Unit I - E
... Water is the solvent of life. It bathes our cells, dissolves and transports compounds in the blood, provides a medium for movement of molecules into and throughout cellular compartments, separates charged molecules, dissipates heat, and participates in chemical reactions. Most compounds in the body, ...
... Water is the solvent of life. It bathes our cells, dissolves and transports compounds in the blood, provides a medium for movement of molecules into and throughout cellular compartments, separates charged molecules, dissipates heat, and participates in chemical reactions. Most compounds in the body, ...
Lecture Slides for Fatty Acid Catabolism
... hydrophobic tail. Those tails are split off as part of digestion to form phytanates. ...
... hydrophobic tail. Those tails are split off as part of digestion to form phytanates. ...
The light reaction of photosynthesis does not include
... photosynthesis occurs only in autotrophs; cellular respiration occurs only in A) heterotrophs photosynthesis uses solar energy to convert inorganics to energy-rich organics; B) respiration breaks down energy-rich organics to synthesize ATP photosynthesis involves the oxidation of glucose; respiratio ...
... photosynthesis occurs only in autotrophs; cellular respiration occurs only in A) heterotrophs photosynthesis uses solar energy to convert inorganics to energy-rich organics; B) respiration breaks down energy-rich organics to synthesize ATP photosynthesis involves the oxidation of glucose; respiratio ...
Protein
... muscles. It can also be broken down to monomers to release energy during cellular respiration. ONLY IN ANIMALS Cellulose – also made up of many glucose units. However, in this case the molecule is not easily broken down to its monomers. It is important for providing a rigid structure in plant cell ...
... muscles. It can also be broken down to monomers to release energy during cellular respiration. ONLY IN ANIMALS Cellulose – also made up of many glucose units. However, in this case the molecule is not easily broken down to its monomers. It is important for providing a rigid structure in plant cell ...
Jordan University of Science and Technology Faculty of Medicine
... 10. Storage Mechanisms and Control in Carbohydrate Metabolism (Chapter 18) a. How is glycogen produced and degraded? b. How does gluconeogenesis produce glucose from pyruvate? c. How is carbohydrate metabolism controlled? d. Why is glucose sometimes diverted through the pentose phosphate pathway? 11 ...
... 10. Storage Mechanisms and Control in Carbohydrate Metabolism (Chapter 18) a. How is glycogen produced and degraded? b. How does gluconeogenesis produce glucose from pyruvate? c. How is carbohydrate metabolism controlled? d. Why is glucose sometimes diverted through the pentose phosphate pathway? 11 ...
Biochemistry I, Spring Term 2001 - Third Exam:
... ii) You took your biochemistry final exam shortly after finishing this meal. The anxiety prompted the release of high levels of epinephrine (adrenaline) during the exam. Explain how the production of epinephrine may be beneficial to your final grade, given that your brain can only use glucose as its ...
... ii) You took your biochemistry final exam shortly after finishing this meal. The anxiety prompted the release of high levels of epinephrine (adrenaline) during the exam. Explain how the production of epinephrine may be beneficial to your final grade, given that your brain can only use glucose as its ...
ppt
... biosynthesis, how can we oxidize acetyl CoA? • “Filling up” reactions – Enhanced aerobic respiration (increase flux) – Gluconeogenesis pathway ...
... biosynthesis, how can we oxidize acetyl CoA? • “Filling up” reactions – Enhanced aerobic respiration (increase flux) – Gluconeogenesis pathway ...
Document
... In this experiment, trypsin will act on an artificial substrate to yield a yellow colored product: Trypsin BAPNA + H2O ...
... In this experiment, trypsin will act on an artificial substrate to yield a yellow colored product: Trypsin BAPNA + H2O ...
Review for Chapter 5 test
... 1. Write the quantities as a ratio according to what the problem asks. ...
... 1. Write the quantities as a ratio according to what the problem asks. ...
Fatty Acid Degradation Catabolism Overview TAG and FA
... • Unsaturated and trans fatty acids – Trans is natural intermediate – Produce 1.5 ATP less for unsaturation, 4 ATP less for di‐unsaturation ...
... • Unsaturated and trans fatty acids – Trans is natural intermediate – Produce 1.5 ATP less for unsaturation, 4 ATP less for di‐unsaturation ...
Elements and Molecules in Organisms
... 25. ____Peptide______ bonds form when water is removed to hold ____amino acids_____ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lip ...
... 25. ____Peptide______ bonds form when water is removed to hold ____amino acids_____ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lip ...
Cellular Respiration
... ATP is added to 3PGA and reduced by NADPH to produce G3P (glyceraldehyde-3P). One G3P is removed from the Calvin cycle to be used to make sugars (most likely glucose) but 5 G3P are used to regenerate RuBP for the next 3 CO2 4. Explain the interactions between pigments, absorption of light, reflectio ...
... ATP is added to 3PGA and reduced by NADPH to produce G3P (glyceraldehyde-3P). One G3P is removed from the Calvin cycle to be used to make sugars (most likely glucose) but 5 G3P are used to regenerate RuBP for the next 3 CO2 4. Explain the interactions between pigments, absorption of light, reflectio ...
