Plasma Total Amino Acids, Plasma Glutamate
... may be due to decreased insulin levels or due to decreased insulin action. This decreased insulin levels in these subjects might have caused a rise in the plasma levels of AAN, AL and GM as insulin is known to possess a suppression effect on tissue proteolysis (13). A parallel increase in plasma GM ...
... may be due to decreased insulin levels or due to decreased insulin action. This decreased insulin levels in these subjects might have caused a rise in the plasma levels of AAN, AL and GM as insulin is known to possess a suppression effect on tissue proteolysis (13). A parallel increase in plasma GM ...
L02_2002
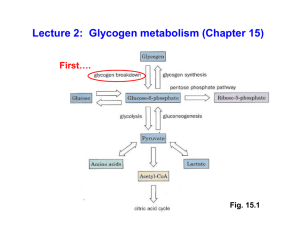
... chain by up to 7 residues long (also donated by UDPG). Glycogen synthase can then attach glucose residues to this glycogen “primer”. Each molecule of glycogen is associated with ONE molecule each of glycogenin and glycogen synthase. ...
... chain by up to 7 residues long (also donated by UDPG). Glycogen synthase can then attach glucose residues to this glycogen “primer”. Each molecule of glycogen is associated with ONE molecule each of glycogenin and glycogen synthase. ...
Lecture 2: Glycogen metabolism (Chapter 15)
... 2. Fatty acid residues cannot be metabolized anaerobically (that is, without oxygen). (If you want to burn fat while you are exercising, you must be able to breathe fairly easily.) 3. Animals cannot convert fat to glucose, so fat metabolism cannot maintain blood glucose levels. (Glucose is ”brain fo ...
... 2. Fatty acid residues cannot be metabolized anaerobically (that is, without oxygen). (If you want to burn fat while you are exercising, you must be able to breathe fairly easily.) 3. Animals cannot convert fat to glucose, so fat metabolism cannot maintain blood glucose levels. (Glucose is ”brain fo ...
Chemistry - Tumkur University
... ionic size, ionization enthalpy, electronegativity (Pauling, Mulliken, and Alfred-Rochow scales).Allotropy in C, S, and P. Inert pair effect, diagonal relationship and anomalous behaviour of first member of each group. (3 Lectures) Atomic Structure: Review of: Bohr’s theory and its limitations, dual ...
... ionic size, ionization enthalpy, electronegativity (Pauling, Mulliken, and Alfred-Rochow scales).Allotropy in C, S, and P. Inert pair effect, diagonal relationship and anomalous behaviour of first member of each group. (3 Lectures) Atomic Structure: Review of: Bohr’s theory and its limitations, dual ...
Discrimination of wine age of Chinese rice wine by
... Amino acid data analysis Table 1 summarized the quantitative analysis results for the 20 amino acids in the 32 Chinese rice wine samples. The most abundant amino acids were Ala, Arg, Glu, Pro, Leu, and Lys, with the average amount above 200 mg/L. The results were in accordance with those obtained by ...
... Amino acid data analysis Table 1 summarized the quantitative analysis results for the 20 amino acids in the 32 Chinese rice wine samples. The most abundant amino acids were Ala, Arg, Glu, Pro, Leu, and Lys, with the average amount above 200 mg/L. The results were in accordance with those obtained by ...
Cloning and Characterization of Unusual Fatty Acid Desaturases
... The seed oil of Anemone leveillei contains significant amounts of sciadonic acid (20:3D5,11,14; SA), an unusual non-methyleneinterrupted fatty acid with pharmaceutical potential similar to arachidonic acid. Two candidate cDNAs (AL10 and AL21) for the C20 D5cis-desaturase from developing seeds of A. ...
... The seed oil of Anemone leveillei contains significant amounts of sciadonic acid (20:3D5,11,14; SA), an unusual non-methyleneinterrupted fatty acid with pharmaceutical potential similar to arachidonic acid. Two candidate cDNAs (AL10 and AL21) for the C20 D5cis-desaturase from developing seeds of A. ...
Comparing the Polarities of the Amino Acids: Side
... ABSTRACT: To obtain an indication of the tendencies of amino acids to leave water and enter a truly nonpolar condensed phase, distribution coefficients between dilute solution in water and dilute solution in wet cyclohexane have been determined for each of the common amino acid side chains a t p H 7 ...
... ABSTRACT: To obtain an indication of the tendencies of amino acids to leave water and enter a truly nonpolar condensed phase, distribution coefficients between dilute solution in water and dilute solution in wet cyclohexane have been determined for each of the common amino acid side chains a t p H 7 ...
