Bio_11_Rev
... •It is a weakened version of the disease; incapable of causing serious harm. When a vaccine is injected, the immune system reads the pathogen and responds by making defensive proteins called antibodies. The immune system creates a defense system against this form of the disease. •In the future, if t ...
... •It is a weakened version of the disease; incapable of causing serious harm. When a vaccine is injected, the immune system reads the pathogen and responds by making defensive proteins called antibodies. The immune system creates a defense system against this form of the disease. •In the future, if t ...
Paradigm Shifts in Biomedical Research
... and Cancer Checkpoints ensure that cells complete one event before proceeding to the next event Cancer is a disease of uncontrolled cell growth, sloppy DNA replication and errors in chromosome segregation ...
... and Cancer Checkpoints ensure that cells complete one event before proceeding to the next event Cancer is a disease of uncontrolled cell growth, sloppy DNA replication and errors in chromosome segregation ...
Slide 1
... Direct microinjection of a chosen gene construct from another member of the same species or from a different species, into the pronucleus of a fertilized ovum. ...
... Direct microinjection of a chosen gene construct from another member of the same species or from a different species, into the pronucleus of a fertilized ovum. ...
Document
... behavior of chromosomes in meiosis and fertilization. • Linkage analysis can give information about the relative location of genes on chromosomes. • The success of Mendelian genetics increased the importance of characterizing the genetic material. • Chromosomes are composed of DNA and protein - the ...
... behavior of chromosomes in meiosis and fertilization. • Linkage analysis can give information about the relative location of genes on chromosomes. • The success of Mendelian genetics increased the importance of characterizing the genetic material. • Chromosomes are composed of DNA and protein - the ...
Unit 2 Terms
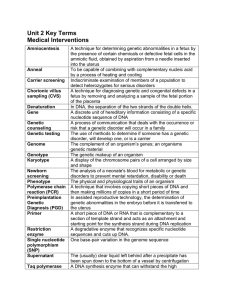
... disease A procedure in which gametes are fertilized in a dish in the laboratory, and the resulting zygote is implanted in the uterus for development In assisted reproductive technology, the determination of genetic abnormalities in the embryo before it is transferred to the uterus Methods used to pr ...
... disease A procedure in which gametes are fertilized in a dish in the laboratory, and the resulting zygote is implanted in the uterus for development In assisted reproductive technology, the determination of genetic abnormalities in the embryo before it is transferred to the uterus Methods used to pr ...
The process represented in the diagram below occurs in many cells
... Scientists have found a gene in the DNA of a certain plant that could be the key to increasing the amount of lycopene, a cancerfighting substance, in tomatoes. 32 The process of inserting this gen ...
... Scientists have found a gene in the DNA of a certain plant that could be the key to increasing the amount of lycopene, a cancerfighting substance, in tomatoes. 32 The process of inserting this gen ...
Genetically Modified Food
... Disadvantages of GM food Unintended modification of similar species due to cross pollination Upsetting the ecosystem Development of super pests Problems about religious, health, etc Destroying the normal farming system Interfering the normal DNA system Widening the financial gaps betw ...
... Disadvantages of GM food Unintended modification of similar species due to cross pollination Upsetting the ecosystem Development of super pests Problems about religious, health, etc Destroying the normal farming system Interfering the normal DNA system Widening the financial gaps betw ...
DNA and Chromosomes
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
B1 - Genetic Variation and Evolution Quiz
... 1. Why are some people against using GM foods? We are uncertain about their health effects. 2. How many chromosomes are there in sperm and egg cells? ...
... 1. Why are some people against using GM foods? We are uncertain about their health effects. 2. How many chromosomes are there in sperm and egg cells? ...
Insects and genetics
... 5. alternative state of a gene or trait f. phenotype 6. segment of DNA on a chromosome coding for a protein or RNA g. chromosome 7. group of coiled DNA strands containing genes 9. genome 8. entire DNA complement of an organism 11. The two scientists who first described the structure of DNA as a doub ...
... 5. alternative state of a gene or trait f. phenotype 6. segment of DNA on a chromosome coding for a protein or RNA g. chromosome 7. group of coiled DNA strands containing genes 9. genome 8. entire DNA complement of an organism 11. The two scientists who first described the structure of DNA as a doub ...
1406 final exam guide.doc
... What is the relationship between aneuploid and Down syndrome What are phages. Transcription can be separated into three stages. What are the stages (initiation, elongation, and termination) What are mutations, point mutations What are pathogens,, cuspid, host range, phage Viruses can reproduce by tw ...
