Document
... Transport Proteins – hemoglobin transports oxygen by blood, other proteins transport molecules across cell membranes. ...
... Transport Proteins – hemoglobin transports oxygen by blood, other proteins transport molecules across cell membranes. ...
Document
... molecules. 1st it is transferred to oxaloacetate, a 4 carbon molecule. The acetyl group is oxidized to carbon dioxide in the citric acid cycle. Large amounts of the electron carrier NADH are generated. These electrons are then passed along an electrontransport chain within the mitochondrial inner me ...
... molecules. 1st it is transferred to oxaloacetate, a 4 carbon molecule. The acetyl group is oxidized to carbon dioxide in the citric acid cycle. Large amounts of the electron carrier NADH are generated. These electrons are then passed along an electrontransport chain within the mitochondrial inner me ...
Biochemistry Review Test
... burst into flames when placed in the gas. The student then repeated the procedure, using one gram of boiled liver and one gram of liver treated with a strong acid. When peroxide was added to each sample of liver, no gas was generated. 5. The gas that was generated was most likely (1.) oxygen (2.) ni ...
... burst into flames when placed in the gas. The student then repeated the procedure, using one gram of boiled liver and one gram of liver treated with a strong acid. When peroxide was added to each sample of liver, no gas was generated. 5. The gas that was generated was most likely (1.) oxygen (2.) ni ...
Organic Compounds
... Organic Compounds • It used to be thought that only living things could synthesize the complicated carbon compounds found in cells • German chemists in the 1800’s learned how to do this in the lab, showing that “organic” compounds can be created by non-organic means. • Today, organic compounds are ...
... Organic Compounds • It used to be thought that only living things could synthesize the complicated carbon compounds found in cells • German chemists in the 1800’s learned how to do this in the lab, showing that “organic” compounds can be created by non-organic means. • Today, organic compounds are ...
Lecture 08 Notes
... • How does the ATP molecule store chemical energy needed to run biological processes? • How are enzymes involved in regulating energy metabolism? • If nearly all life on Earth uses ATP, what does that i ...
... • How does the ATP molecule store chemical energy needed to run biological processes? • How are enzymes involved in regulating energy metabolism? • If nearly all life on Earth uses ATP, what does that i ...
doc
... Cellular respiration is an example of a metabolic pathway, which is a series of chemical reactions in cells. ...
... Cellular respiration is an example of a metabolic pathway, which is a series of chemical reactions in cells. ...
Cellular Respiration Releases Energy from Organic Compounds
... Oxygen in the e- transport chain In this case, oxygen is the final electron acceptor, ...
... Oxygen in the e- transport chain In this case, oxygen is the final electron acceptor, ...
Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... NOTE: This rxn needs NAD+, which is high in a low-energy state. So, energy is low and we catabolize proteins for energy. Glutamate breakdown yields NADH; plus, the pyruvate from step one also can be used for energy. We also generated ketoglutarate. ...
... NOTE: This rxn needs NAD+, which is high in a low-energy state. So, energy is low and we catabolize proteins for energy. Glutamate breakdown yields NADH; plus, the pyruvate from step one also can be used for energy. We also generated ketoglutarate. ...
MedBiochem Exam For each of the following questions, choose the
... 34. Oligomycin interferes with synthesis of "high energy" compounds by A. blocking the transfer of electrons from cytochrome b to cytochrome c. B. uncoupling electron transport from oxidative phosphorylation. C. closing the proton channel through the stalk of ATP synthetase. D. inhibiting the adenin ...
... 34. Oligomycin interferes with synthesis of "high energy" compounds by A. blocking the transfer of electrons from cytochrome b to cytochrome c. B. uncoupling electron transport from oxidative phosphorylation. C. closing the proton channel through the stalk of ATP synthetase. D. inhibiting the adenin ...
1 - Lone Star College System
... Contain many glucose (monosaccharide) units 2. Starch – storage form of glucose in plants 3. Glycogen – storage form of glucose in animals 4. Cellulose a. Found in plant cell walls b. Humans are unable to digest (passes through digestive tract as fiber) ...
... Contain many glucose (monosaccharide) units 2. Starch – storage form of glucose in plants 3. Glycogen – storage form of glucose in animals 4. Cellulose a. Found in plant cell walls b. Humans are unable to digest (passes through digestive tract as fiber) ...
