* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit One
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
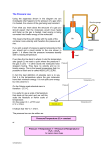
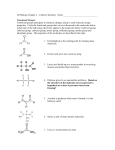
LHWHS AP Biology Unit One - The Chemistry of Life Practice Test Questions NAME_____________________ Test Outline ~40 multiple choice (similar to packet of practice AP questions) ~18 short answer and problems (similar to quiz, lab, and hw questions) Understand all labs, hw, quizzes, notes, and text book ( Chapters 2, 3, 4, 8.1-8.4, and the intro to sections 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5 ) 1. How many mL of 0.003 M NaOH are needed to neutralize 75 mL of 0.068 M HCl ? 1700 mL 2. What are the concentrations of CH3COOH and CH3COO - in a 0.65 M acetate buffer solution, which has a pH of 4.24. The pKa for acetate is 4.76. 0.15 M CH3COO0.50 M CH3COOH 3. What is the pH of 0.075 M solution of weak acid HA if the Ka is 3.8 × 10-6 pH = 3.27 4. Many of the most important molecules in the cell are polymers made by linking together long strings of monomers. a) What does making a polymer do to the entropy of the system ? -ΔS......decrease in entropy (randomness) .......many things becoming one thing b) Since making polymers is an endothermic process, how does the cell get around this endergonic (+ ΔG) process and continue to make macromolecules ? Reactions in the cell are coupled with the breakdown of ATP which can provide the energy needed to make larger molecules from smaller molecules. 5. An automobile accident victim has lost a great deal of blood. Should paramedics administer (1) water , (2) fluid that approximates intracellular fluid, or (3) fluid that approximates extracellular fluid. Explain your answer. (3) Blood is extracellular (outside the cell) fluid 6. Provide a simple description of the function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates - made of C, H, O generally in a 1 :2: 1 ratio, polar molecules - can be broken down and used for energy - can form the structural components of cells and nucleic acids - can function as receptors / signal molecules in cell membrane Lipids - "greasy or oily" hydrocarbon chains, generally non-polar - can be broken down and used for energy - can function as receptors / signal molecules in cell membrane - also includes pigments, vitamins, and hormones Proteins - chains of amino acids, largest fraction of a cell (besides water), - made of C, H, O, and N atoms - large molecules, molecular weight is in thousands to millions amu - includes enzymes (thousands of enzymes in every cell) - structual components of cells and tissues - can function as receptors / signal molecules in cell membrane - can be broken down and used for energy - can function as transport molecules controlling what comes in and out of a cell - examples include collagen, antibodies, digestive enzymes, hemoglobin Nucleic Acids - make of DNA and RNA - made of C, H, O, N, and P atoms genetic material passed onto offspring 7. Do the "Concept check 8.2" on page 148. (Answers in Appendix A) 8. What are the pH, pOH, [H+], and [OH_] of 0.0068 M HCl ? pH = 2.16 [H+] = 0.0068 pOH = 11.84 [OH-] = 1.45 × 10-12 9. How many mL of 0.04 M NaOH are needed to neutralize 40 mL of 0.15 M HCl ? 150 mL ---------------------- 10. Predict the shift in equilibrium (left or right) for the acetate buffer system when........ CH3COOH <======> H+ + CH3COO - a) a solution of HCl is added to the beaker left__________ b) sodium acetate (NaCH3CO2) salt is added to the beaker__left________ c) sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is added to the beaker_____right__ --------------------11. Which of the following would have the highest pH ? Explain your reasoning. 0.1 M acetic acid.......Ka = 1.8 × 10 -5 0.1 M citric acid........Ka = 3.2 × 10 -7 0.1 M boric acid........Ka = 5.4 × 10 -10 Boric acid has the lowest value for Ka. It has the least amount of ionization. It has the lowest concentration of [H+]. It has the highest pH -------------------12. What is the ratio of conjugate base to acid for a primary phosphate buffer system which has a pH of 2.58. The Ka of hydrogen phosphate is 7.94 × 10-3. pH = pKa + log [A-] [HA] 3/1 13. What is the pH of 0.08 M solution of weak acid HA if Ka for HA is 5.0 × 10-6 ? pH = 3.2 14. Determine the percentage of water in an apple using the data below Name of substance __Apple_________ Mass of dish ___1.35 g_______ Mass of dish and sample (before heating) ____9.65 g____ Mass of dish and sample (after heating) ____2.96 g_____ 80 .6 % Circle the structure which is larger in each pair 15. Nucleus of cell .........OR.........Glucose molecule 16. Eukaryote cell..........OR...........carbon atom 17. Protein molecule..........OR.........hydrogen ion 18. hydrogen ion...........OR ..........fatty acid molecule ------------------------------------ 19. Define hydrophobic and hydrophilic . Hydrophobic materials will not blend or dissolve in water very readily. Generally, this is characteristic of non- polar molecules. Hydrophilic materials will blend, mix, and dissolve in water. Generally, this is characteristic of polar molecules. 20. Provide an example of a protein hemoglobin, albumin 21. List and very briefly explain the five types of biochemical reactions. Group Transfer - moving one group of atoms/molecules from one molecule to another ex: moving phosphate groups Reduction / Oxidation reactions - moving charges (electrons) between molecules ex: ioinzation of hydrogen ions in acidic solutions ex: reacting glucose with Benedict's solution Rearragement - moving groups of atoms/molecules around on the same molecule ex: moving a phosphate group to a different location on the same molecule Cleavage - breaking a molecule apart ex: glucose breaking in half to form pyruvate Condensation - joining two molecules together resulting in the formation of water ex: amino acids bonding together 22. List two properties or characteristic of...... see #6 carbohydrates - polar, used for energy proteins - large molecules, often containing polar and non-polar regions, control chemical reactions in the cell, can control passage of materials in and out of the cell nucleic acids - can be large molecules, major component of genes lipids - generally non-polar, major component of cell membranes 23. Maleic acid is the cis isomer (CH2)2(COOH)2 Fumaric acid is the trans isomer (CH2)2(COOH)2 Draw the geometric isomers. Is there a chiral carbon ? These drawings should be in your notes. The COOH groups are on the same side of the double bond for the cis isomer. The COOH groups are on different sides of the double bond for the trans isomer. There is not a chiral carbon. There is not a carbon with 4 different things bonded to it. All carbons only have 3 things (hydrogen, oxygen, another carbon) bonded to it. 24. In your Oxidation of Sugars lab, glucose and fructose both reacted positively with Benedict's Reagent. Starch and sucrose did not. a. Describe what it means for a sugar to be oxidized. A carbon atom in the sugar molecule lost electrons For example, the charge (oxidation state) of the carbon atom increased from +1 to +3 as it looses two electrons. b. Why didn't starch and sucrose react with Benedict's. Starch and sucrose did not have a carbon atom 'available' to loose electrons. c. What did you have to do to starch and sucrose to get a positive test with Benedict's ? Adding HCl (hydrochloric acid) to starch and sucrose caused these molecules to break apart. Once broken apart, carbon atoms were exposed and 'available' to be oxidized by the Benedict's solution.