Nutrition and Digestive System
... so it can grow, maintain its body, reproduce, and supply or produce expected ___________. ...
... so it can grow, maintain its body, reproduce, and supply or produce expected ___________. ...
Molecules of Life! - Highline Public Schools
... • Are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen • They are in a 1:2:1 ratio- meaning for every 1 carbon there are 2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen Carbohydrates are used to store energy!! Plants and some animals use carbohydrates for structural purposes such as plant stem walls. ...
... • Are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen • They are in a 1:2:1 ratio- meaning for every 1 carbon there are 2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen Carbohydrates are used to store energy!! Plants and some animals use carbohydrates for structural purposes such as plant stem walls. ...
Metabolism - ZANICHELLI.it
... • Produces 2 ATP and 2 NADH • Occurs in 10 steps. Glucose + 2 ATP + 4 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ 2 pyruvate + 4 ATP + 2 ADP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 H2O ...
... • Produces 2 ATP and 2 NADH • Occurs in 10 steps. Glucose + 2 ATP + 4 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ 2 pyruvate + 4 ATP + 2 ADP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 H2O ...
final-exam-tables-ba..
... Ribsomes in the cytoplasm make proteins that are designed to remain in the cell to make new organelles. Ribosomes attached to the surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum make proteins that are designed to be exported from the cell. The ER is a network of membranes that move proteins and other sub ...
... Ribsomes in the cytoplasm make proteins that are designed to remain in the cell to make new organelles. Ribosomes attached to the surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum make proteins that are designed to be exported from the cell. The ER is a network of membranes that move proteins and other sub ...
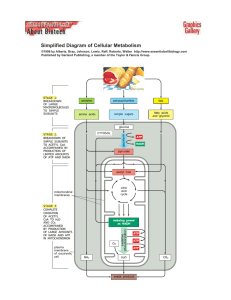
Simplified Diagram of Cellular Metabolism
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
Chapter 7: Where it Starts – Photosynthesis
... - This type of photosystem uses ___________ photophosphorylation - ________ is split by _______ energy, and an e- enters the chlorophyll _____ - The chlorophyll’s original ____ is used to form ___________ - _______ is also formed; this is a much more __________ use of the energy (cyclic, light, wate ...
... - This type of photosystem uses ___________ photophosphorylation - ________ is split by _______ energy, and an e- enters the chlorophyll _____ - The chlorophyll’s original ____ is used to form ___________ - _______ is also formed; this is a much more __________ use of the energy (cyclic, light, wate ...
Unit 1 – Biochemisty
... I can describe and identify (visually) the structure of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. ...
... I can describe and identify (visually) the structure of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. ...
The Major Transitions in Evolution
... What to do? Work with B. Papp and Á. Kun • Use Heinrich’s scope analyis to identify absolutely essential INTERNAL molecules • Look for those molecules that yield the largest increase in metabolic scope • Stop when there is a functional metabolism • Check the results with flux balance analysis (FBA) ...
... What to do? Work with B. Papp and Á. Kun • Use Heinrich’s scope analyis to identify absolutely essential INTERNAL molecules • Look for those molecules that yield the largest increase in metabolic scope • Stop when there is a functional metabolism • Check the results with flux balance analysis (FBA) ...
Solutions to Questions in the Cellular Respiration booklet
... #5. Glycolysis and the intermediate step occur in the cytoplasm. While Krebs’s Cycle or Citric Acid and Electron ...
... #5. Glycolysis and the intermediate step occur in the cytoplasm. While Krebs’s Cycle or Citric Acid and Electron ...
Macromolecules and Cells – Study Guide
... H) smallest part of an organism that can carry on all life processes ...
... H) smallest part of an organism that can carry on all life processes ...
EOC Review - Chavis Biology
... C. Electrons are passed to proteins. D. Oxygen picks up electrons. 14. Chemosynthesis is a process through which some organisms use energy from chemicals in their environment to build sugars in the absence of F. ATP. H. glucose. G. water. J. sunlight. 15. Which of the following is a reactant in phot ...
... C. Electrons are passed to proteins. D. Oxygen picks up electrons. 14. Chemosynthesis is a process through which some organisms use energy from chemicals in their environment to build sugars in the absence of F. ATP. H. glucose. G. water. J. sunlight. 15. Which of the following is a reactant in phot ...
The Chemistry of Life
... Put C, H, O, N together in different ways to build living organisms What are bodies made of? ...
... Put C, H, O, N together in different ways to build living organisms What are bodies made of? ...
question #5
... because they have phosphate groups as part of their composition,composed of phosphorous and oxygen. The phosphate groups are needed for the bonds that link the nucleotides together. ...
... because they have phosphate groups as part of their composition,composed of phosphorous and oxygen. The phosphate groups are needed for the bonds that link the nucleotides together. ...
BIOC*4520 - University of Guelph
... Explain the role of entropy and enthalpy, Gibbs free energy change, equilibrium constants, coupled reactions and redox reactions in biochemical processes. ...
... Explain the role of entropy and enthalpy, Gibbs free energy change, equilibrium constants, coupled reactions and redox reactions in biochemical processes. ...
Protein
... storage polysaccharide that is found in plant roots and other tissues. It stores monosaccharides that can be broken down later to release useful energy during cellular respiration – ONLY IN PLANTS Glycogen – also made up of many glucose units, it is an important storage polysaccharide in the liver ...
... storage polysaccharide that is found in plant roots and other tissues. It stores monosaccharides that can be broken down later to release useful energy during cellular respiration – ONLY IN PLANTS Glycogen – also made up of many glucose units, it is an important storage polysaccharide in the liver ...
Biochemistry Test Review Cards
... 3. What is a solution and how is it different from a suspension? A solution has evenly distributed particles and a suspension has particles which will not evenly distribute within the solution. ...
... 3. What is a solution and how is it different from a suspension? A solution has evenly distributed particles and a suspension has particles which will not evenly distribute within the solution. ...
Organic Compounds
... carbohydrates (sugars and starches), lipids (fats), proteins, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). • These molecules are usually in the form of polymers, long chains of similar subunits. Because they are large, these molecules are called macromolecules. The subunits are called monomers. • The cell also ...
... carbohydrates (sugars and starches), lipids (fats), proteins, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). • These molecules are usually in the form of polymers, long chains of similar subunits. Because they are large, these molecules are called macromolecules. The subunits are called monomers. • The cell also ...
Biomolecules
... Protein: the work horse of the biomolecules. These molecules carry out most of the functions of the cell, act as building blocks, and allow organisms to move and do many other things. ...
... Protein: the work horse of the biomolecules. These molecules carry out most of the functions of the cell, act as building blocks, and allow organisms to move and do many other things. ...
Reading Guide for Week 4
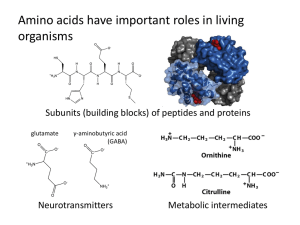
... precursor metabolites, but you should understand that the central metabolic pathways produce them using catabolic processes and that they go on to synthesize the subunits of the 4 main categories of biological macromolecules using anabolic processes: Subunits (made from precursor metabolites) amino ...
... precursor metabolites, but you should understand that the central metabolic pathways produce them using catabolic processes and that they go on to synthesize the subunits of the 4 main categories of biological macromolecules using anabolic processes: Subunits (made from precursor metabolites) amino ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.