Quick Links
... The ‘normal’ tomato and potato are the result of selective breeding – indirect, rather than direct, genetic modification. You can’t tell the GM/transgenic potato and tomato from the ‘normal’ ones just by looking. Genes can be moved from one organism to another, because DNA works the same whether you ...
... The ‘normal’ tomato and potato are the result of selective breeding – indirect, rather than direct, genetic modification. You can’t tell the GM/transgenic potato and tomato from the ‘normal’ ones just by looking. Genes can be moved from one organism to another, because DNA works the same whether you ...
Genetic Engineering - Somers Public Schools
... What is genetic engineering Cont… • It often involves the isolation, manipulation and reintroduction of DNA into cells or model organisms, usually to express a protein. • The aim is to introduce new characteristics such as making a crop resistant to a herbicide, introducing a novel trait, or produc ...
... What is genetic engineering Cont… • It often involves the isolation, manipulation and reintroduction of DNA into cells or model organisms, usually to express a protein. • The aim is to introduce new characteristics such as making a crop resistant to a herbicide, introducing a novel trait, or produc ...
Cloning and Gene Therapy
... • Scientists thought it would be impossible to clone a mammal • In 1997 a sheep was successfully cloned • Since then cows, pigs, mice and other mammals have been cloned • Cloned animals may suffer from genetic defects and health problems ...
... • Scientists thought it would be impossible to clone a mammal • In 1997 a sheep was successfully cloned • Since then cows, pigs, mice and other mammals have been cloned • Cloned animals may suffer from genetic defects and health problems ...
Concepts of Genetics
... ….the structure of DNA was described as a double helix by Watson and Crick ...
... ….the structure of DNA was described as a double helix by Watson and Crick ...
Genetic Technology
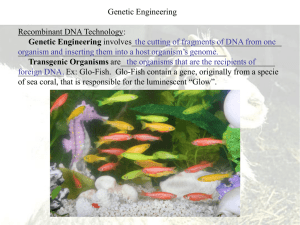
... inserting them into a host organism of the same or different species. aka: recombinant DNA technology ...
... inserting them into a host organism of the same or different species. aka: recombinant DNA technology ...
Gene Technology
... Identify the 3.2 billion base pairs of DNA that makes up humans Large portion of DNA does not code, only 1% to 1.5% make proteins Only 30,000 to 40,000 genes (much less than expected) ...
... Identify the 3.2 billion base pairs of DNA that makes up humans Large portion of DNA does not code, only 1% to 1.5% make proteins Only 30,000 to 40,000 genes (much less than expected) ...
Genetic Engineering Short Notes
... can replicate independantly of the main chromosome 5. Vector- something used to carry the gene of interest into another cell ...
... can replicate independantly of the main chromosome 5. Vector- something used to carry the gene of interest into another cell ...
Unit 4 Part2 wksht3
... 2. What do we call the new DNA that has the gene added to it? _________________________________ ...
... 2. What do we call the new DNA that has the gene added to it? _________________________________ ...
B1: You and Your Genes
... B1: You and Your Genes Part 1: how the genome and the environment affect an organism’s features I know that....... the genome is the entire genetic material of an organism and a copy of the genome is present in every cell to control how it functions that the genome is packaged into chromosomes, whic ...
... B1: You and Your Genes Part 1: how the genome and the environment affect an organism’s features I know that....... the genome is the entire genetic material of an organism and a copy of the genome is present in every cell to control how it functions that the genome is packaged into chromosomes, whic ...
CAPT Embedded Task: Biotechnology: Should There Be a
... Efforts are now underway to produce transgenic chickens that will be resistant to the bacterial infections that sometimes cause food poisoning. A Jersey calf whose cells were modified with genes for producing lysostaphin, a protein that kills Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, a leading cause of mastit ...
... Efforts are now underway to produce transgenic chickens that will be resistant to the bacterial infections that sometimes cause food poisoning. A Jersey calf whose cells were modified with genes for producing lysostaphin, a protein that kills Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, a leading cause of mastit ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... In the future, genetic engineering may correct some human genetic disorders. The process, called gene therapy, will involve inserting copies of a gene directly into a person’s cells. For example, hemophilia might be treated by replacing the defective allele on the X chromosome. Some people are conce ...
... In the future, genetic engineering may correct some human genetic disorders. The process, called gene therapy, will involve inserting copies of a gene directly into a person’s cells. For example, hemophilia might be treated by replacing the defective allele on the X chromosome. Some people are conce ...
Genetics Vocabulary List
... Gene: The basic unit of heredity that consists of a segment of DNA on a chromosome Heredity: The passing of genes from parent to offspring Traits: Characteristics that inherited from parent to offspring DNA: The genetic material found in all living cells Chromosomes: The physical structure in the ce ...