... What is the relationship between aneuploid and Down syndrome What are phages. Transcription can be separated into three stages. What are the stages (initiation, elongation, and termination) What are mutations, point mutations What are pathogens,, cuspid, host range, phage Viruses can reproduce by tw ...
Green Chapter 17 Test Review
... How is incomplete dominance different from regular genetics? What would it look like? ...
... How is incomplete dominance different from regular genetics? What would it look like? ...
2 Types of Selective Breeding
... the ___________ EX: Cows that ___________ milk, vegetables that _____________ 2 Types of Selective Breeding 1) ____________________ – crossing 2 individuals with similar sets of genes to produce specific traits (may lead to genetic disorders) 2) _______________– crossing 2 genetically different indi ...
... the ___________ EX: Cows that ___________ milk, vegetables that _____________ 2 Types of Selective Breeding 1) ____________________ – crossing 2 individuals with similar sets of genes to produce specific traits (may lead to genetic disorders) 2) _______________– crossing 2 genetically different indi ...
... Law of Dominance -dominate alleles (capital letter) suppress recessive alleles (lowercase letter) Law of Segregation -during fertilization gametes randomly pair to produce four sets of alleles (monohyrid) TT=homozygous dominant, Tt=heterozygous, tt=homozygous recessive Genotype is the combin ...
8 How Cellular Information is Altered
... under a set of specific set of environmental conditions Direct selection: an example of direct selection to find a mutant resistant to an antibiotic or toxic compound Indirect selection: isolate mutants that are deficient in their capacity to produce a necessary growth factor ...
... under a set of specific set of environmental conditions Direct selection: an example of direct selection to find a mutant resistant to an antibiotic or toxic compound Indirect selection: isolate mutants that are deficient in their capacity to produce a necessary growth factor ...
Biology: Genetic Technology questions
... 3. Mutts (non purebred) dogs from an animal shelter often make great pets because they generally live long, healthy lives. What would a geneticist call a “mutt” and how would they explain its health. ...
... 3. Mutts (non purebred) dogs from an animal shelter often make great pets because they generally live long, healthy lives. What would a geneticist call a “mutt” and how would they explain its health. ...
Cell 103 Heredity and Society
... - Understand gene mutation and relate it to inherited and non-inherited diseases such sickle cell anemia and cancer - Understand to which extend environment is involved in gene expression or its damage - Describe the techniques used to manipulate genes - Use scientific knowledge learned to debate cu ...
... - Understand gene mutation and relate it to inherited and non-inherited diseases such sickle cell anemia and cancer - Understand to which extend environment is involved in gene expression or its damage - Describe the techniques used to manipulate genes - Use scientific knowledge learned to debate cu ...
Genetically Modified Crops
... Plant breeding entails successive rounds of selection of high quality plants with favorable characteristics. ...
... Plant breeding entails successive rounds of selection of high quality plants with favorable characteristics. ...
DNA Technology
... a medicine that can be used against malaria, this compound can be genetically engineered to change color of a plant in the presents of TNT and such. So if this could be made cheaply by bacteria all this things could be done. Basic genetic engineering is taking segments of genes and putting them in o ...
... a medicine that can be used against malaria, this compound can be genetically engineered to change color of a plant in the presents of TNT and such. So if this could be made cheaply by bacteria all this things could be done. Basic genetic engineering is taking segments of genes and putting them in o ...
Genetic Modification of Plants using Agrobacterium
... The process begins when a plant is wounded, often near the base of the stem. This causes the release of compounds that attract Agrobacterium to the damaged cells. Transcription of genes on one of the bacterium’s plasmids begins, transferring a 20 kbase piece of singlestranded T-DNA into the plant nu ...
... The process begins when a plant is wounded, often near the base of the stem. This causes the release of compounds that attract Agrobacterium to the damaged cells. Transcription of genes on one of the bacterium’s plasmids begins, transferring a 20 kbase piece of singlestranded T-DNA into the plant nu ...
Obtaining the gene of interest: 2 ways: 1. Using a radioactive DNA
... • Bone marrow cells (stem cells giving rise to blood and immune system) are prime candidates. • Success = cells will multiply and express the normal gene, engineered cells will supply the missing protein, patient will be cured. • Ex:Treatment of infants with SCID. But it was halted- they got leukemi ...
... • Bone marrow cells (stem cells giving rise to blood and immune system) are prime candidates. • Success = cells will multiply and express the normal gene, engineered cells will supply the missing protein, patient will be cured. • Ex:Treatment of infants with SCID. But it was halted- they got leukemi ...
Code DNA!
... This is the process of copying DNA to RNA. The process of nuclear division in cells that produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell. ...
... This is the process of copying DNA to RNA. The process of nuclear division in cells that produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell. ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.