2016 Final review level
... ____When one species benefits and the other is harmed. ____When one species is hunted and eaten. ____When one species benefits but the other is neither helped or harmed. Biochemical Cycles Review the following cycles: (carbon, nitrogen, water) ...
... ____When one species benefits and the other is harmed. ____When one species is hunted and eaten. ____When one species benefits but the other is neither helped or harmed. Biochemical Cycles Review the following cycles: (carbon, nitrogen, water) ...
Ch. 9 Cellular Respiration
... NADH and FADH2 are from Krebs and glycolysis NADH and FADH2 release H to these reactions H is split into H+ and eThe e- move through the carriers to the biggest e- acceptor (moving down hill – releasing potential energy and increasing ...
... NADH and FADH2 are from Krebs and glycolysis NADH and FADH2 release H to these reactions H is split into H+ and eThe e- move through the carriers to the biggest e- acceptor (moving down hill – releasing potential energy and increasing ...
Topic 17
... • Heterotroph (depends on other life forms) – Organic molecules – Ex. Sugars, proteins, lipids ...
... • Heterotroph (depends on other life forms) – Organic molecules – Ex. Sugars, proteins, lipids ...
Grade Four Science Assessment
... Layer B if you found both plant fossils and animal fossils in the same layer? ...
... Layer B if you found both plant fossils and animal fossils in the same layer? ...
Unit 2 - OCCC.edu
... ________________________ is the process of breaking food down into molecules small enough to absorb _______________________ digestion, including chewing, increases the surface area of food _______________________ digestion splits food into small molecules that can pass through membranes; these are u ...
... ________________________ is the process of breaking food down into molecules small enough to absorb _______________________ digestion, including chewing, increases the surface area of food _______________________ digestion splits food into small molecules that can pass through membranes; these are u ...
The Biosphere – Ch
... Trophic Levels and Ecological Pyramids Each step in a food chain or food web is called a trophic level. Producers make up the first trophic level. Consumers make up higher trophic levels. Each consumer depends on the trophic level below it for energy. An ecological pyramid is a diagram that shows th ...
... Trophic Levels and Ecological Pyramids Each step in a food chain or food web is called a trophic level. Producers make up the first trophic level. Consumers make up higher trophic levels. Each consumer depends on the trophic level below it for energy. An ecological pyramid is a diagram that shows th ...
Bacterial Metabolism and Growth
... – All NADH molecules formed in the previous steps bring the electrons they have gained to the electron ...
... – All NADH molecules formed in the previous steps bring the electrons they have gained to the electron ...
Ecosystems, Energy And Production
... A fairly constant relationship exists between chlorophyll and photosynthesis at any given light intensity. Assimilation number – The milligrams of C fixed per m3 during an average hour of daylight is divided by the mg of chlorophyll a in the same volume. Mg C per hour ___________ mg chlorophyll a = ...
... A fairly constant relationship exists between chlorophyll and photosynthesis at any given light intensity. Assimilation number – The milligrams of C fixed per m3 during an average hour of daylight is divided by the mg of chlorophyll a in the same volume. Mg C per hour ___________ mg chlorophyll a = ...
Ecology Part 3
... In the Carbon Cycle, carbon is recycled mainly through the process of photosynthesis, cellular respiration and burning of fossil fuels. Carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbon monoxide emissions have been increasing in the atmosphere. It allows light energy in, but traps the reflected heat energy in atmosp ...
... In the Carbon Cycle, carbon is recycled mainly through the process of photosynthesis, cellular respiration and burning of fossil fuels. Carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbon monoxide emissions have been increasing in the atmosphere. It allows light energy in, but traps the reflected heat energy in atmosp ...
Honors Chemistry II Review 1. Express the following in scientific
... Which reactant is limiting if there are 80kg of water to be removed and 65kg of Li2O available? How many kg of the excess reactant remain? 20. After lithium hydroxide is produced aboard the space shuttle, it is used to remove exhaled carbon dioxide from the air supply according to the following equa ...
... Which reactant is limiting if there are 80kg of water to be removed and 65kg of Li2O available? How many kg of the excess reactant remain? 20. After lithium hydroxide is produced aboard the space shuttle, it is used to remove exhaled carbon dioxide from the air supply according to the following equa ...
MIDTERM Study packet 2016
... ____________________- process that takes place when a liquid changes to a gas. ____________________ - process that takes place when a gas changes to a liquid. ____________________ - process by which plants give off water vapor through their “pores”. ____________________ - process in which water fall ...
... ____________________- process that takes place when a liquid changes to a gas. ____________________ - process that takes place when a gas changes to a liquid. ____________________ - process by which plants give off water vapor through their “pores”. ____________________ - process in which water fall ...
Cellular Respiration Chapter 9
... through the major pathways of anaerobic and aerobic respiration. I can compare reactants and products for each process. I can account for how aerobic respiration produces more ATP per monosaccharide. ...
... through the major pathways of anaerobic and aerobic respiration. I can compare reactants and products for each process. I can account for how aerobic respiration produces more ATP per monosaccharide. ...
