 1107 Biomolecules Lab Fall 2003
... a substance changes form a solid to a liquid. Molecules in a solid state are packed together in an orderly fashion with very much movement, while molecules in a liquid state are moving around in a random pattern termed Brownian motion. Therefore, the melting point is affected by anything that affect ...
... a substance changes form a solid to a liquid. Molecules in a solid state are packed together in an orderly fashion with very much movement, while molecules in a liquid state are moving around in a random pattern termed Brownian motion. Therefore, the melting point is affected by anything that affect ...
Feline Attractant, cis,trans-Nepetalactone: Metabolism in
... Collagen Gels: Design for a Vitreous Replacement Abstract. Clear, stable gels have been prepared from purified tropocollagen from calf skin; the collagen was solubilized with a proteolytic enzyme (Proctase) and stabilized by ultraviolet irradiation under nitrogen. These gels are clear, possess alter ...
... Collagen Gels: Design for a Vitreous Replacement Abstract. Clear, stable gels have been prepared from purified tropocollagen from calf skin; the collagen was solubilized with a proteolytic enzyme (Proctase) and stabilized by ultraviolet irradiation under nitrogen. These gels are clear, possess alter ...
Direct Comparison DNA and Amino Acid Sequences Based on a
... results than with BLASTX. Since this method is based on dynamic programming calculation, it requires considerable computational time. To reduce the computation time, we performed a parallel computation on a workstation cluster using a PVM programming. When using up to 11 CPUs, the computational time ...
... results than with BLASTX. Since this method is based on dynamic programming calculation, it requires considerable computational time. To reduce the computation time, we performed a parallel computation on a workstation cluster using a PVM programming. When using up to 11 CPUs, the computational time ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.