AP-Bio-exam-review-outline-may-2
... Non cyclic light reactions- ATP made by chemiosmosis, ATP synthase, H+ pump, NADPH, oxygen from photolysis (splitting of water) P700 and P680 NADPH and ATP needed for Calvin Cycle Chloroplasts, thylakoid membrane – light/stroma- dark Photosystem II (P680), photolysis, primary electron accept ...
... Non cyclic light reactions- ATP made by chemiosmosis, ATP synthase, H+ pump, NADPH, oxygen from photolysis (splitting of water) P700 and P680 NADPH and ATP needed for Calvin Cycle Chloroplasts, thylakoid membrane – light/stroma- dark Photosystem II (P680), photolysis, primary electron accept ...
Atoms
... Polar water molecules act like magnets and attract each other Hydrogen Bonds The attraction of the Hydrogen end (+) of one molecule for the Oxygen end (-) of another water molecule. They are the strongest bonds that can form between molecules ...
... Polar water molecules act like magnets and attract each other Hydrogen Bonds The attraction of the Hydrogen end (+) of one molecule for the Oxygen end (-) of another water molecule. They are the strongest bonds that can form between molecules ...
Chem Reactions (and Balancing Equations)
... •What Happened to the Other Oxygen Atom? •This equation is not balanced! •Two hydrogen atoms from a hydrogen molecule (H2) combines with one of the oxygen atoms from an oxygen molecule (O2) to form H2O. Then, the remaining oxygen atom combines with two more hydrogen atoms (from another H2 molecule) ...
... •What Happened to the Other Oxygen Atom? •This equation is not balanced! •Two hydrogen atoms from a hydrogen molecule (H2) combines with one of the oxygen atoms from an oxygen molecule (O2) to form H2O. Then, the remaining oxygen atom combines with two more hydrogen atoms (from another H2 molecule) ...
ch8and9notes2011
... O2,then ,serves as the final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain,getting rid of wastes(low energy electrons and H+ ions.) 2) Every time 2 high energy electrons transport down the transport chain,their energy is used to transport H+ across the membrane…..H+ ions build up in the intermem ...
... O2,then ,serves as the final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain,getting rid of wastes(low energy electrons and H+ ions.) 2) Every time 2 high energy electrons transport down the transport chain,their energy is used to transport H+ across the membrane…..H+ ions build up in the intermem ...
Bio Respiration 2009 Yingxin
... O ATP is formed as electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to oxygen via electron carriers (NADH > NAD+, FADH2 > FAD) O Each NADH generates 3 ATP (10 NADH > 28 ATP. Note: 2 ATP is used up in transporting 2 NADH produced from glycolysis from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria), each FADH2 generat ...
... O ATP is formed as electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to oxygen via electron carriers (NADH > NAD+, FADH2 > FAD) O Each NADH generates 3 ATP (10 NADH > 28 ATP. Note: 2 ATP is used up in transporting 2 NADH produced from glycolysis from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria), each FADH2 generat ...
Chapter 29: Light Waves Interference Constructive Interference
... waves are in phase • Lasers also produce monochromatic light: all the same frequency (color)! • NOT sources of energy: laser pointers run on batteries ...
... waves are in phase • Lasers also produce monochromatic light: all the same frequency (color)! • NOT sources of energy: laser pointers run on batteries ...
Revision
... • Most of the UK’s electricity is produced by power stations that are fuelled by fossil fuels, which contain carbon. • carbon dioxide, CO2 • carbon monoxide, CO (when there is not enough oxygen, so burning is incomplete) • particulate carbon, C (soot and smoke from incomplete burning) • sulfur dioxi ...
... • Most of the UK’s electricity is produced by power stations that are fuelled by fossil fuels, which contain carbon. • carbon dioxide, CO2 • carbon monoxide, CO (when there is not enough oxygen, so burning is incomplete) • particulate carbon, C (soot and smoke from incomplete burning) • sulfur dioxi ...
Mitochondria Mitochondria are the organelles that function as the
... carbohydrate can be broken into during digestion, gets oxidized and broken into two 3carbon molecules (pyruvates), which are then fed into the Kreb's Cycle. Glycolysis is the beginning of cellular respiration and takes place in the cytoplasm. Two molecules of ATP are required for glycolysis, but fou ...
... carbohydrate can be broken into during digestion, gets oxidized and broken into two 3carbon molecules (pyruvates), which are then fed into the Kreb's Cycle. Glycolysis is the beginning of cellular respiration and takes place in the cytoplasm. Two molecules of ATP are required for glycolysis, but fou ...
EOCT Study Guide
... An example of this is the gene for human insulin. When the gene is transferred into a bacterium, the bacterium will use the “recombined” genetic code to produce human insulin. This is how human insulin is mass-produced. This insulin has saved the lives of many people with diabetes. Not only does gen ...
... An example of this is the gene for human insulin. When the gene is transferred into a bacterium, the bacterium will use the “recombined” genetic code to produce human insulin. This is how human insulin is mass-produced. This insulin has saved the lives of many people with diabetes. Not only does gen ...
Extra Credit to replace the Survival of the Fittest Lab
... 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carb ...
... 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carb ...
