enviro bio cellular respiration powerpoint 2013
... ATP energy in the absence of oxygen. The products are Lactic Acid and ATP. ...
... ATP energy in the absence of oxygen. The products are Lactic Acid and ATP. ...
Cellular Respiration notes Cellular respiration is
... 1. Cellular respiration is carried out by every cell in both plants and animals and is essential for daily living. 2. It does not occur at any set time or at the same point in time. In fact, neighboring cells are simultaneously involved in different stages of cellular respiration. 3. Cellular respir ...
... 1. Cellular respiration is carried out by every cell in both plants and animals and is essential for daily living. 2. It does not occur at any set time or at the same point in time. In fact, neighboring cells are simultaneously involved in different stages of cellular respiration. 3. Cellular respir ...
Lecture 17/18 - Aerobic and Anaerobic Metabolism
... 1.) What are the 3 “stages” of cellular respiration? 2.) Is glycolysis an aerobic or anaerobic pathway? If you oxidize one molecule of glucose, what is the approximate net yield of ATP? 3.) The reactions of glycolysis can all be categorized into one type of chemical reaction, what are these reaction ...
... 1.) What are the 3 “stages” of cellular respiration? 2.) Is glycolysis an aerobic or anaerobic pathway? If you oxidize one molecule of glucose, what is the approximate net yield of ATP? 3.) The reactions of glycolysis can all be categorized into one type of chemical reaction, what are these reaction ...
Notes on chemistry of life
... FQ: What are atoms and what are they made of? ET: take out your vocabulary flipper from Friday. Review all the terms. ...
... FQ: What are atoms and what are they made of? ET: take out your vocabulary flipper from Friday. Review all the terms. ...
Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration
... • Cellular respiration: cells make ATP by breaking down organic compounds • Both autotrophs and heterotrophs undergo cellular respiration – Break down organic compounds into simple molecules and energy – Some energy used to make more ATP, some is used by the cells to do work ...
... • Cellular respiration: cells make ATP by breaking down organic compounds • Both autotrophs and heterotrophs undergo cellular respiration – Break down organic compounds into simple molecules and energy – Some energy used to make more ATP, some is used by the cells to do work ...
Solution Worksheet Respiration
... Chemical reactions that involve the loss of hydrogen and electrons are called oxidation reactions. Chemical reactions that result in the uptake of hydrogen and electrons are called reduction reactions. In general, the breaking down of larger molecules into smaller molecules are oxidation reactions. ...
... Chemical reactions that involve the loss of hydrogen and electrons are called oxidation reactions. Chemical reactions that result in the uptake of hydrogen and electrons are called reduction reactions. In general, the breaking down of larger molecules into smaller molecules are oxidation reactions. ...
Cellular Respiration
... Yields 62 kJ of energy, from a possible 2870 kJ/glucose (only a 2.2% energy conversion) Most energy is still trapped in pyruvate and the 2 NADH molecules, but some lost as heat Earliest cells in Earth’s history thought to have used this method of energy metabolism since oxygen is not required and en ...
... Yields 62 kJ of energy, from a possible 2870 kJ/glucose (only a 2.2% energy conversion) Most energy is still trapped in pyruvate and the 2 NADH molecules, but some lost as heat Earliest cells in Earth’s history thought to have used this method of energy metabolism since oxygen is not required and en ...
Anatomy & Physiology Ch. 2 Chemistry Comes Alive
... with particles that do not settle out. Colloids scatter light, and some can undergo sol-gel transformations, changing reversibly from liquid to more solid (gel) state. Examples include gelatin and cytoplasm. ...
... with particles that do not settle out. Colloids scatter light, and some can undergo sol-gel transformations, changing reversibly from liquid to more solid (gel) state. Examples include gelatin and cytoplasm. ...
Plant Kingdom Slides
... Leaf Structures • Mesophyll: photosynthetic layer – Palisade mesophyll: tightly packed cells that absorb light. Function: photosynthesis – Spongy mesophyll: air spaces for gas and water movement. • Cuticle: Waxy coating that protects leaf and prevent water loss. • Veins – contain vascular tissue (x ...
... Leaf Structures • Mesophyll: photosynthetic layer – Palisade mesophyll: tightly packed cells that absorb light. Function: photosynthesis – Spongy mesophyll: air spaces for gas and water movement. • Cuticle: Waxy coating that protects leaf and prevent water loss. • Veins – contain vascular tissue (x ...
CHAPTER 3
... chemical energy stored in food into forms needed to perform activities Metabolism- the total chemical reactions in sn organism - The chemical reactions of metabolism require enzymes ...
... chemical energy stored in food into forms needed to perform activities Metabolism- the total chemical reactions in sn organism - The chemical reactions of metabolism require enzymes ...