Mass Rearing of Juvenile Fish
... similar in all the experimental groups. This indicates that fish larvae have specific nutritional requirements for amino acids, and if some of the essential amino acids are not readily available fish show reduced protein synthesis and growth, even if the rest of the nutrients are present in adequate ...
... similar in all the experimental groups. This indicates that fish larvae have specific nutritional requirements for amino acids, and if some of the essential amino acids are not readily available fish show reduced protein synthesis and growth, even if the rest of the nutrients are present in adequate ...
Yield Potential, Plant Assimilatory Capacity, and Metabolic Efficiencies
... “Q-cycle” is associated with cyt b6 f. Electrons are transferred from cyt b6 f to PSI via plastocyanin (PC). In noncyclic electron transport, e2 are then transferred from PSI via ferredoxin (Fd) to FNR (ferredoxin-NADP reductase), which leads to reduction of NADP. The dashed line (– – –) indicates c ...
... “Q-cycle” is associated with cyt b6 f. Electrons are transferred from cyt b6 f to PSI via plastocyanin (PC). In noncyclic electron transport, e2 are then transferred from PSI via ferredoxin (Fd) to FNR (ferredoxin-NADP reductase), which leads to reduction of NADP. The dashed line (– – –) indicates c ...
Molecular architecture of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
... in solution apparent in low-resolution structures of both E3 on its own (M. Smolle, D. Byron and J.G. Lindsay, unpublished work) as well as a complex formed between E3 and two molecules of E3BP-didomain (consisting of the LD and SBD; Figure 1C). Further contributing factors could be differences in b ...
... in solution apparent in low-resolution structures of both E3 on its own (M. Smolle, D. Byron and J.G. Lindsay, unpublished work) as well as a complex formed between E3 and two molecules of E3BP-didomain (consisting of the LD and SBD; Figure 1C). Further contributing factors could be differences in b ...
Amino acid concentrations in fluids from the bovine oviduct and
... occur during the oviductal phase of development reflecting an important role of the oviduct during that phase. The importance of amino acids in embryo development in vitro has received much more attention in recent studies [1-4]. Essential and/or non-essential amino acids are common supplements in s ...
... occur during the oviductal phase of development reflecting an important role of the oviduct during that phase. The importance of amino acids in embryo development in vitro has received much more attention in recent studies [1-4]. Essential and/or non-essential amino acids are common supplements in s ...
The electric field induced by light can explain cellular responses to
... The phenomenon of light absorption to produce electronic excitation of atoms and molecules has long been accepted by photochemists and photobiologists. When molecules are excited by light and immediately take part in chemical reactions, an improvement in the kinetics of the reactions is observed [1] ...
... The phenomenon of light absorption to produce electronic excitation of atoms and molecules has long been accepted by photochemists and photobiologists. When molecules are excited by light and immediately take part in chemical reactions, an improvement in the kinetics of the reactions is observed [1] ...
Eight bacterial proteins, including UDP-N
... immunoglobulins [4]. Zinc-finger and Lcu-zipper proteins as well as Ca2+-binding proteins with EF-hands contain functionally specialized domains with oligopeptide repeats. Repeats of longer oligopeptides (often longer than 10-15 ...
... immunoglobulins [4]. Zinc-finger and Lcu-zipper proteins as well as Ca2+-binding proteins with EF-hands contain functionally specialized domains with oligopeptide repeats. Repeats of longer oligopeptides (often longer than 10-15 ...
Medicine "Lactobacterin" is a microbial mass of antagonistically
... of culture medium. Luminescence spectrum of the medicine was obtained. It can be divided into three signals areas: 280 – 300 nm - nucleic acid, 340 nm – NADH, 360 – 440 nm – components of culture medium. Vital activity of Lactobacilli was investigated. The changing of the peak height at 340 nm, that ...
... of culture medium. Luminescence spectrum of the medicine was obtained. It can be divided into three signals areas: 280 – 300 nm - nucleic acid, 340 nm – NADH, 360 – 440 nm – components of culture medium. Vital activity of Lactobacilli was investigated. The changing of the peak height at 340 nm, that ...
Essentials of Glycobiology Lecture 42 June 9, 1998 Jeff Esko
... Glycoside primers - Mimicking what already works Inhibitors of glycolipids and GPI anchors ...
... Glycoside primers - Mimicking what already works Inhibitors of glycolipids and GPI anchors ...
