Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology
... host cell (bacterium, yeast, or other cell), restriction enzymes (endonucleases), DNA ligase. Gene therapy: The treatment of certain diseases by introducing specific engineered genes in a patients cells. Vector: Is what is needed to carry the gene into the host cell; plasmids are often used as vecto ...
... host cell (bacterium, yeast, or other cell), restriction enzymes (endonucleases), DNA ligase. Gene therapy: The treatment of certain diseases by introducing specific engineered genes in a patients cells. Vector: Is what is needed to carry the gene into the host cell; plasmids are often used as vecto ...
Recombinant DNA technology
... What is DNA? DNA= Deoxyribu-Nucelic Acid • DNA is a very large molecule, made up of smaller units called nucleotides • Each nucleotide has three parts: a sugar (ribose), a phosphate molecule, and a nitrogenous base. • The nitrogenous base is the part of the nucleotide that carries genetic ...
... What is DNA? DNA= Deoxyribu-Nucelic Acid • DNA is a very large molecule, made up of smaller units called nucleotides • Each nucleotide has three parts: a sugar (ribose), a phosphate molecule, and a nitrogenous base. • The nitrogenous base is the part of the nucleotide that carries genetic ...
People Pieces
... sequences. The genome is the entire DNA of an organism. In 2003, the Human Genome Project (HGP) was completed. This provided the actual sequence, or spelling, of the human DNA. Research is continuing to understand the actual details of the genes, as well as the function of each gene. Researchers are ...
... sequences. The genome is the entire DNA of an organism. In 2003, the Human Genome Project (HGP) was completed. This provided the actual sequence, or spelling, of the human DNA. Research is continuing to understand the actual details of the genes, as well as the function of each gene. Researchers are ...
Genetic Engineering
... Manipulating DNA Tools of Molecular Biology • DNA extraction – DNA can be extracted from cells by simple chemical ...
... Manipulating DNA Tools of Molecular Biology • DNA extraction – DNA can be extracted from cells by simple chemical ...
Document
... Rapid type of reproduction where only one parent is involved, which passes on all of its genes to the offpsring. These are therefore CLONES of each other and of the parent. Biodiversity A measure of how much richness of life there is in an ecosystem. Some of the species may have potential uses as bu ...
... Rapid type of reproduction where only one parent is involved, which passes on all of its genes to the offpsring. These are therefore CLONES of each other and of the parent. Biodiversity A measure of how much richness of life there is in an ecosystem. Some of the species may have potential uses as bu ...
INSERT A-3c
... 3. Why can a person carrying a translocation be normal except, for the inability to have children? Explanation/Answer: If all of the DNA is present and the breakage for the translocation did not occur within a gene, then the phenotype of the individual can be normal. However, when that individual’s ...
... 3. Why can a person carrying a translocation be normal except, for the inability to have children? Explanation/Answer: If all of the DNA is present and the breakage for the translocation did not occur within a gene, then the phenotype of the individual can be normal. However, when that individual’s ...
Gene Technology
... This gene is then implanted into the bacterial plasmid. This is a circular piece of DNA in the bacteria. It is cut to make room for the required gene. Enzymes do the cutting and also ensure that the required gene is ‘glued’ in place. ...
... This gene is then implanted into the bacterial plasmid. This is a circular piece of DNA in the bacteria. It is cut to make room for the required gene. Enzymes do the cutting and also ensure that the required gene is ‘glued’ in place. ...
Finally…Genetically Modified Food
... • Introduce gene or genes artificially • Plants can be described as “transgenic” • Began in late 1970s – development of DNA manipulation • Gained knowledge of how to cut DNA molecules at particular points and glue back together – recombinant DNA technology • How it works: Propagate selected DNA thro ...
... • Introduce gene or genes artificially • Plants can be described as “transgenic” • Began in late 1970s – development of DNA manipulation • Gained knowledge of how to cut DNA molecules at particular points and glue back together – recombinant DNA technology • How it works: Propagate selected DNA thro ...
Gene Technology
... • 3. The donor gene is spliced into the plasmid DNA by connecting the ends of the DNA. The ends of the DNA are called sticky ends b/c they stick together due to base-pairing. ...