Question
... What is the function of the coenzymes, NADH and FADH2 ? a. Charging electrons to power ATP synthase b. Catalyzing the formation of acetyl-CoA c. Providing electrons and H+ to the electron transport chain d. Transporting CO2 into the mitochondria e. Acting as a terminal electron acceptor ...
... What is the function of the coenzymes, NADH and FADH2 ? a. Charging electrons to power ATP synthase b. Catalyzing the formation of acetyl-CoA c. Providing electrons and H+ to the electron transport chain d. Transporting CO2 into the mitochondria e. Acting as a terminal electron acceptor ...
Life in Aquatic Ecosystems
... In aquatic ecology, biologists often classify organisms according to how they obtain Plants energy to live, grow and reproduce. As sunlight is the ultimate source of energy for all Invertebrates organisms, a basic distinction lies between those who use its energy directly — Vertebrates autotrophs — ...
... In aquatic ecology, biologists often classify organisms according to how they obtain Plants energy to live, grow and reproduce. As sunlight is the ultimate source of energy for all Invertebrates organisms, a basic distinction lies between those who use its energy directly — Vertebrates autotrophs — ...
Respiratory System
... We have seen how the mitochondria in the cell use oxygen to carry out cellular respiration, and we have seen how the body gets oxygen to the cells via the circulatory system. We have also learned how the circulatory system transports the carbon dioxide created as waste by cellular respiration in wha ...
... We have seen how the mitochondria in the cell use oxygen to carry out cellular respiration, and we have seen how the body gets oxygen to the cells via the circulatory system. We have also learned how the circulatory system transports the carbon dioxide created as waste by cellular respiration in wha ...
World of Plants Notes
... Plants need transport systems as all parts of the plant need water (taken in through the roots) and food (made in the green parts of the plant). Plants therefore need transport systems to move these substances around. Describe the pathways of movement of water and food in xylem and phloem Xylem vess ...
... Plants need transport systems as all parts of the plant need water (taken in through the roots) and food (made in the green parts of the plant). Plants therefore need transport systems to move these substances around. Describe the pathways of movement of water and food in xylem and phloem Xylem vess ...
Unit 2 The Chemistry of Life
... Some are broken down for cell use and others are parts of cell structures. Olive oil, meat, butter-> have a molecule called glycerol which are bonded to molecules called fatty ...
... Some are broken down for cell use and others are parts of cell structures. Olive oil, meat, butter-> have a molecule called glycerol which are bonded to molecules called fatty ...
Biochemistry Practice Questions
... c. –NH2 and –COOH d. –NH2 and –CH2OH 22. What occurs when a peptide bond forms between two amino acids? a. Oxygen is released b. Water is released c. Oxygen is added d. Water is added 23.Enzymes influence chemical reactions in living systems by a. Providing the substrate required for the reactions t ...
... c. –NH2 and –COOH d. –NH2 and –CH2OH 22. What occurs when a peptide bond forms between two amino acids? a. Oxygen is released b. Water is released c. Oxygen is added d. Water is added 23.Enzymes influence chemical reactions in living systems by a. Providing the substrate required for the reactions t ...
Adaptation and Natural Selection
... environment are more likely to live long enough to produce offspring and pass their traits on to the next generation. – In terms of evolution and natural selection, the number one goal of any organism is to pass its genes on to the next generation through the production of offspring. ...
... environment are more likely to live long enough to produce offspring and pass their traits on to the next generation. – In terms of evolution and natural selection, the number one goal of any organism is to pass its genes on to the next generation through the production of offspring. ...
South Pasadena · AP Chemistry
... stock 280 tables, 1750 chairs, 550 bookshelves, 300 china cabinets, and 325 sideboards. He asked his assistant to figure out how many dining room sets they could sell, how much money they would make if they sold all the sets possible, and what they would have left that could not be sold as part of t ...
... stock 280 tables, 1750 chairs, 550 bookshelves, 300 china cabinets, and 325 sideboards. He asked his assistant to figure out how many dining room sets they could sell, how much money they would make if they sold all the sets possible, and what they would have left that could not be sold as part of t ...
Microbial physiology. Microbial metabolism. Enzymes. Nutrition
... Many of the amino acids are used in building bacterial proteins, but some may also be broken down for energy. If this is the way amino acids are used, they are broken down to some form that can enter the Kreb’s cycle. These reactions include: ...
... Many of the amino acids are used in building bacterial proteins, but some may also be broken down for energy. If this is the way amino acids are used, they are broken down to some form that can enter the Kreb’s cycle. These reactions include: ...
Photosynthesis

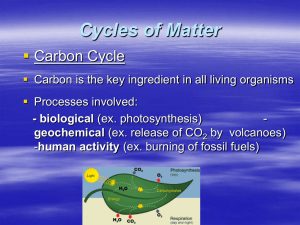
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.