fulltext
... to sugar alcohols and cyclitols includes the biosynthetic pathways leading to glucitol, inositols, and pseudosaccharides. Extensively used are reaction schemes, sequences, and mechanisms with the enzymes involved and detailed explanations employing sound chemical principles and mechanisms. Keywords: ...
... to sugar alcohols and cyclitols includes the biosynthetic pathways leading to glucitol, inositols, and pseudosaccharides. Extensively used are reaction schemes, sequences, and mechanisms with the enzymes involved and detailed explanations employing sound chemical principles and mechanisms. Keywords: ...
Descriptive Chemistry for Midterm Exam #2
... Occurrence: found in more compounds than any other element on earth. It is the most abundant element in universe. Oxidation states: 0 in H2, +1 in compounds with other non-metals, −1 in metal hydrides. Industrial Preparation of H2: This is carried out through the reduction of +1 oxidation state in H ...
... Occurrence: found in more compounds than any other element on earth. It is the most abundant element in universe. Oxidation states: 0 in H2, +1 in compounds with other non-metals, −1 in metal hydrides. Industrial Preparation of H2: This is carried out through the reduction of +1 oxidation state in H ...
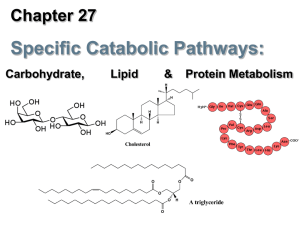
Chapter 8: Energy generation:glycolysis
... The glycolysis pathway can be divided into two phases, the first phase comprising steps 1–5 and culminating in synthesis of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, and the second phase made up of steps 6–10, when glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is metabolized into pyruvate. The first phase does not generate ATP. In ...
... The glycolysis pathway can be divided into two phases, the first phase comprising steps 1–5 and culminating in synthesis of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, and the second phase made up of steps 6–10, when glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is metabolized into pyruvate. The first phase does not generate ATP. In ...
baking update
... Flour proteins contain amino acids with reactive sulfhydryl groups. In the native or reduced state, the flour proteins exist as separate entities. During the oxidation process, pairs of sulfhydryls become linked together in disulfide bonds. Because each protein has several sulfhydryl groups, one pro ...
... Flour proteins contain amino acids with reactive sulfhydryl groups. In the native or reduced state, the flour proteins exist as separate entities. During the oxidation process, pairs of sulfhydryls become linked together in disulfide bonds. Because each protein has several sulfhydryl groups, one pro ...
Solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS), strategies, resins and
... - attachment of the C-terminal residue is achieved by heating the resin in DMF with the appropiate amino acid cesium salt in the presence of KI - cleavage is affected by treatment of resin with HF or TFMSA, or by hydrogenolysis - alcohols can be released using reducing agents like DIBALH or LiBH4 - ...
... - attachment of the C-terminal residue is achieved by heating the resin in DMF with the appropiate amino acid cesium salt in the presence of KI - cleavage is affected by treatment of resin with HF or TFMSA, or by hydrogenolysis - alcohols can be released using reducing agents like DIBALH or LiBH4 - ...
The Metabolism of the Amino Acids of Escherichia
... bacteria had the disadvantage that more 14Cwas liberated into the medium after prolonged incubation in the absence of protozoa, but provided that incubations of less than 3 hr were used, the amount released was small. The number of bacteria engulfed was determined after incubation of the protozoa wi ...
... bacteria had the disadvantage that more 14Cwas liberated into the medium after prolonged incubation in the absence of protozoa, but provided that incubations of less than 3 hr were used, the amount released was small. The number of bacteria engulfed was determined after incubation of the protozoa wi ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... Nitrogen fixation can be performed by rhizobia soil bacteria in symbiosis with legume plants. This process has been extensively studied, and the entire genome sequences of select Rhizobiaceae bacteria (such as Azorhizobium, Allorhizobium, Bradyrhizobium, Mesorhizobium, Rhizobium, and Sinorhizobium) ...
... Nitrogen fixation can be performed by rhizobia soil bacteria in symbiosis with legume plants. This process has been extensively studied, and the entire genome sequences of select Rhizobiaceae bacteria (such as Azorhizobium, Allorhizobium, Bradyrhizobium, Mesorhizobium, Rhizobium, and Sinorhizobium) ...
Higher Chemistry - Mobile Resource
... It can also be shown that rates of reactions are very slow compared to the number of collisions actually happening. (This makes sense because if all collisions were successful and led to a reaction happening then there would be no slow reactions). So if 2 colliding molecules are moving slowly they w ...
... It can also be shown that rates of reactions are very slow compared to the number of collisions actually happening. (This makes sense because if all collisions were successful and led to a reaction happening then there would be no slow reactions). So if 2 colliding molecules are moving slowly they w ...
Enzyme Activities Support the Use of Liver Lipid–Derived Ketone
... The only published study that has measured lipid and ketone-body utilization in an active shark showed that amino acids and ketones are the preferred substrates of mitochondria isolated from red muscle of I. oxyrinchus (Ballantyne et al. 1992). Palmitoyl carnitine was not oxidized, indicating that f ...
... The only published study that has measured lipid and ketone-body utilization in an active shark showed that amino acids and ketones are the preferred substrates of mitochondria isolated from red muscle of I. oxyrinchus (Ballantyne et al. 1992). Palmitoyl carnitine was not oxidized, indicating that f ...
Chapter 6 PowerPoint File
... • The first step is an electron acceptor called NAD+. – The transfer of electrons from organic fuel to NAD+ reduces it to NADH. ...