... Gene: The basic unit of heredity that consists of a segment of DNA on a chromosome Heredity: The passing of genes from parent to offspring Traits: Characteristics that inherited from parent to offspring DNA: The genetic material found in all living cells Chromosomes: The physical structure in the ce ...
4-1 - GSCS
... Produce the product of the gene – diabetic individuals cannot produce own insulin 1978 – human gene for making insulin was transferred into bacteria – insulin manufactured by bacteria has the advantage of being human insulin which decreases the possibility of an allergic reaction (unlike insulin ...
... Produce the product of the gene – diabetic individuals cannot produce own insulin 1978 – human gene for making insulin was transferred into bacteria – insulin manufactured by bacteria has the advantage of being human insulin which decreases the possibility of an allergic reaction (unlike insulin ...
Inheritance - World of Teaching
... complement of genetic material. In humans this would be 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) ...
... complement of genetic material. In humans this would be 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) ...
Final Exam Review Sheet
... Understand how to make and select genetically engineered stem cells for gene knockouts Know the Cre-loxP system for gene knockouts Know the reasons for non-identical expression of foreign genes in genetically modified organisms (GMOs) Be familiar with the animal genetic engineering examples covered ...
... Understand how to make and select genetically engineered stem cells for gene knockouts Know the Cre-loxP system for gene knockouts Know the reasons for non-identical expression of foreign genes in genetically modified organisms (GMOs) Be familiar with the animal genetic engineering examples covered ...
Activity 3.1.7: Designer Genes: Industrial Application Genetic
... off together in clusters or groups. ...
... off together in clusters or groups. ...
No Slide Title
... and introduced into host plant genome. Reporter genes (selectable markers) are spliced into the recombinant T-DNA. Successful integration is indicated by expression of reporter genes. ...
... and introduced into host plant genome. Reporter genes (selectable markers) are spliced into the recombinant T-DNA. Successful integration is indicated by expression of reporter genes. ...
Ch. 13 Genetic Engineering, Chapter Summary Date
... 6. a techniques scientist used to make many copies of a certain gene. 8. produced by combining DNA from different species or different sources. 14. a technique that breed specific animals and plants with desired traits. This technique takes advantage of naturally occurring genetic variation in a gro ...
... 6. a techniques scientist used to make many copies of a certain gene. 8. produced by combining DNA from different species or different sources. 14. a technique that breed specific animals and plants with desired traits. This technique takes advantage of naturally occurring genetic variation in a gro ...
Manipulating DNA - Lemon Bay High School
... has changed the way we interact with living things. This transgenic tobacco plant, which glows in the dark, was grown from a tobacco cell transformed with the firefly luciferase gene. The plant illustrates how DNA from one organism contains information that can specify traits in another organism. ...
... has changed the way we interact with living things. This transgenic tobacco plant, which glows in the dark, was grown from a tobacco cell transformed with the firefly luciferase gene. The plant illustrates how DNA from one organism contains information that can specify traits in another organism. ...
GMOs: Benefits and Disadvantages
... Introduction: Genetically modified (changed) (GM) foods are foods derived (made) from genetically modified organisms. GMO’s have had specific changes introduced into their DNA by genetic engineering techniques. These techniques are extremely precise; specific DNA sequences are cut out from the paren ...
... Introduction: Genetically modified (changed) (GM) foods are foods derived (made) from genetically modified organisms. GMO’s have had specific changes introduced into their DNA by genetic engineering techniques. These techniques are extremely precise; specific DNA sequences are cut out from the paren ...
GMO`s
... Introduction: Genetically modified (changed) (GM) foods are foods derived (made) from genetically modified organisms. GMO’s have had specific changes introduced into their DNA by genetic engineering techniques. These techniques are extremely precise; specific DNA sequences are cut out from the paren ...
... Introduction: Genetically modified (changed) (GM) foods are foods derived (made) from genetically modified organisms. GMO’s have had specific changes introduced into their DNA by genetic engineering techniques. These techniques are extremely precise; specific DNA sequences are cut out from the paren ...
Title of Assignment:
... 2. Mutation and sexual reproduction lead to genetic variation in a population. 1. e. Students know the role of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus in the secretion of proteins. 3. A multicellular organism develops from a single zygote, and its phenotype depends on its genotype, which is es ...
... 2. Mutation and sexual reproduction lead to genetic variation in a population. 1. e. Students know the role of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus in the secretion of proteins. 3. A multicellular organism develops from a single zygote, and its phenotype depends on its genotype, which is es ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.