Sample
... 87) Proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids all perform vital functions for an organism. Discuss some of these vital functions and what could happen to an animal if one of these biological molecules were removed from their diet. Answer: Proteins play important roles in the structure of cells, as well as ...
... 87) Proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids all perform vital functions for an organism. Discuss some of these vital functions and what could happen to an animal if one of these biological molecules were removed from their diet. Answer: Proteins play important roles in the structure of cells, as well as ...
8)Discuss the roles of cofactors and coenzymes in enzyme activity.
... Anabolism: Synthesis of biomolecules from small precursors. Catabolism: Breakdown of large molecules to their precursors generating the energy. Substrate: The molecule on which the enzyme acts. Chemical bonds are either made or broken within the substrate molecule. Active site: The polypeptide chai ...
... Anabolism: Synthesis of biomolecules from small precursors. Catabolism: Breakdown of large molecules to their precursors generating the energy. Substrate: The molecule on which the enzyme acts. Chemical bonds are either made or broken within the substrate molecule. Active site: The polypeptide chai ...
Gene7-07
... anticodons that read new codons Missense mutations change a single codon and so may cause the replacement of one amino acid by another in a protein sequence. Nonsense codon means a termination codon. Suppressor (extragenic) is usually a gene coding a mutant tRNA that reads the mutated codon either i ...
... anticodons that read new codons Missense mutations change a single codon and so may cause the replacement of one amino acid by another in a protein sequence. Nonsense codon means a termination codon. Suppressor (extragenic) is usually a gene coding a mutant tRNA that reads the mutated codon either i ...
Reduced Expression of Aconitase Results in an
... and isocitrate dehydrogenase transform acetyl CoA into ␣-ketoglutarate, which, depending on relative demand, can either be further reduced to succinyl CoA or be utilized as a precursor for Glu synthesis (Hodges, 2002). The operation of the Krebs cycle in the light has been shown to be modified to th ...
... and isocitrate dehydrogenase transform acetyl CoA into ␣-ketoglutarate, which, depending on relative demand, can either be further reduced to succinyl CoA or be utilized as a precursor for Glu synthesis (Hodges, 2002). The operation of the Krebs cycle in the light has been shown to be modified to th ...
Conformation-Reactivity Relationship for Pyridoxal Schiff`s Bases
... P y r i d o x a l phosphate--amino acid Schiff s bases are key intermediates in many important biological reactions catalyzed by enzymes which require pyridoxal phosphate as a cofactor. These include transaminases, decarboxylases, synthetases, racemases, etc. (Snell & Dimari, 1970). All of these rea ...
... P y r i d o x a l phosphate--amino acid Schiff s bases are key intermediates in many important biological reactions catalyzed by enzymes which require pyridoxal phosphate as a cofactor. These include transaminases, decarboxylases, synthetases, racemases, etc. (Snell & Dimari, 1970). All of these rea ...
Sequence Entropy and the Absolute Rate of Amino Acid Substitutions
... specific stability contribution is small relative to the background contribution, so that this second term fulfills the role of the ‘thermal bath’ in statistical physics. This statistical mechanics formalism can now be applied to modeling the amino acid substitution rate. ...
... specific stability contribution is small relative to the background contribution, so that this second term fulfills the role of the ‘thermal bath’ in statistical physics. This statistical mechanics formalism can now be applied to modeling the amino acid substitution rate. ...
Phosphorylation of two cytosolic proteins
... phosphorylation of pp2l and pp23 to a level similar to that obtained with two different anti-CD3 mAbs (Fig. 4). By contrast, the phorbol ester TPA, which binds to, and activates, protein kinase C (Bell, 1986), failed to elicit pp2l and pp23 phosphorylation. These results are in agreement with the tw ...
... phosphorylation of pp2l and pp23 to a level similar to that obtained with two different anti-CD3 mAbs (Fig. 4). By contrast, the phorbol ester TPA, which binds to, and activates, protein kinase C (Bell, 1986), failed to elicit pp2l and pp23 phosphorylation. These results are in agreement with the tw ...
Exam_2005 - The University of Sydney
... The pathway is located in both the cytoplasm and the mitochondria The cycle reacts fuel molecules with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide The cycle generates CoA and NADH Most of the ATP in the cell is made directly by enzymes of the Krebs Cycle by substrate level phosphorylation. ...
... The pathway is located in both the cytoplasm and the mitochondria The cycle reacts fuel molecules with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide The cycle generates CoA and NADH Most of the ATP in the cell is made directly by enzymes of the Krebs Cycle by substrate level phosphorylation. ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.