Cells and Energy Review ____ 1. Which of the following statements
... b. all ATP is made in the cytoplasm. c. only fermentation is taking place. d. glycolysis has stopped. ____ 38. During aerobic cellular respiration, in which of the following locations do ATP molecules form? a. cytoplasm only c. mitochondrial matrix and outer membrane b. Mitochondrial matrix d. cytop ...
... b. all ATP is made in the cytoplasm. c. only fermentation is taking place. d. glycolysis has stopped. ____ 38. During aerobic cellular respiration, in which of the following locations do ATP molecules form? a. cytoplasm only c. mitochondrial matrix and outer membrane b. Mitochondrial matrix d. cytop ...
corrected version for study guide
... Chemical energy- the energy stored in the bonds of ATP that can used to complete all cell work aerobic respiration- respiration that uses oxygen alcoholic fermentation- Anaerobic respiration where alcohol and carbon dioxide are the ...
... Chemical energy- the energy stored in the bonds of ATP that can used to complete all cell work aerobic respiration- respiration that uses oxygen alcoholic fermentation- Anaerobic respiration where alcohol and carbon dioxide are the ...
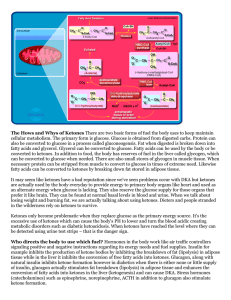
Pathology Ketone bodies are created at moderate
... necessary protein can be stripped from muscle to convert to glucose in times of extreme need. Likewise fatty acids can be converted to ketones by breaking down fat stored in adipose tissue. It may seem like ketones have a bad reputation since we've seen problems occur with DKA but ketones are actual ...
... necessary protein can be stripped from muscle to convert to glucose in times of extreme need. Likewise fatty acids can be converted to ketones by breaking down fat stored in adipose tissue. It may seem like ketones have a bad reputation since we've seen problems occur with DKA but ketones are actual ...
Phase 1 - Systems Biology Research Group
... tested using a genome-scale model of yeast, but has yet to be applied to engineer E. coli designs [Metab Eng, 2001. 3(2): p. 111-4]. –OptStrain: OptStrain is a hierarchical computational framework incorporating mixed integer programming that identifies pathways that are targets for recombination of ...
... tested using a genome-scale model of yeast, but has yet to be applied to engineer E. coli designs [Metab Eng, 2001. 3(2): p. 111-4]. –OptStrain: OptStrain is a hierarchical computational framework incorporating mixed integer programming that identifies pathways that are targets for recombination of ...
Features of Life and the Cell
... • Chemical reactions change substances into different ones by breaking and forming chemical bonds. – Reactants: changed during a chemical reaction. – Products: made by a chemical reaction. • Bond energy - the amount of energy that it takes to break a ...
... • Chemical reactions change substances into different ones by breaking and forming chemical bonds. – Reactants: changed during a chemical reaction. – Products: made by a chemical reaction. • Bond energy - the amount of energy that it takes to break a ...
Sample exam questions Chapter 11 Carbohydrates
... A. They cannot convert pyruvate to oxaloacetate by carboxylation B. They cannot convert pyruvate to phosphoenol pyruvate C. They cannot convert acetyl-Coenzyme A into pyruvate or oxaloacetate to initiate the gluconeogenesis pathway * D. Fatty acid degradation does not produce sufficient energy in th ...
... A. They cannot convert pyruvate to oxaloacetate by carboxylation B. They cannot convert pyruvate to phosphoenol pyruvate C. They cannot convert acetyl-Coenzyme A into pyruvate or oxaloacetate to initiate the gluconeogenesis pathway * D. Fatty acid degradation does not produce sufficient energy in th ...
Chapter 26 - Palm Beach State College
... fatty acids • Resulting free fatty acids (FFAs) and glycerol enter adipocytes to be made into triglycerides for storage • Chylomicron remnant—the remainder of a chylomicron after the triglycerides have been extracted and degraded by liver ...
... fatty acids • Resulting free fatty acids (FFAs) and glycerol enter adipocytes to be made into triglycerides for storage • Chylomicron remnant—the remainder of a chylomicron after the triglycerides have been extracted and degraded by liver ...
Chapter 26 Nutrition and Metabolism *Lecture PowerPoint
... • Secreted by enteroendocrine cells of ileum and colon • Sense that food has arrived in the stomach • Secrete PYY long before chyme reaches the ileum in amounts proportionate to calories consumed • Primary effect is to signal satiety and terminate eating • Signal that ends a meal ...
... • Secreted by enteroendocrine cells of ileum and colon • Sense that food has arrived in the stomach • Secrete PYY long before chyme reaches the ileum in amounts proportionate to calories consumed • Primary effect is to signal satiety and terminate eating • Signal that ends a meal ...
Cellular Respiration
... • If no oxygen is available- the process stops. • If oxygen becomes available, the process moves onto oxidative reduction & the kreb’s cycle. • Possible for 36 ATP to be made. ...
... • If no oxygen is available- the process stops. • If oxygen becomes available, the process moves onto oxidative reduction & the kreb’s cycle. • Possible for 36 ATP to be made. ...
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase-A New Target in the Fight against Obesity
... A person is healthy. It means that the person has a low BMI but may carry lots of body fat. WARNING FOR OBESITY: Family member who died from heart disease. You can still be slim and not workout, but not ...
