5. Nucleotides are covalently linked to form nucleic acids by the
... organic molecules (e.g. nucleotides, amino acids, or polysaccharides) into long chains. 14. _______________________________ are small molecules that frequently associate with the active site of an enzyme and assist with its catalytic function. For question 15, fill in the blanks with the correct wor ...
... organic molecules (e.g. nucleotides, amino acids, or polysaccharides) into long chains. 14. _______________________________ are small molecules that frequently associate with the active site of an enzyme and assist with its catalytic function. For question 15, fill in the blanks with the correct wor ...
Document
... Activity of phosphofructokinase, which catalyzes step 3 of glycolysis, is affected by several substances that act as allosteric modulators. Effects of some of these modulators are shown in the following graphs. Which of these substances apparently acts to decrease the affinity of the enzyme? Explain ...
... Activity of phosphofructokinase, which catalyzes step 3 of glycolysis, is affected by several substances that act as allosteric modulators. Effects of some of these modulators are shown in the following graphs. Which of these substances apparently acts to decrease the affinity of the enzyme? Explain ...
Vocabulary Review
... When glucose and fructose which are monosaccharides are added together, they make a disaccharide called ...
... When glucose and fructose which are monosaccharides are added together, they make a disaccharide called ...
Name
... There should be 9 other cards left over in your “nitrogen” pile. Set these aside, we will come back to them later. Group 3: Sugars 15. Sugars are the building blocks of Carbohydrates. They are hydrates of carbon, having the general formula “Cn(H2O)n. Sugars are burned “oxidized” to release energy in ...
... There should be 9 other cards left over in your “nitrogen” pile. Set these aside, we will come back to them later. Group 3: Sugars 15. Sugars are the building blocks of Carbohydrates. They are hydrates of carbon, having the general formula “Cn(H2O)n. Sugars are burned “oxidized” to release energy in ...
Use of Reduced Carbon Compounds
... cell growth directly, whereas we are more used to thinking of animals that get many of their monomers from food. --- The simplest building blocks for biosynthesis are the one carbon, oxidized molecules such as CO2 (carbon fixation) ...
... cell growth directly, whereas we are more used to thinking of animals that get many of their monomers from food. --- The simplest building blocks for biosynthesis are the one carbon, oxidized molecules such as CO2 (carbon fixation) ...
Phosphate group
... • Some made but must be activated before they will work • Some inactivated after perform their catalytic function ...
... • Some made but must be activated before they will work • Some inactivated after perform their catalytic function ...
Full Content Review
... Photosynthesis – see book diagram ch. 8 • What: The process of making glucose using the energy from light, water, and carbon dioxide • Where: Happens in the chloroplast • When: all the time – there are reactions that require light (day) and reactions that do not ...
... Photosynthesis – see book diagram ch. 8 • What: The process of making glucose using the energy from light, water, and carbon dioxide • Where: Happens in the chloroplast • When: all the time – there are reactions that require light (day) and reactions that do not ...
Organic and Inorganic Molecules - Cal State LA
... Acidic amino acids: R group contains a carboxyl (-COOH) group (example: aspartic acid, glutamic acid) Basic amino acids: R group contains an amino group or nitrogen-containing group (example: lysine, histidine) Polar amino acids: R group contains lots of hydroxyl groups (-OH; very soluble in water) ...
... Acidic amino acids: R group contains a carboxyl (-COOH) group (example: aspartic acid, glutamic acid) Basic amino acids: R group contains an amino group or nitrogen-containing group (example: lysine, histidine) Polar amino acids: R group contains lots of hydroxyl groups (-OH; very soluble in water) ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... nuclear weapons production decades ago. The bacteria's cleaning power comes from their ability to "inhale" toxic metals and "exhale" them in a non-toxic form, explains team member Brian Lower, assistant professor in the School of Environment and Natural Resources at Ohio State University. Using a un ...
... nuclear weapons production decades ago. The bacteria's cleaning power comes from their ability to "inhale" toxic metals and "exhale" them in a non-toxic form, explains team member Brian Lower, assistant professor in the School of Environment and Natural Resources at Ohio State University. Using a un ...