Document
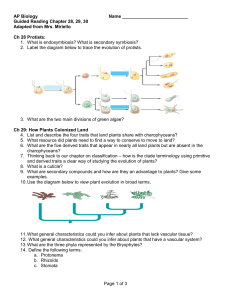
... If a plant has no cambium – the plant makes all the cells it will ever have during its intial growth. As the plant grows further, these cells just enlarge. ...
... If a plant has no cambium – the plant makes all the cells it will ever have during its intial growth. As the plant grows further, these cells just enlarge. ...
Plants - GZ @ Science Class Online
... allowing oxygen to move in and out. Two guard cells on either side of the stomata open and close extension the openings. ...
... allowing oxygen to move in and out. Two guard cells on either side of the stomata open and close extension the openings. ...
8.2 HL Respiration pPractice Questions
... same time, one NADH + H+ is formed. o This is known as the link reaction. o In the Krebs cycle, each acetyl group (CH3CO) formed in the link reaction yields two CO2. o The names of the intermediate compounds in the cycle are not required. o Thus it would be acceptable to note: C2 C4 C6 C5 + = → →, a ...
... same time, one NADH + H+ is formed. o This is known as the link reaction. o In the Krebs cycle, each acetyl group (CH3CO) formed in the link reaction yields two CO2. o The names of the intermediate compounds in the cycle are not required. o Thus it would be acceptable to note: C2 C4 C6 C5 + = → →, a ...
Biomes - AC Reynolds High
... in solution. A pH of 7.0 is neutral. Values below 7.0, to a minimum of 0.0, indicate increasing acidity. Values above 7.0, to a maximum of 14.0, indicate increasing alkalinity. Soil pH (a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of the soil)ハ ハ・Soil pH is one of the most important soil properties that a ...
... in solution. A pH of 7.0 is neutral. Values below 7.0, to a minimum of 0.0, indicate increasing acidity. Values above 7.0, to a maximum of 14.0, indicate increasing alkalinity. Soil pH (a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of the soil)ハ ハ・Soil pH is one of the most important soil properties that a ...
Biomes - geo-revision.net
... in solution. A pH of 7.0 is neutral. Values below 7.0, to a minimum of 0.0, indicate increasing acidity. Values above 7.0, to a maximum of 14.0, indicate increasing alkalinity. Soil pH (a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of the soil)ハ ハ・Soil pH is one of the most important soil properties that a ...
... in solution. A pH of 7.0 is neutral. Values below 7.0, to a minimum of 0.0, indicate increasing acidity. Values above 7.0, to a maximum of 14.0, indicate increasing alkalinity. Soil pH (a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of the soil)ハ ハ・Soil pH is one of the most important soil properties that a ...
9783941216242_Leseprobe02
... specifically arranged, forming a large absorption area as well as an energetic funnel. The delocalised electron system of the chlorophyll molecules absorb light energy, thus being transferred from the ground state to the excited state. Afterwards, the absorbed light energy is transported via non– ra ...
... specifically arranged, forming a large absorption area as well as an energetic funnel. The delocalised electron system of the chlorophyll molecules absorb light energy, thus being transferred from the ground state to the excited state. Afterwards, the absorbed light energy is transported via non– ra ...
Introduction to Ecology Notes
... This ammonia is then converted to nitrates and nitrites by other bacteria. Denitrification: Process where bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas. ...
... This ammonia is then converted to nitrates and nitrites by other bacteria. Denitrification: Process where bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas. ...
Exam 2 Review - Iowa State University
... glycolysis? If all are true, select alternative D. a) Two ATP are needed per glucose in the energy investment phase of glycolysis b) Four ATP per glucose are produced during the energy yielding phase of glycolysis c) The two NADH produced per glucose can be oxidized back to NAD+ by the mitochondrial ...
... glycolysis? If all are true, select alternative D. a) Two ATP are needed per glucose in the energy investment phase of glycolysis b) Four ATP per glucose are produced during the energy yielding phase of glycolysis c) The two NADH produced per glucose can be oxidized back to NAD+ by the mitochondrial ...
Microbial Biogeochemistry
... • Methanotrophs: CH4 + O2 CO2 + 2H2O (chemoorganoheterotrophs) • Example, Ralstonia sp., Pseudomonas sp. Anaerobic Environment Fermentors (chemoorganoheterotrophs) • Break down cellulose, etc. and ferment sugars into: • alcohols acetate • organic acids hydrogen • Many bacterial groups can conduct ...
... • Methanotrophs: CH4 + O2 CO2 + 2H2O (chemoorganoheterotrophs) • Example, Ralstonia sp., Pseudomonas sp. Anaerobic Environment Fermentors (chemoorganoheterotrophs) • Break down cellulose, etc. and ferment sugars into: • alcohols acetate • organic acids hydrogen • Many bacterial groups can conduct ...
Ecosystems
... Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work? What happens to energy in an ecosystem? A. Food chains and food webs help us understand how eaters, the eaten, and the decomposed are interconnected in an ecosystem. B. The sequence of organisms as they are eaten is a food chain. 1. Trophic levels are ...
... Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work? What happens to energy in an ecosystem? A. Food chains and food webs help us understand how eaters, the eaten, and the decomposed are interconnected in an ecosystem. B. The sequence of organisms as they are eaten is a food chain. 1. Trophic levels are ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.