Exam#2-`95
... different motor units. 9. Glycogenin is the name of the protein core of glycogen. 10. Inorganic phosphate (Pi) is an acid and its accumulation in muscle contributes to metabolic acidosis. 11. 31P MRS can provide an accurate calculation of intramuscular pH. 12. The creatine kinase reaction, in the di ...
... different motor units. 9. Glycogenin is the name of the protein core of glycogen. 10. Inorganic phosphate (Pi) is an acid and its accumulation in muscle contributes to metabolic acidosis. 11. 31P MRS can provide an accurate calculation of intramuscular pH. 12. The creatine kinase reaction, in the di ...
Document
... 3. Ketone body biogenesis and cholesterol synthesis are related in that they share the metabolic intermediate, _HMG-CoA/acetoacetyl-CoA_, and utilize _acetyl-CoA__ as a substrate for their biogenesis. The synthetic pathway for ketone bodies takes place in the __mitochondria__ (subcellular compartmen ...
... 3. Ketone body biogenesis and cholesterol synthesis are related in that they share the metabolic intermediate, _HMG-CoA/acetoacetyl-CoA_, and utilize _acetyl-CoA__ as a substrate for their biogenesis. The synthetic pathway for ketone bodies takes place in the __mitochondria__ (subcellular compartmen ...
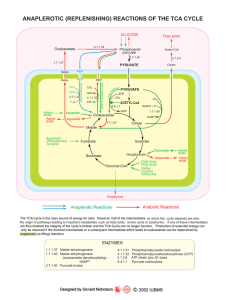
anaplerotic (replenishing) reactions of the tca cycle - Sigma
... Fatty acids Valine Leucine Isoleucine ...
... Fatty acids Valine Leucine Isoleucine ...
Cellular Respiration
... •Energy in food in form of high energy electrons •Electrons captured when food is broken down •Held by electron carriers •NADH, FADH2 ...
... •Energy in food in form of high energy electrons •Electrons captured when food is broken down •Held by electron carriers •NADH, FADH2 ...
BASIC CHEMISTRY
... substrate: molecules upon which an enzyme acts. The enzyme is shaped so that it can only lock up with a specific substrate ...
... substrate: molecules upon which an enzyme acts. The enzyme is shaped so that it can only lock up with a specific substrate ...
Making basic science clinically relevant for learners: the biochemistry example Eric Niederhoffer
... acids, ketone bodies, branched-chain amino acids)? • How is skeletal muscle phosphofructokinase-1 regulated? • What are the key Ca2+ regulated steps? • How does nervous tissue (neurons and glial cells) produce ATP (carbohydrates, fatty acids, ketone bodies, branched-chain amino acids)? • How do glia ...
... acids, ketone bodies, branched-chain amino acids)? • How is skeletal muscle phosphofructokinase-1 regulated? • What are the key Ca2+ regulated steps? • How does nervous tissue (neurons and glial cells) produce ATP (carbohydrates, fatty acids, ketone bodies, branched-chain amino acids)? • How do glia ...
Unit 2 - Part 1
... Why do organisms need enzymes? Reactions occur very slow on their own Enzymes speed up reactions 2. How are enzymes specific? They have a specific shape that only allows them to work on specific substrates. ...
... Why do organisms need enzymes? Reactions occur very slow on their own Enzymes speed up reactions 2. How are enzymes specific? They have a specific shape that only allows them to work on specific substrates. ...
Fundamentals of Paramedic Pharmacology
... prevents polar drugs, ions and large non polar substances from crossing ...
... prevents polar drugs, ions and large non polar substances from crossing ...
video slide
... in the exoskeleton of insects and the cell walls of fungi. • Chitin can be used as surgical thread because it is gradually reabsorbed by the body. • Chitin is not very digestible; only species that eat mainly insects can break it down easily. ...
... in the exoskeleton of insects and the cell walls of fungi. • Chitin can be used as surgical thread because it is gradually reabsorbed by the body. • Chitin is not very digestible; only species that eat mainly insects can break it down easily. ...
Enzymes & Energy
... phosphorylating it to ATP. 2 more ATPs are made. Two pyruvic acid molecules are formed from the single original glucose. ...
... phosphorylating it to ATP. 2 more ATPs are made. Two pyruvic acid molecules are formed from the single original glucose. ...
Close Reading for Macromolecules
... 25. ____Peptide______ bonds form when water is removed to hold ____amino acids_____ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lip ...
... 25. ____Peptide______ bonds form when water is removed to hold ____amino acids_____ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lip ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.