Bio392 - Chapter 2-3 - notes
... • Number 6 on the periodic table Why is it so unique? It can form 4 covalent bonds because it has 4 electrons in its outer shell ...
... • Number 6 on the periodic table Why is it so unique? It can form 4 covalent bonds because it has 4 electrons in its outer shell ...
AP Biology Summer Session Lecture 6
... ATP uses the energy of an existing proton gradient to power ATP synthesis. This proton gradient develops between the intermembrane space and the matrix. ...
... ATP uses the energy of an existing proton gradient to power ATP synthesis. This proton gradient develops between the intermembrane space and the matrix. ...
Chemistry of Cells
... energy • Although fats are not strictly polymers, they are large molecules assembled from smaller molecules by dehydration reactions. • A fat is constructed from two kinds of smaller molecules, glycerol and fatty acids. ...
... energy • Although fats are not strictly polymers, they are large molecules assembled from smaller molecules by dehydration reactions. • A fat is constructed from two kinds of smaller molecules, glycerol and fatty acids. ...
Energetics
... Metabolism: The sum of the chemical reactions in an organism A metabolic pathway is a sequence of enzymatically catalyzed chemical reactions in a cell Metabolic pathways are determined by enzymes ...
... Metabolism: The sum of the chemical reactions in an organism A metabolic pathway is a sequence of enzymatically catalyzed chemical reactions in a cell Metabolic pathways are determined by enzymes ...
Nutrition
... B) When ATP or glucose levels drop the body can then convert glycogen back to glucose 1) glycogenolysis – production of glucose from glycogen 2) gluconeogenesis – formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate molecules (such as fat and protein) 3) Both processes occur in the liver D. Lipid Metabolism 1 ...
... B) When ATP or glucose levels drop the body can then convert glycogen back to glucose 1) glycogenolysis – production of glucose from glycogen 2) gluconeogenesis – formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate molecules (such as fat and protein) 3) Both processes occur in the liver D. Lipid Metabolism 1 ...
Organic Compounds
... – glucose, maltose, amylose, fructose, sucrose • The monomer of carbohydrates is the monosaccharide (one sugar) of which there are a number of types – glucose is the most biologically important • Carbon:Hydrogen:Oxygen in a 1:2:1 atomic ratio – glucose = C6H12O6 • Because they contain oxygen, they a ...
... – glucose, maltose, amylose, fructose, sucrose • The monomer of carbohydrates is the monosaccharide (one sugar) of which there are a number of types – glucose is the most biologically important • Carbon:Hydrogen:Oxygen in a 1:2:1 atomic ratio – glucose = C6H12O6 • Because they contain oxygen, they a ...
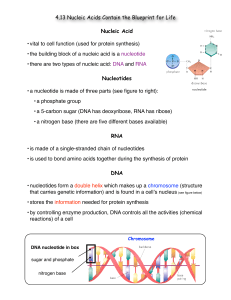
4.13 notes
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
Macromolecules and Your Body
... Regulating actions of hormones Help immune system Influences inflammatory response Causes contraction of smooth muscle for labor • Contributes to production of mucus in stomach ...
... Regulating actions of hormones Help immune system Influences inflammatory response Causes contraction of smooth muscle for labor • Contributes to production of mucus in stomach ...
Power point presentation
... protein….. 1000’s of amino acids covalently bonded together into a knot like structure we call a globular shape. ...
... protein….. 1000’s of amino acids covalently bonded together into a knot like structure we call a globular shape. ...
Notes
... In the cytoplasm of a cell, the process of glycolysis breaks up __________________ into two molecules of pyruvate. You also get two____________ and free up two ______________ that are picked up by a carrier. The second part oxidates pyruvate inside the mitochondria. Each pyruvate loses a ___________ ...
... In the cytoplasm of a cell, the process of glycolysis breaks up __________________ into two molecules of pyruvate. You also get two____________ and free up two ______________ that are picked up by a carrier. The second part oxidates pyruvate inside the mitochondria. Each pyruvate loses a ___________ ...
Macromolecules
... acids together toAmino Side make proteins The process is called dehydration synthesis Peptide bonds form to hold the amino acids together ...
... acids together toAmino Side make proteins The process is called dehydration synthesis Peptide bonds form to hold the amino acids together ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.