Lesson Objective: Vocabulary: Lesson Question: Focus Question
... triphosphate (ATP) by breaking down organic compounds. Both autotrophs and heterotrophy undergo cellular respiration to breakdown organic compounds into simpler molecules to release energy. Some energy is used to make ATP which is then used by the cells to do work. The figure below shows that ...
... triphosphate (ATP) by breaking down organic compounds. Both autotrophs and heterotrophy undergo cellular respiration to breakdown organic compounds into simpler molecules to release energy. Some energy is used to make ATP which is then used by the cells to do work. The figure below shows that ...
Study Guide Responses
... Which element of a control system detects a change? receptor An atom that has lost two electrons is called a(n) cation. The subatomic particles that are responsible for the chemical behavior of atoms are the electrons. Monomers are joined together to form more complex molecules through dehydration s ...
... Which element of a control system detects a change? receptor An atom that has lost two electrons is called a(n) cation. The subatomic particles that are responsible for the chemical behavior of atoms are the electrons. Monomers are joined together to form more complex molecules through dehydration s ...
Calvin cycle
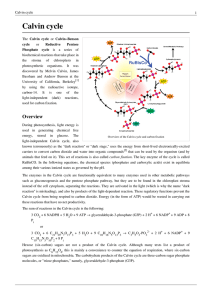
... used in generating chemical free energy, stored in glucose. The Overview of the Calvin cycle and carbon fixation light-independent Calvin cycle, also known (erroneously) as the "dark reaction" or "dark stage," uses the energy from short-lived electronically-excited carriers to convert carbon dioxide ...
... used in generating chemical free energy, stored in glucose. The Overview of the Calvin cycle and carbon fixation light-independent Calvin cycle, also known (erroneously) as the "dark reaction" or "dark stage," uses the energy from short-lived electronically-excited carriers to convert carbon dioxide ...
Khan Academy 15min cell respiration
... An ATP synthase (EC 3.6.3.14) is a general term for an enzyme that can synthesize adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate by using some form of energy. This energy is often in the form of protons moving down an electrochemical gradient, such as from the ...
... An ATP synthase (EC 3.6.3.14) is a general term for an enzyme that can synthesize adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate by using some form of energy. This energy is often in the form of protons moving down an electrochemical gradient, such as from the ...
Unit One
... 23. Maleic acid is the cis isomer (CH2)2(COOH)2 Fumaric acid is the trans isomer (CH2)2(COOH)2 Draw the geometric isomers. Is there a chiral carbon ? These drawings should be in your notes. The COOH groups are on the same side of the double bond for the cis isomer. The COOH groups are on different s ...
... 23. Maleic acid is the cis isomer (CH2)2(COOH)2 Fumaric acid is the trans isomer (CH2)2(COOH)2 Draw the geometric isomers. Is there a chiral carbon ? These drawings should be in your notes. The COOH groups are on the same side of the double bond for the cis isomer. The COOH groups are on different s ...
sample
... The electron transport chain involves a chain of electron carriers located on the inner mitochondrial membrane (cristae). The cristae have a large surface area so there are more electron carriers, which increases ATP synthesis. The reduced coenzymes, NADH 2 and FADH 2, produced during glycolysis, th ...
... The electron transport chain involves a chain of electron carriers located on the inner mitochondrial membrane (cristae). The cristae have a large surface area so there are more electron carriers, which increases ATP synthesis. The reduced coenzymes, NADH 2 and FADH 2, produced during glycolysis, th ...
Ch 3 Biochemistry Notes
... D. Energy from ATP • Life needs a constant supply of energy • Chemical bonds store energy. • Food molecules are the $1,000 dollar bills of energy storage. They function as fuel molecules, storing large quantities of energy in a stable form over long periods of time. ...
... D. Energy from ATP • Life needs a constant supply of energy • Chemical bonds store energy. • Food molecules are the $1,000 dollar bills of energy storage. They function as fuel molecules, storing large quantities of energy in a stable form over long periods of time. ...
Biology Midterm Study Guide Ch 1-9 spring 11
... 134. Label which of the following passes high-energy electrons into the electron transport chain? a. NADH and FADH2 c. citric acid b. ATP and ADP d. acetyl – CoA 135. The energy of the electrons passing along the electron transport chain is used to ...
... 134. Label which of the following passes high-energy electrons into the electron transport chain? a. NADH and FADH2 c. citric acid b. ATP and ADP d. acetyl – CoA 135. The energy of the electrons passing along the electron transport chain is used to ...
Plant Adaptation Pop Quiz
... ____ 27. The haploid form in a plant’s life cycle is called the gametophyte. ____ 28. A haploid stage following a diploid stage in a plant’s life cycle is called alternation of generations. ____ 29. In plants, haploid gametes are produced as a result of mitosis. ____ 30. The seed coat protects the ...
... ____ 27. The haploid form in a plant’s life cycle is called the gametophyte. ____ 28. A haploid stage following a diploid stage in a plant’s life cycle is called alternation of generations. ____ 29. In plants, haploid gametes are produced as a result of mitosis. ____ 30. The seed coat protects the ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.