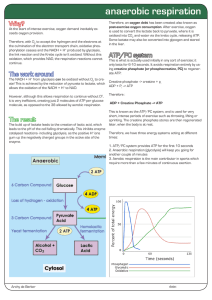
2 ATP - The Driggers Dirt
... ATP can be made by aerobic or anaerobic mechanisms (with or without oxygen). The first organisms on earth would have used anaerobic respiration since O was not readily available. Aerobic respiration is an efficient way to covert glucose to ATP The pathways starts in the cytoplasm called ...
... ATP can be made by aerobic or anaerobic mechanisms (with or without oxygen). The first organisms on earth would have used anaerobic respiration since O was not readily available. Aerobic respiration is an efficient way to covert glucose to ATP The pathways starts in the cytoplasm called ...
Elements Found in Living Things - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 25. ____Peptide______ bonds form when water is removed to hold ____amino acids_____ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lip ...
... 25. ____Peptide______ bonds form when water is removed to hold ____amino acids_____ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lip ...
Chapter 8: Energy and Metabolism
... a. Energy is readily measured by its conversion into II. Oxidation-Reduction: The Flow of Energy in Living Things A. Life Exists on Earth Because It Is Able to Capture Energy From the 1. Energy from the sun transformed into energy 2. Process called 3. Done by 4. Combine water and carbon dioxide to m ...
... a. Energy is readily measured by its conversion into II. Oxidation-Reduction: The Flow of Energy in Living Things A. Life Exists on Earth Because It Is Able to Capture Energy From the 1. Energy from the sun transformed into energy 2. Process called 3. Done by 4. Combine water and carbon dioxide to m ...
Al - Iraqia university/ college of medicine
... amino acid cysteine ends with an —SH group, which often serves to connect one chain of amino acids to another by a disulfide bond, —S—S—. Several amino acids commonly found in cells are shown Fig.2.21. Peptides : Two amino acids join by a dehydration reaction between carboxyl group of one & amino gr ...
... amino acid cysteine ends with an —SH group, which often serves to connect one chain of amino acids to another by a disulfide bond, —S—S—. Several amino acids commonly found in cells are shown Fig.2.21. Peptides : Two amino acids join by a dehydration reaction between carboxyl group of one & amino gr ...
anaerobic respiration
... catalysed reactions- including glycolysis, as the positive H+ ions gum up the negatively charged groups in the active site of the enzyme. ...
... catalysed reactions- including glycolysis, as the positive H+ ions gum up the negatively charged groups in the active site of the enzyme. ...
Physiology of Respiration - International Fire Training Centre
... this amount is known as tidal air. By taking a very deep breath, a further 3 litres may be taken in, and on subsequent very deep exhalation, this may be increased by a further 1½ litres. The total amount thus exhaled, i.e. about 4½ litres on average, is known as the vital capacity and varies with di ...
... this amount is known as tidal air. By taking a very deep breath, a further 3 litres may be taken in, and on subsequent very deep exhalation, this may be increased by a further 1½ litres. The total amount thus exhaled, i.e. about 4½ litres on average, is known as the vital capacity and varies with di ...
Macromolecules and Enzymes final draft
... 3. A carbohydrate is an organic compound that is composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The unique structure of carbohydrates makes them useful material for building cell walls in plants. Which of the following is a function of carbohydrates in animals? A. digesting food B. fighting disease C. s ...
... 3. A carbohydrate is an organic compound that is composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The unique structure of carbohydrates makes them useful material for building cell walls in plants. Which of the following is a function of carbohydrates in animals? A. digesting food B. fighting disease C. s ...
Energy in a Cell - Monroe Township School District
... Describe Photosynthesis • The process of changing light energy to chemical energy • Energy stored as sugar • Occurs in plants and some algae • Plants need light energy, CO2, and H2O • Takes place in the chloroplasts, using chlorophyll, the green pigment in plants ...
... Describe Photosynthesis • The process of changing light energy to chemical energy • Energy stored as sugar • Occurs in plants and some algae • Plants need light energy, CO2, and H2O • Takes place in the chloroplasts, using chlorophyll, the green pigment in plants ...
UG Curriculum
... The chemistry portion should strive towards providing information on the functional groups, hydrophobic and hydrophilic moieties and weak valence forces that organize macromolecules. Details on structure need not be emphasized. Discussion on metabolic processes should put emphasis on the overall cha ...
... The chemistry portion should strive towards providing information on the functional groups, hydrophobic and hydrophilic moieties and weak valence forces that organize macromolecules. Details on structure need not be emphasized. Discussion on metabolic processes should put emphasis on the overall cha ...
What you need to Know for Chapter 1 Quiz
... o What is the function of carbohydrates? o Be able to draw alpha glucose, beta glucose, galactose, and fructose o Describe the differences between the different glycosidic linkages (i.e alpha versus beta and location (1,4 vs 1,6). o What are some common disaccharides? o Describe the structure and fu ...
... o What is the function of carbohydrates? o Be able to draw alpha glucose, beta glucose, galactose, and fructose o Describe the differences between the different glycosidic linkages (i.e alpha versus beta and location (1,4 vs 1,6). o What are some common disaccharides? o Describe the structure and fu ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.