... A person is healthy. It means that the person has a low BMI but may carry lots of body fat. WARNING FOR OBESITY: Family member who died from heart disease. You can still be slim and not workout, but not ...
3 – Efficiency of Cellular Respiration
... 10) Define and compare the terms metabolic rate and basal metabolic rate (BMR). What percentage of your dialy caloric intake is used to maintain your BMR? How does fat tissue affect your BMR? 11) Why is ATP an inhibitor of phosphofructokinase? What happens to glucose if there is excess ATP? 12) Desc ...
... 10) Define and compare the terms metabolic rate and basal metabolic rate (BMR). What percentage of your dialy caloric intake is used to maintain your BMR? How does fat tissue affect your BMR? 11) Why is ATP an inhibitor of phosphofructokinase? What happens to glucose if there is excess ATP? 12) Desc ...
Chem 562 - SDSU Chemistry
... Chem 563 (Nucleic Acid Function and Protein Synthesis) and Chem 564 (Receptor Biochemistry and Protein Modification), that complete an advanced undergraduate education in biochemistry. Metabolism refers to the complete set of chemical reactions that sustain life. Metabolism begins with the extractio ...
... Chem 563 (Nucleic Acid Function and Protein Synthesis) and Chem 564 (Receptor Biochemistry and Protein Modification), that complete an advanced undergraduate education in biochemistry. Metabolism refers to the complete set of chemical reactions that sustain life. Metabolism begins with the extractio ...
protein
... is likely to pose no risk of adverse health effects to almost all individuals in the general population UL is not used as recommended levels of intake. ULs are useful because of the increased use of dietary supplements and fortified foods. ULs apply to chronic daily use. For some nutrients, there ma ...
... is likely to pose no risk of adverse health effects to almost all individuals in the general population UL is not used as recommended levels of intake. ULs are useful because of the increased use of dietary supplements and fortified foods. ULs apply to chronic daily use. For some nutrients, there ma ...
Chapter 8 Your Body`s Metabolism
... Metabolic processes follows specific pathways • Anabolic which use energy to build new substances • Catabolic which produce energy by breaking down molecules ...
... Metabolic processes follows specific pathways • Anabolic which use energy to build new substances • Catabolic which produce energy by breaking down molecules ...
Chapter 26
... • Secreted by enteroendocrine cells of ileum and colon • Sense that food has arrived in the stomach • Secrete PYY long before chyme reaches the ileum in amounts proportionate to calories consumed • Primary effect is to signal satiety and terminate eating • Signal that ends a meal ...
... • Secreted by enteroendocrine cells of ileum and colon • Sense that food has arrived in the stomach • Secrete PYY long before chyme reaches the ileum in amounts proportionate to calories consumed • Primary effect is to signal satiety and terminate eating • Signal that ends a meal ...
Biomolecule Reading
... Polymers such as starches and proteins are formed when their building blocks (monomers) are joined together. The joining of two monomers to each other is called dehydration synthesis because a hydrogen (H) and a hydroxide (OH) are removed from the monomers when they are joined together. The hydrogen ...
... Polymers such as starches and proteins are formed when their building blocks (monomers) are joined together. The joining of two monomers to each other is called dehydration synthesis because a hydrogen (H) and a hydroxide (OH) are removed from the monomers when they are joined together. The hydrogen ...
PPT File
... Is the diffusion of H+ ions energy releasing or energy requiring? Is the formation of ATP from ADP energy releasing or energy requiring? Link these two statements in explaining the formation of ATP. ...
... Is the diffusion of H+ ions energy releasing or energy requiring? Is the formation of ATP from ADP energy releasing or energy requiring? Link these two statements in explaining the formation of ATP. ...
Inborn errors of metabolism – Small molecule disease Intro
... calories with stress that is low in fat and high in carbohydrates. Cornstarch therapy is occasionally used during overnight fasting in patients with particularly severe disorders. Diagnosis is aided by checking the urine for organic acids and most importantly, a plasma acylcarnitine profile. Prototy ...
... calories with stress that is low in fat and high in carbohydrates. Cornstarch therapy is occasionally used during overnight fasting in patients with particularly severe disorders. Diagnosis is aided by checking the urine for organic acids and most importantly, a plasma acylcarnitine profile. Prototy ...
Biomolecules
... Biomolecules = 4 essential carbon based molecules http://www.genomenewsnetwork.org/articles/11_00/crystal_structure_image.shtml ...
... Biomolecules = 4 essential carbon based molecules http://www.genomenewsnetwork.org/articles/11_00/crystal_structure_image.shtml ...
Cellular Respiration NOTES
... fermentation (or ANaerobic) respiration. Regardless of the organism (bacteria to human), all organisms use glycolysis as an initial step. Remember, glycolysis results in a net gain of 2 ATP (useful) and 2 NADH (without oxygen, not very useful) and the pyruvate molecules. So, in order to recycle the ...
... fermentation (or ANaerobic) respiration. Regardless of the organism (bacteria to human), all organisms use glycolysis as an initial step. Remember, glycolysis results in a net gain of 2 ATP (useful) and 2 NADH (without oxygen, not very useful) and the pyruvate molecules. So, in order to recycle the ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.