... • 3. The donor gene is spliced into the plasmid DNA by connecting the ends of the DNA. The ends of the DNA are called sticky ends b/c they stick together due to base-pairing. ...
Genetics Review Game
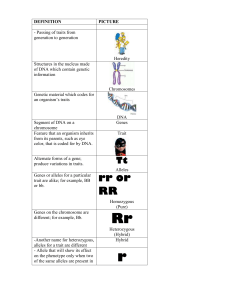
... If the combination of genes is the same, the trait is ________. If the combination of genes is different, the trait is _______. Homozygous, Heterozygous ...
... If the combination of genes is the same, the trait is ________. If the combination of genes is different, the trait is _______. Homozygous, Heterozygous ...
PowerPoint Genetic Technology Notes
... and animals. Genetic modification could lead to better, less expensive, and more nutritious food as well as less ___________ manufacturing processes. GM Crops Since their introduction in ________, genetically modified (GM) plants have become an important component of our food supply. Example: Plants ...
... and animals. Genetic modification could lead to better, less expensive, and more nutritious food as well as less ___________ manufacturing processes. GM Crops Since their introduction in ________, genetically modified (GM) plants have become an important component of our food supply. Example: Plants ...
definition - Humble ISD
... -Another name for heterozygous, alleles for a trait are different - Allele that will show its effect on the phenotype only when two of the same alleles are present in ...
... -Another name for heterozygous, alleles for a trait are different - Allele that will show its effect on the phenotype only when two of the same alleles are present in ...
Gene Regulation
... Operons are generally not found in Eukaryotes. Gene regulation is controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex that those of the lac operon. TATA box is found in Eukaryotic genes. It helps position RNA polymerase to begin transcription of the DNA. The promoter is ...
... Operons are generally not found in Eukaryotes. Gene regulation is controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex that those of the lac operon. TATA box is found in Eukaryotic genes. It helps position RNA polymerase to begin transcription of the DNA. The promoter is ...
Genetics 2. A typical cell of any organism contains genetic
... Genetics vocabulary building, students identify and share vocabulary meaning. Timeframe: 10 to 20 minutes Standard(s): ...
... Genetics vocabulary building, students identify and share vocabulary meaning. Timeframe: 10 to 20 minutes Standard(s): ...
Evolution and Genetics
... Individuals in a population that have traits or abilities that give them a competitive advantage over other population members are more likely to survive and reproduce. ...
... Individuals in a population that have traits or abilities that give them a competitive advantage over other population members are more likely to survive and reproduce. ...
Changes in DNA can produce Variation
... May soon allow scientists to correct certain recessive genetic disorders by replacing defective genes with copies of a healthy one. ...
... May soon allow scientists to correct certain recessive genetic disorders by replacing defective genes with copies of a healthy one. ...
a10c Biotechnology
... DNA and Biotechnology 1. What are some applications of biotechnology in the fields of medicine, food production, agriculture, criminal investigation, and genetic research? 2. What is a restriction enzyme, and what does it catalyze? How do restriction enzymes differ in what they cleave? What do they ...
... DNA and Biotechnology 1. What are some applications of biotechnology in the fields of medicine, food production, agriculture, criminal investigation, and genetic research? 2. What is a restriction enzyme, and what does it catalyze? How do restriction enzymes differ in what they cleave? What do they ...
GM?
... Where is GM food from? Some crops, plants are modified in the lab to gain desired traits such as “increased resistance to herbicides” or “improved nutrition.” In the past, to improve the quality of crops is very time-consuming and not all successful. But right now, scientists have the techniques to ...
... Where is GM food from? Some crops, plants are modified in the lab to gain desired traits such as “increased resistance to herbicides” or “improved nutrition.” In the past, to improve the quality of crops is very time-consuming and not all successful. But right now, scientists have the techniques to ...
the Powerpoint in PDF format
... Restriction enzymes = scissors - cuts a specific sequence (restriction site) of nucleotides and leaves sticky ends Ends can overlap with parts of other DNA ...
... Restriction enzymes = scissors - cuts a specific sequence (restriction site) of nucleotides and leaves sticky ends Ends can overlap with parts of other DNA ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.