... • The first step is an electron acceptor called NAD+. – The transfer of electrons from organic fuel to NAD+ reduces it to NADH. ...
Unit Title:
... ENRG1. Identify the reactants, products, and basic purposes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in the cells of photosynthetic organisms. (2.4) ENRG2. Explain the important role that ATP serves in metabolism. (2.5) EN ...
... ENRG1. Identify the reactants, products, and basic purposes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in the cells of photosynthetic organisms. (2.4) ENRG2. Explain the important role that ATP serves in metabolism. (2.5) EN ...
Sporopollenin biosynthetic enzymes interact and constitute a
... Copyright © 2013 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved. ...
... Copyright © 2013 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved. ...
Enzymes of Glycolysis Are Functionally Associated
... aldolase, phosphoglycerate mutase, and enolase) were also identified in an intermembrane space/outer mitochondrial membrane fraction. Enzyme activity assays confirmed that the entire glycolytic pathway was present in preparations of isolated Arabidopsis mitochondria, and the sensitivity of these act ...
... aldolase, phosphoglycerate mutase, and enolase) were also identified in an intermembrane space/outer mitochondrial membrane fraction. Enzyme activity assays confirmed that the entire glycolytic pathway was present in preparations of isolated Arabidopsis mitochondria, and the sensitivity of these act ...
2 - Griffith Research Online
... of the reacting duplex. Interstrand disulfide crosslinks, introduced by oxidation of thiouracil and thioguanine bases, abolished the specificity of human FEN1 for hydrolysis one nucleotide into the 5'-duplex. Site-specific hydrolysis of the phosphate diester bonds of nucleic acids with aberrant stru ...
... of the reacting duplex. Interstrand disulfide crosslinks, introduced by oxidation of thiouracil and thioguanine bases, abolished the specificity of human FEN1 for hydrolysis one nucleotide into the 5'-duplex. Site-specific hydrolysis of the phosphate diester bonds of nucleic acids with aberrant stru ...
Camp 1 - University of California, Santa Cruz
... • Pyruvate metabolized three ways: • depends on organism & presence/absence of O2 ...
... • Pyruvate metabolized three ways: • depends on organism & presence/absence of O2 ...
System Superior Reproducibility for Complex Gradients
... low volume, fast cycling time of the Waters Alliance Separations Module's gradient proportioning valve, coupled with advanced control software and efficient mixing provides capability for generating fast gradients. Several rapid gradient separations have been developed for the analysis of selected a ...
... low volume, fast cycling time of the Waters Alliance Separations Module's gradient proportioning valve, coupled with advanced control software and efficient mixing provides capability for generating fast gradients. Several rapid gradient separations have been developed for the analysis of selected a ...
Table of Trends in Enzyme Activities
... We randomly sampled the initial states (at the one-minute time point after the beginning of heat stress) of enzymatic activities in four-fold ranges (two-fold up and down) with respect to the normal steadystate values of enzyme activities. For example, the steady state for ceramide synthase is 1.65e ...
... We randomly sampled the initial states (at the one-minute time point after the beginning of heat stress) of enzymatic activities in four-fold ranges (two-fold up and down) with respect to the normal steadystate values of enzyme activities. For example, the steady state for ceramide synthase is 1.65e ...
Metabolic regulation of Escherichia coli cultivated under anaerobic
... condition [11], while ArcAB regulates under both anaerobic and microaerobic conditions [12,13]. It has been shown that ArcA/B system exerts more significant effect on the cell metabolism under microaerobic condition than under aerobic or anaerobic condition. The effect of ArcAB system on the flux di ...
... condition [11], while ArcAB regulates under both anaerobic and microaerobic conditions [12,13]. It has been shown that ArcA/B system exerts more significant effect on the cell metabolism under microaerobic condition than under aerobic or anaerobic condition. The effect of ArcAB system on the flux di ...
Lipid Biosynthesis Inhibitors - Plant and Soil Sciences eLibrary
... annualbroadleafweeds duringgerminationand early seedling growth. Symptoms of herbicidal activity in grasses include stunting of early seedling growth and interference with the emergence and unfolding of leaves from the coleoptile (3, 39, ...
... annualbroadleafweeds duringgerminationand early seedling growth. Symptoms of herbicidal activity in grasses include stunting of early seedling growth and interference with the emergence and unfolding of leaves from the coleoptile (3, 39, ...
Handout 2 - CHO chemistry
... 1. All monosaccharides are aldehydes or ketones with multiple hydroxyl groups (i.e., alcohol groups). 2. Smallest is D-glyceraldehyde (as in glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate in glycolysis). 3. Nutritionally most important is D-glucose. 4. L-forms are mirror images. ...
... 1. All monosaccharides are aldehydes or ketones with multiple hydroxyl groups (i.e., alcohol groups). 2. Smallest is D-glyceraldehyde (as in glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate in glycolysis). 3. Nutritionally most important is D-glucose. 4. L-forms are mirror images. ...
Renal Fanconi syndrome: taking a proximal look at the nephron
... least partially redundant, as knock-out mice do not have an apparent abnormal phenotype, except for some changes in lipid metabolites after fasting [29]. They only develop a relevant clinical phenotype, when the related enzyme D-PBE is also deleted [30, 31]. So how does a heterozygote missense mutat ...
... least partially redundant, as knock-out mice do not have an apparent abnormal phenotype, except for some changes in lipid metabolites after fasting [29]. They only develop a relevant clinical phenotype, when the related enzyme D-PBE is also deleted [30, 31]. So how does a heterozygote missense mutat ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.